J Korean Acad Nurs.
2019 Aug;49(4):398-410. 10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.398.
Development of a Quantitative Model on Adolescent Cyberbullying Victims in Korea: A System Dynamics Approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Konkuk University GLOCAL Campus, Chungju, Korea. hem2003@kku.ac.kr
- KMID: 2456144
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.398
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study used a system dynamics methodology to identify correlation and nonlinear feedback structures among factors affecting adolescent cyberbullying victims (CV) in Korea and to construct and verify a simulation model.
METHODS
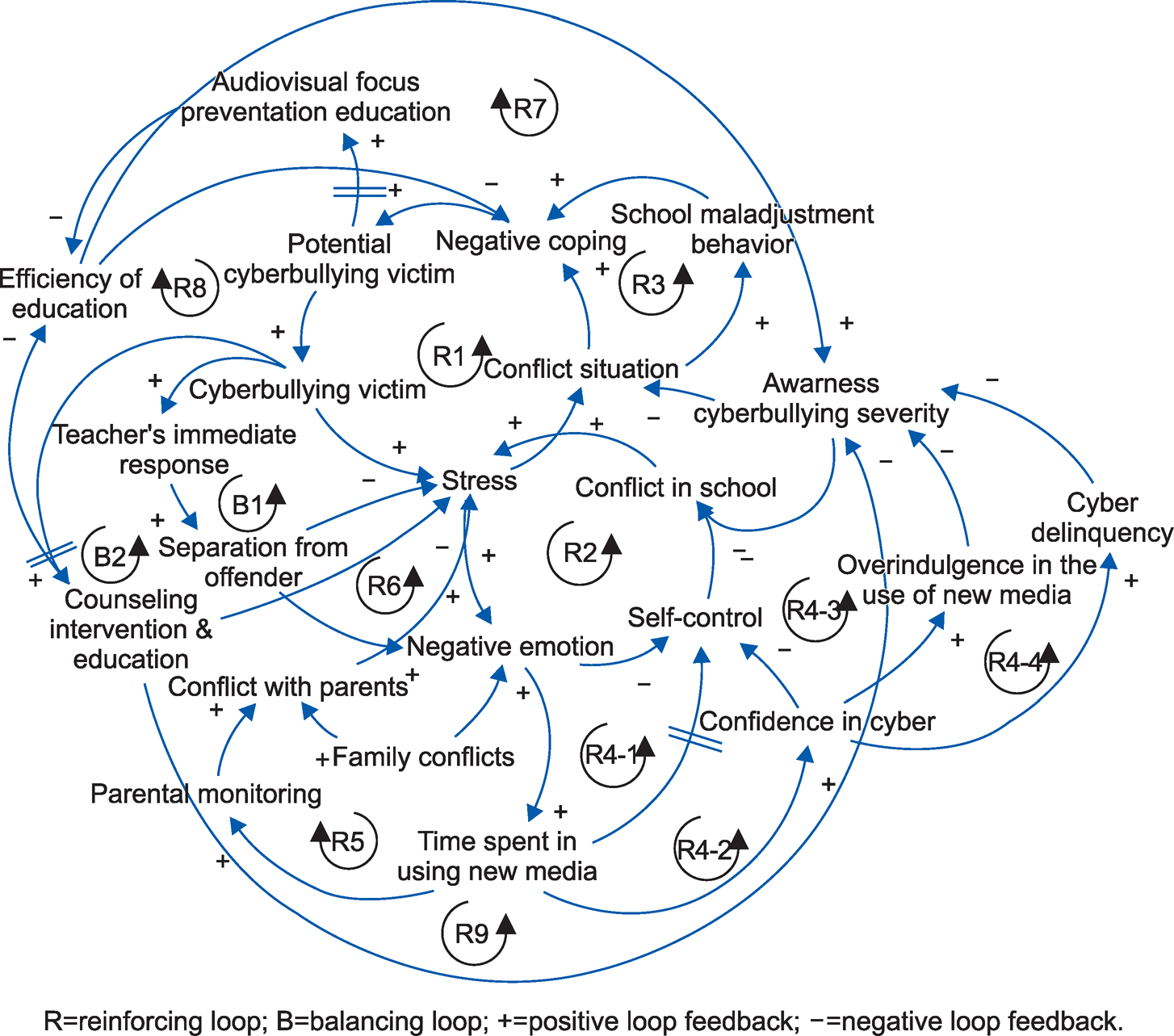
Factors affecting CV were identified by reviewing a theoretical background in existing literature and referencing various statistical data. Related variables were identified through content validity verification by an expert group, after which a causal loop diagram (CLD) was constructed based on the variables. A stock-flow diagram (SFD) using Vensim Professional 7.3 was used to establish a CV model.
