Ann Dermatol.
2019 Aug;31(Suppl):S49-S51. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S49.
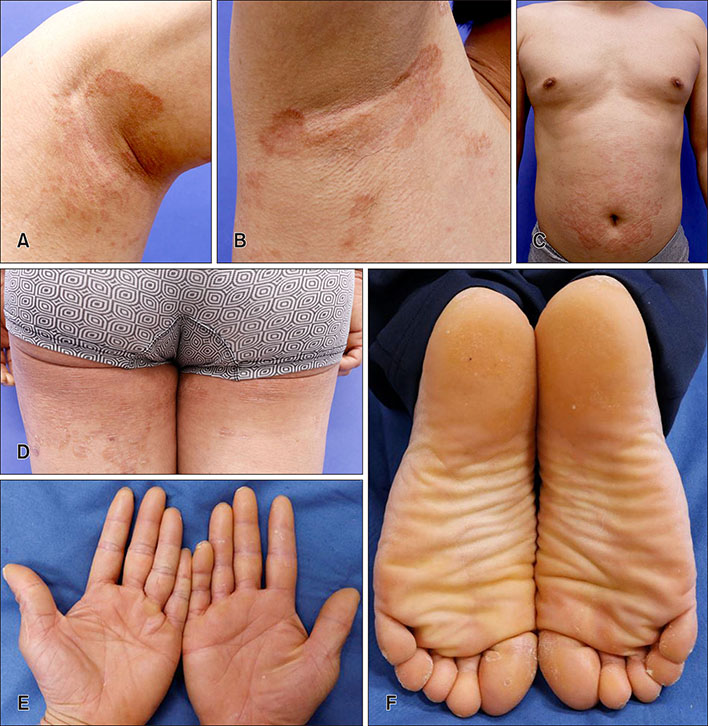
A Case of Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis in Korean
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Eulji University Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. dwkoo@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2456677
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S49
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ishida-Yamamoto A. Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva. J Dermatol. 2016; 43:280–285.
Article2. Common JE, O'Toole EA, Leigh IM, Thomas A, Griffiths WA, Venning V, et al. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity of erythrokeratoderma variabilis. J Invest Dermatol. 2005; 125:920–927.
Article3. Balci DD, Yaldiz M. Erythrokeratodermia variabilis: successful palliative treatment with acitretin. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008; 74:649–650.
Article4. Lee JS, Sung YH, Lee JH, Park JK. Erythrokeratodermia variabilis with alopecia universalis. Ann Dermatol. 1990; 2:17–20.
Article5. Nam HM, Kim UK, Park K, Park SD. Erythrokeratodermia variabilis with congenital deaf-mutism. Korean J Dermatol. 2011; 49:379–381.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis in Korean
- Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis with Alopecia Universalis
- Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis with Congenital Deaf-Mutism
- Erythrokeratodermia Variabilis Showing Gradual Disappearance of Erythema
- Ceratocystis quercicola sp. nov. from Quercus variabilis in Korea