Clin Endosc.
2019 Jul;52(4):369-372. 10.5946/ce.2018.130.
A Rare Case of Lymph Node Metastasis from Early Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan. anctan180@gmail.com
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Tenri Hospital, Tenri, Nara, Japan.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Tenri Hospital, Tenri, Nara, Japan.
- KMID: 2455635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.130
Abstract
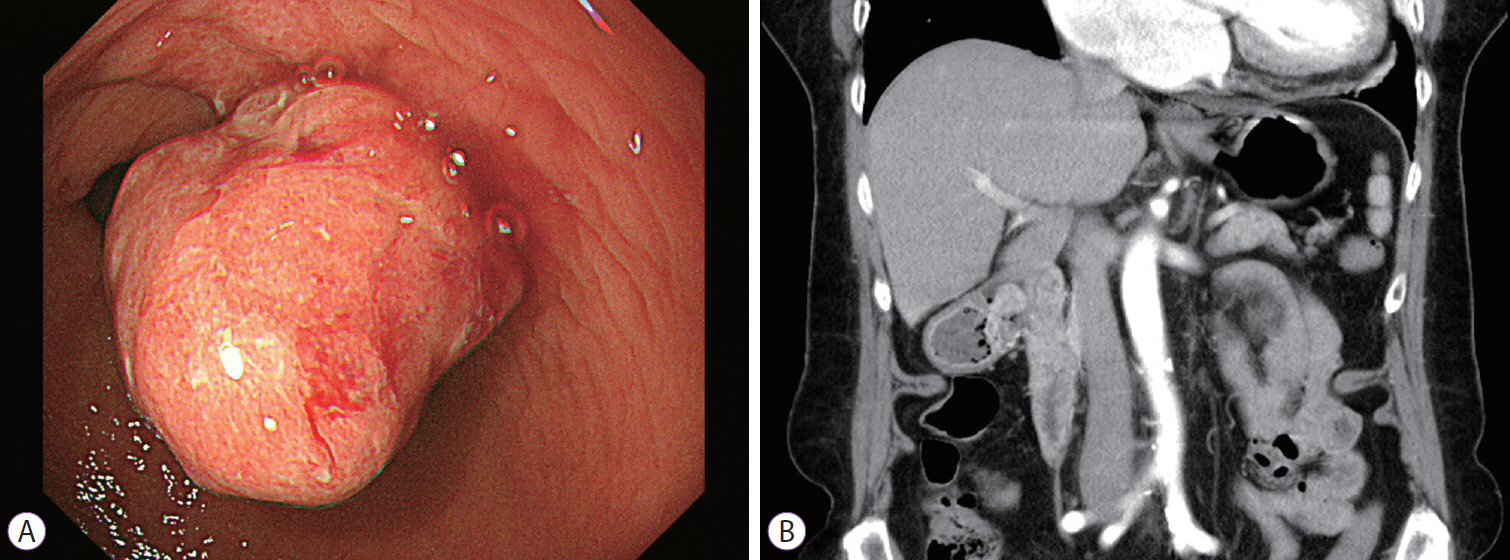
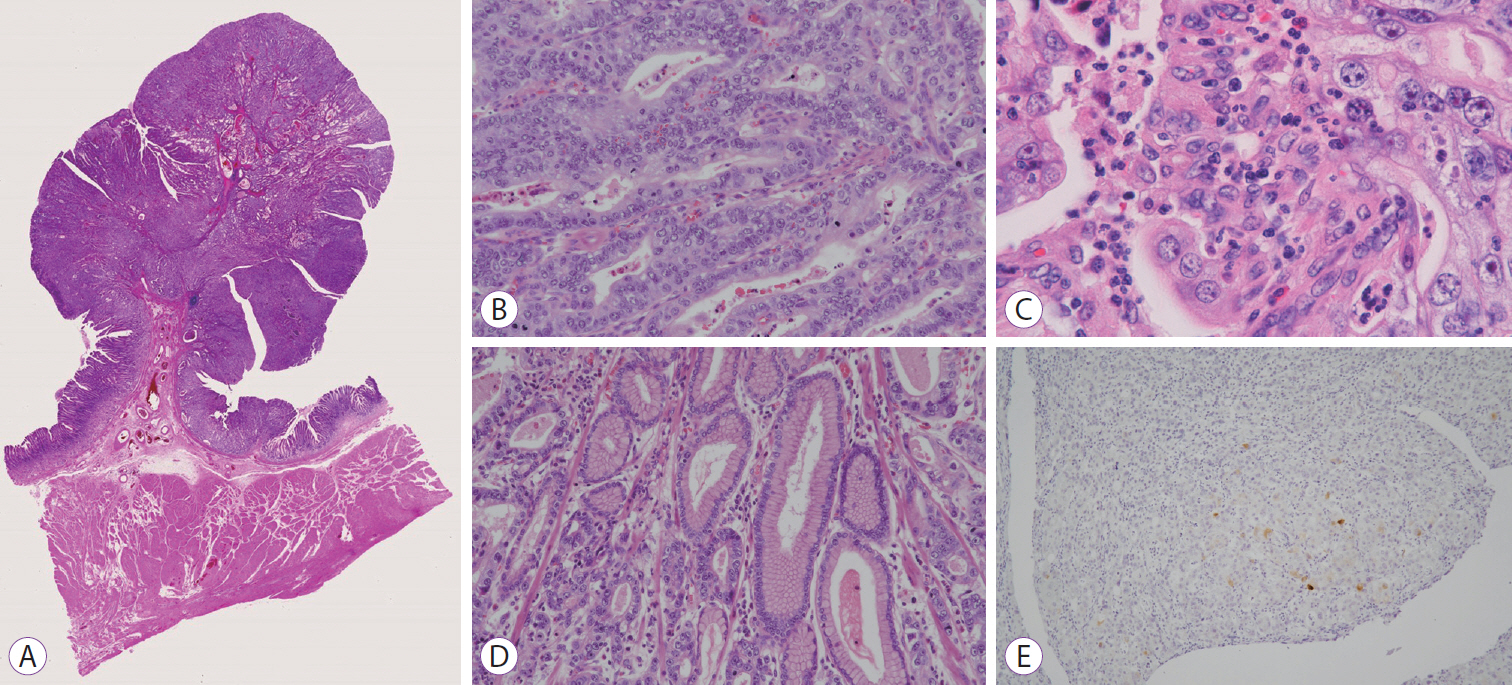
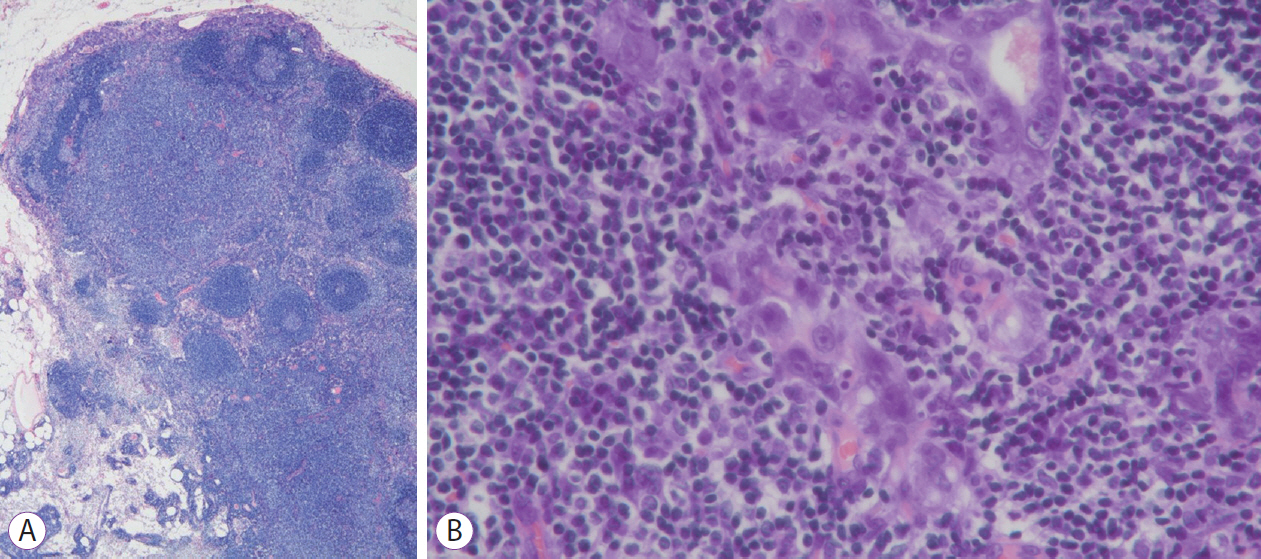
- Gastric cancers that fulfill the Japanese criteria for curative endoscopic resection show a low risk of lymph node (LN) metastasis. Here, we report a case of LN metastasis from early gastric cancer that fulfilled the curative criteria. A 74-year-old Japanese woman was referred to our hospital for treatment of early gastric cancer identified at the site of a hyperplastic polyp that had been diagnosed 10 years prior to presentation. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography did not show any lymphadenopathy and laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy was performed. Histopathological examination revealed a predominantly moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma that measured 15 mm in size and was confined to the mucosa. However, a