RESULTS
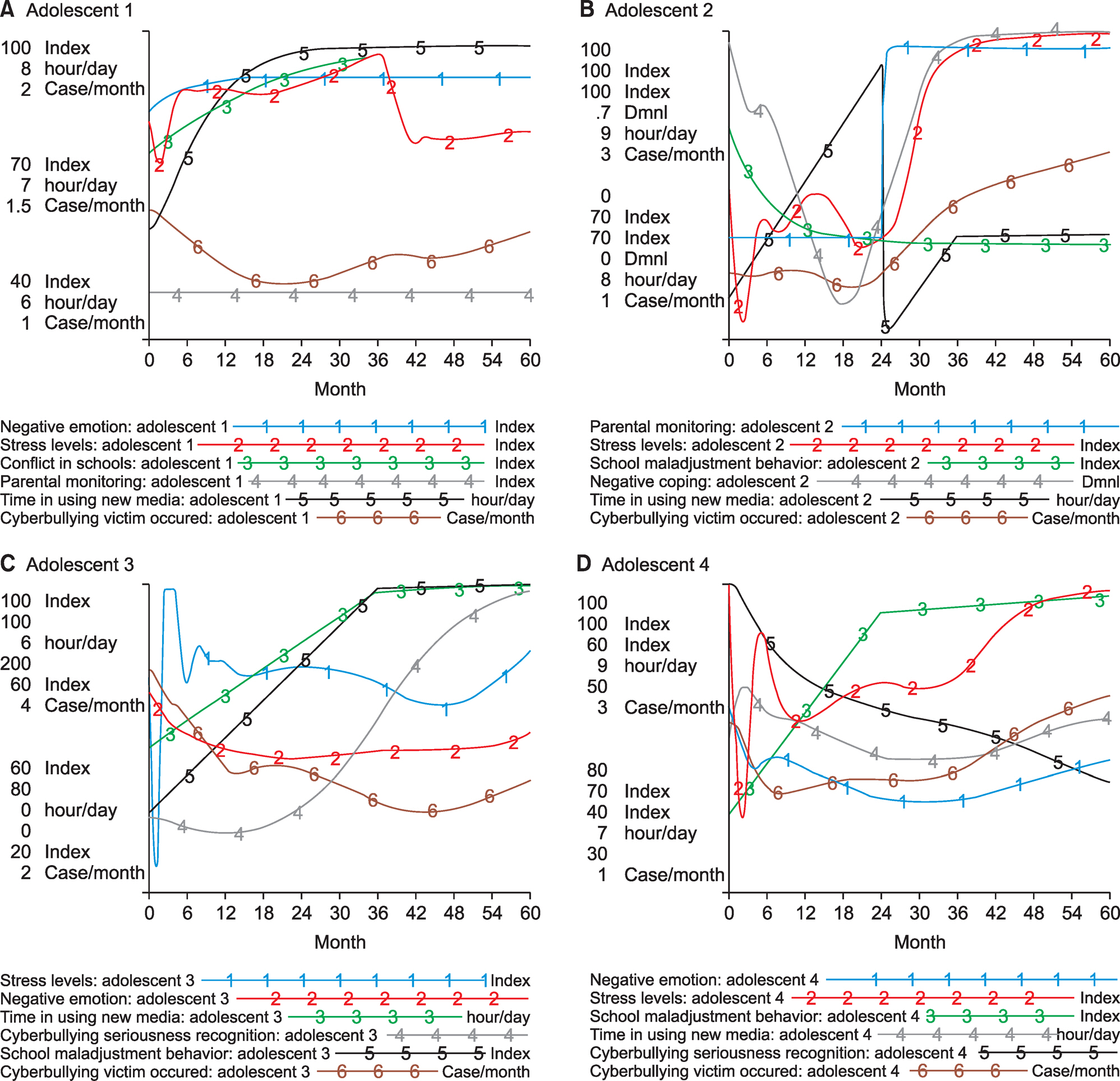
Based on the literature review and expert verification, 22 variables associated with CV were identified and the CLD was prepared. Next, a model was developed by converting the CLD to an SFD. The simulation results showed that the variables such as negative emotions, stress levels, high levels of conflict in schools, parental monitoring, and time spent using new media had the strongest effects on CV. The model's validity was verified using equation check, sensitivity analysis for time-step and simulation with 4 CV adolescent.
