Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2019 Aug;23(3):211-218. 10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.3.211.
ABO-incompatible liver transplantation using only rituximab for patients with low anti-ABO antibody titer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. choiyoungrok@gmail.com
- 2Department of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2456017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.3.211
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
Graft survival after ABO-incompatible (ABOi) living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) has increased due to advances in desensitization methods. We analyzed early outcomes following ABOi LDLT using only rituximab without any additional desensitization methods in recipients with low anti-ABO antibody titers (≤1:32).
METHODS
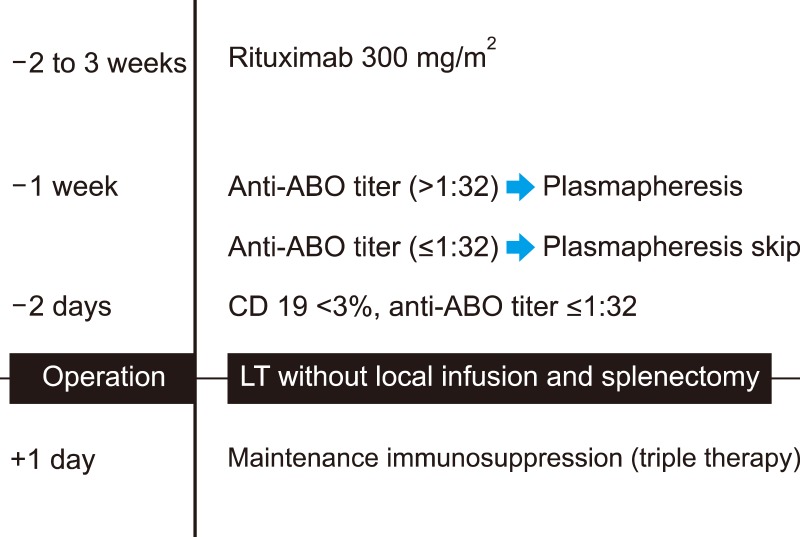
Ten adult patients underwent ABOi LDLT between September 2014 and December 2016. All patients were administered a single dose of rituximab (300 mg/m2) prior to LDLT. Three patients with baseline anti-ABO titer >1:32 underwent multiple sessions of plasmapheresis to reduce titers to <1:32 (rituximab+plasmapheresis, RP). Seven patients with low anti-ABO titer (≤1:32) did not undergo plasmapheresis (rituximab-only, RO). ABO-compatible LDLT patients during the same period were included for comparison (n=22).
RESULTS
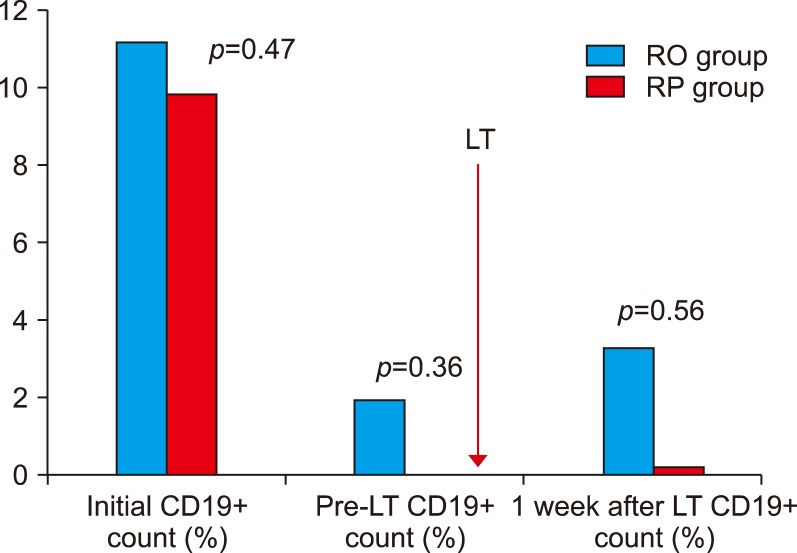
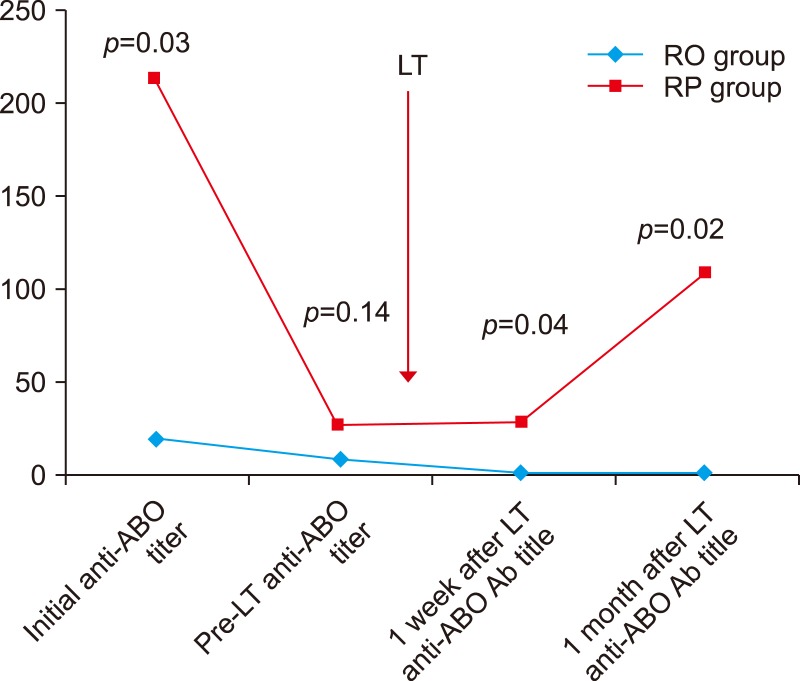
Post-transplantation titers were significantly lower in the RO than in the RP and showed no rebound rise (POD7 1.14±0.38 vs 28.0±31.7, p=0.04), (POD30 1.26±0.45 vs 108±107, p=0.02). There were no significant differences in rejection, biliary complications and infection between groups. There were no significant differences in outcome between the RO group and ABO-compatible except for infection.