single metastatic regional LN was observed. A few cancer cells showed positive staining for alpha-fetoprotein. It should be noted that early gastric cancer can be accompanied by LN metastasis even if it fulfills the criteria for curative endoscopic resection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ono H, Yao K, Fujishiro M, et al. Guidelines for endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:3–15.
Article2. Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, et al. Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer. 2000; 3:219–225.
Article3. Kim DJ, Kim W. A case of single lymph node metastasis near the common hepatic artery following a curative endoscopic resection for gastric mucosal cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2014; 17:387–391.
Article4. Hasegawa F, Kiyozaki H, Takata O, et al. Lymphatic invasion in small differentiated-type mucosal gastric cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2012; 5:234–238.
Article5. Chang YC, Nagasue N, Abe S, Taniura H, Kumar DD, Nakamura T. Comparison between the clinicopathologic features of AFP-positive and AFP-negative gastric cancers. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992; 87:321–325.6. Murakami T, Yao T, Mitomi H, et al. Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics of gastric adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation: a study of 29 cases. Gastric Cancer. 2016; 19:498–507.
Article7. Tazaki S, Yoshida H. [A case of AFP-producing early gastric cancer that grew in the short-term]. Progress of Digestive Endoscopy. 2015; 87:116–117.
Article8. Hanaoka N, Tanabe S, Mikami T, Okayasu I, Saigenji K. Mixed-histologic-type submucosal invasive gastric cancer as a risk factor for lymph node metastasis: feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:427–432.
Article9. Nakamura T, Nakano G. Histopathological classification and malignant change in gastric polyps. J Clin Pathol. 1985; 38:754–764.
Article10. Mönig SP, Zirbes TK, Schröder W, et al. Staging of gastric cancer: correlation of lymph node size and metastatic infiltration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 173:365–367.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Gastric Cancer
- Risk Factors Affecting Lymph Node Metastasis and Recurrence in Early Gastric Cancer
- Perigastric Lymph Node Metastasis from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in a Patient with Early Gastric Cancer: The First Case Report
- Correlation Between Expression of p53, Bcl-2 Protein and Ki-67 Labelling Index and Lymph Node Metastasis in Early Gastric Cancer
- A Case of Thyroid Metastasis Originating from Early Gastric Cancer