CONCLUSION
The system dynamics model constructed in this study can be used to develop intervention strategies in schools that are focused on counseling that can prevent cyberbullying and assist in the victims' recovery by formulating a feedback structure and capturing the dynamic changes observed in CV. To prevent cyberbullying, it is necessary to develop more effective strategies such as prevention education, counseling and treatment that considers factors pertaining to the individual, family, school, and media.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim HY, Min JS. A study on the factors of youth cyberbul-lying: Foused on off-line bullying and social media addiction. Journal of the Korea Entertainment Industry Association. 2014; 8(4):323–333. https://doi.org/10.21184/jkeia.2014.12.8.4.323.
Article2. Ministry of Education. Analysis of the results of the first school violence survey in 2018 [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Education;c2018. [cited 2018 Sep 25]. Available from:. https://moe.go.kr/boardCnts/view.do?boardID=294&board-Seq=75144&lev=0&searchType=null&statusYN=C&page=1&s=moe&m=0503&opType=N.3. Oh IS. The relations of traditional bullying, cyberbullying and types of aggression in terms of gender. Korea Journal of Counseling. 2014; 15(5):1871–1885. https://doi.org/10.15703/kjc.15.5.201410.1871.4. Lee SM, Yoo SK. The relationship between peer victimization and depression/anxiety: Meditating effects of passive/evasive behavior and aggressive behavior. Korea Journal of Counseling. 2013; 14(2):1209–1226. https://doi.org/10.15703/kjc.14.2.201304.1209.5. Hinduja S, Patchin JW. Offline consequences of online victimization: School violence and delinquency. Journal of School Violence. 2007; 6(3):89–112. https://doi.org/10.1300/J202v06n03_06.6. Chung YJ. Effects of positive affect induction on reducing negative affects among cyberbullying victims [dissertation]. Seoul: Seoul National University;2010. p. 1–196.7. Hinduja S, Patchin JW. Cyberbullying: Identification, prevention, and response [Internet]. Miami (FL): Cyberbullying Research Center;c2014. [cited 2018 Sep 20]. Available from:. https://cyberbullying.org/Cyberbullying-Identification-Prevention-Response.pdf.8. Messias E, Kindrick K, Castro J. School bullying, cyber-bullying, or both: Correlates of teen suicidality in the 2011 CDC youth risk behavior survey. Comprehensive Psychiatry. 2014; 55(5):1063–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.02.005.
Article9. Oh SH. Policy implications of the cyber bullying: A comparative analysis on the cases and policies between Korea and the United States [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Hanyang University;2014. p. 1–121.10. Lee CH, Shin NM, Ha EB. A study on the situation of youth cyberbullying and measures to prevent it. Sejong: National Youth Policy Institute;2014. Dec. Report No.: 14-R07.11. Seong YS. Cyber bullying countermeasures focusing on SNS. National Youth Policy Institute, editor. NYPI Planning Seminar: Youth and SNS Communication [Internet]. Sejong: National Youth Policy Institute;c2012. [cited 2018 Aug 20]. Available from:. https://www.nypi.re.kr/contents/site.do.12. Shin N, Ahn H. Cyberbullying among Korean adolescents: Facts and factors related to victimization and offending experiences. Journal of Research in Education. 2013; 49:1–21.13. Kim Y. The relationship between cyberbullying, sociality and school life adaptation among middle school students: Focusing on mediating effects of empathy and self-control [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Sogang University;2016. p. 1–82.14. Choi JO. Influence of cyber bullying victimization on cyber bullying: Mediating effects of anxiety and moderation effects of stress coping strategy. Crisisonomy. 2015; 11(5):195–214.15. Kowalski RM, Limber SP, Agatston PW. Cyberbullying: Bullying in the digital age. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell;2012. p. 1–283.16. Lee K, Jeong SH. Predictors of cyberbullying behaviors among adolescents: Application of theory of planned behavior and social learning theory. Journal of Cybercommunication Academic Society. 2014; 31(2):129–162.17. Kim DH, Moon TH, Kim DH. System Dynamics. Goyang: DaeYoung Co.;2001. p. 52–54.18. Goldsmith SK, Pellmar TC, Kleinman AM, Bunney WE. Reducing suicide: A national imperative. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press;2002. p. 1–586.19. Jang KS. A study on establishment of clinical career development model of nurses [dissertation]. Seoul: Yonsei University;2000. p. 1–201.20. Spradley JP. The ethnographic interview. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston;1979. p. 1–244.21. Ventana Systems, Inc. Vensim Software [Computer Program]. Version 7.3. Harvard (MA): Ventana Systems, Inc;2018. Available from:. https://vensim.com/vensim-software/.22. Lynn MR. Determination and quantification of content validity. Nursing Research. 1986; 35(6):382–386. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006199-198611000-00017.