CONCLUSIONS
This study shows that recipients with low baseline anti-ABO antibody titer (≤1:32) can undergo ABOi LDLT using conventional immunosuppression and rituximab alone.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Successful ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation using splenectomy and intravenous immunoglobulin in high isoagglutinin titer patients
Boram Lee, Jai Young Cho, Hae Won Lee, YoungRok Choi, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Ho-Seong Han
Korean J Transplant. 2020;34(2):109-113. doi: 10.4285/kjt.2020.34.2.109.Long-term outcomes of emergency ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation using a modified desensitization protocol for highly sensitized patients with acute liver failure: A case report
Boram Lee, Jai Young Cho, Ho-Seong Han, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Hae Won Lee, Jun Suh Lee, Moonhwan Kim, YoungRok Choi
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(4):571-574. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.4.571.
Reference
-
1. Song GW. ABO incompatability in liver transplantation. Hanyang Med Rev. 2014; 34:202–210.
Article2. Egawa H, Oike F, Buhler L, Shapiro AM, Minamiguchi S, Haga H, et al. Impact of recipient age on outcome of ABO-incompatible living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2004; 77:403–411. PMID: 14966415.
Article3. Ashizawa T, Matsuno N, Yokoyama T, Kihara Y, Kuzuoka K, Taira S, et al. The role of plasmapheresis therapy for perioperative management in ABO-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:3629–3632. PMID: 17175351.
Article4. Winters JL. Plasma exchange: concepts, mechanisms, and an overview of the American Society for Apheresis guidelines. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012; 2012:7–12. PMID: 23233554.
Article5. Mokrzycki MH, Kaplan AA. Therapeutic plasma exchange: complications and management. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994; 23:817–827. PMID: 8203364.
Article6. Passalacqua S, Staffolani E, Busnach G, Roccatello D, Pasquali S, Cappelli P, et al. Apheresis Study Group of the Italian Society of Nephrology. The Italian Registry for therapeutic apheresis. A report from the Apheresis Study Group of the Italian Society of Nephrology. J Clin Apher. 2005; 20:101–106. PMID: 15880354.
Article7. Song GW, Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. ABO-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation under the desensitization protocol with rituximab. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16:157–170. PMID: 26372830.
Article8. Egawa H, Teramukai S, Haga H, Tanabe M, Mori A, Ikegami T, et al. Impact of rituximab desensitization on blood-type-incompatible adult living donor liver transplantation: a Japanese multicenter study. Am J Transplant. 2014; 14:102–114. PMID: 24279828.
Article9. Rummler S, Bauschke A, Baerthel E, Juette H, Maier K, Malessa C, et al. ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation in focus of antibody rebound. Transfus Med Hemother. 2017; 44:46–51. PMID: 28275333.
Article10. Kawagishi N, Satomi S. Current aspects of ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Clin Case Rep Rev. 2016; 2:375–379.
Article11. Krishnan NS, Zehnder D, Briggs D, Higgins R. Human leukocyte antigen antibody incompatible renal transplantation. Indian J Nephrol. 2012; 22:409–414. PMID: 23440400.
Article12. Szczepiorkowski ZM, Winters JL, Bandarenko N, Kim HC, Linenberger ML, Marques MB, et al. Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice--evidence-based approach from the Apheresis Applications Committee of the American Society for Apheresis. J Clin Apher. 2010; 25:83–177. PMID: 20568098.
Article13. Masterson R, Hughes P, Walker RG, Hogan C, Haeusler M, Robertson AR, et al. ABO incompatible renal transplantation without antibody removal using conventional immunosuppression alone. Am J Transplant. 2014; 14:2807–2813. PMID: 25389083.
Article14. Yamamoto H, Uchida K, Kawabata S, Isono K, Miura K, Hayashida S, et al. Feasibility of monotherapy by rituximab without additional desensitization in ABO-incompatible living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2018; 102:97–104. PMID: 28938311.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Overcoming high pre-transplant isoagglutinin titers using high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, salvage plasmapheresis, and booster rituximab without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a case report
- Impact of baseline anti-ABO antibody titer on biliary complications following ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation
- Current Issues in ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- Laboratory support of ABO antibody monitoring for ABO-incompatible solid organ transplantation