Article23. Kim SW. System thinking and scenario planning. Cheongju: Chungbuk National University Press;2010. p. 1–411.24. Seo WJ, Ebesutani C, Kim M, Lee TS. A validation study of the Cyberbullying Scale-Korean version. The Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2015; 20(4):839–854. https://doi.org/10.17315/kjhp.2015.20.4.008.25. Jun D, Kim D. A study on adult’s cyberviolence. Korean Journal of Local Government & Administration Studies. 2016; 30(3):25–44. https://doi.org/10.18398/kjlgas.2016.30.3.25.26. Sterman JD. Business dynamics, system thinking and modeling for a complex world. Boston (MA): McGraw-Hill Publishing Company;2000. p. 1–32.27. Lee S. A study on the approaches of moral education for preventing cyber bullying of elementary school students [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Seoul National University of Education;2016. p. 1–112.28. Ministry of Science and ICT; Korea Internet & Security Agency. 2017 Survey on the internet usage. Naju: Korea Internet & Security Agency;2018. Mar. Report No.:120005.29. Borca G, Bina M, Keller PS, Gilbert LR, Begotti T. Internet use and developmental tasks: Adolescents’ point of view. Computers in Human Behavior. 2015; 52:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.05.029.
Article30. Gottfredson MR, Hirschi T. A General Theory of Crime. Stanford (CA): Stanford University Press;1990. p. 1–154.31. Kim KS, Kim KH. A prediction model for internet game addiction in adolescents: Using a decision tree analysis. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2010; 40(3):378–388. https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.378.
Article32. Mendoza K. Surveying parental mediation: Connections, challenges and questions for media literacy. Journal of Media Literacy Education. 2009; 1(1):28–41.33. Bae JM, Cho ES, Cho YM, Kim KE. A study on parents’ observation of adolescent children’s smartphone use problem and their parenting experiences. Journal of Family Relations. 2015; 20(1):143–164.34. Choi YJ, Oh IS. The victims’ reactions in bullying situation according to bystanders’ behavioral reactions: Focus on the need for control, perceived control, and coping strategies. The Korea Educational Review. 2018; 24(2):5–23. https://doi.org/10.29318/ker.24.2.1.
Article35. Smith JD, Schneider BH, Smith PK, Ananiadou K. The effectiveness of whole-school antibullying programs: A synthesis of evaluation research. School Psychology Review. 2004; 33(4):547–560.
Article36. Chaffee MW, McNeill MM. A model of nursing as a complex adaptive system. Nursing Outlook. 2007; 55(5):232–241.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.outlook.2007.04.003.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Empathy, cyberbullying, and cybervictimization among Filipino adolescents
- Cyberbullying, Problematic Internet Use, and Psychopathologic Symptoms among Korean Youth
- Psychopathology Associated with Cyberbullying among Middle School Students
- Non-linear System Dynamics Simulation Modeling of Adolescent Obesity: Using Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey
- The Moderating Effect of Internet Ethics on the Relationship Between Cyberbullying Victimization and Perpetration Among Korean Adults