Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2019 Aug;12(3):273-278. 10.21053/ceo.2018.00381.
Serum Vitamin D and Long-term Outcomes of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Affiliations
-
- 1One Otorhinolaryngology Clinic, Paju, Korea. guzi9170@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2455368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.00381
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of the present study was to examine the effect of serum vitamin D concentrations on the long-term recurrence rates of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) patients.
METHODS
The present study was conducted with patients diagnosed with BPPV from June 2014 to April 2016. Whether the patients' sex, age, types and locations of semicircular canals, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and vitamin D concentrations affect their recurrence rates was examined using Pearson chi-square tests, independent samples t-tests and Cox proportional hazards regression analyses. The effects of vitamin D concentrations on long-term recurrence rates were examined using Kaplan-Meier estimates and log-rank tests.
RESULTS
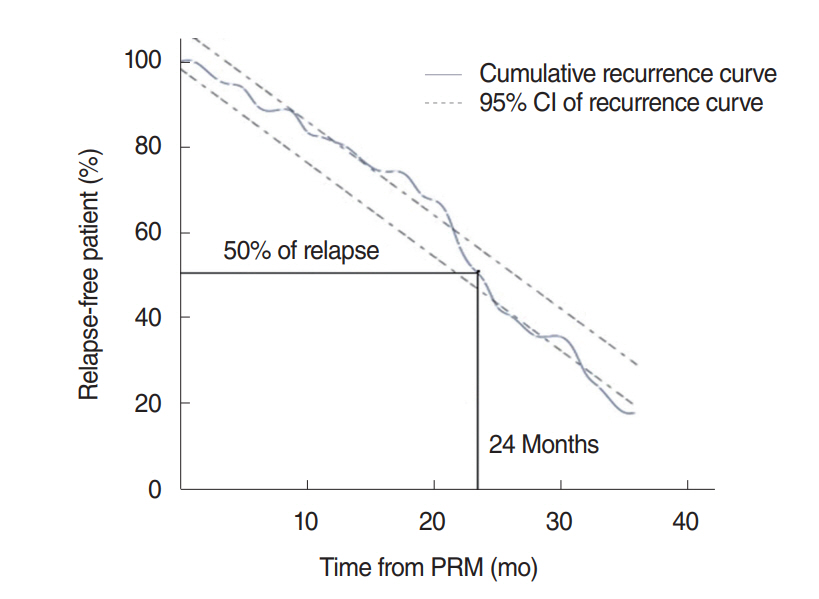
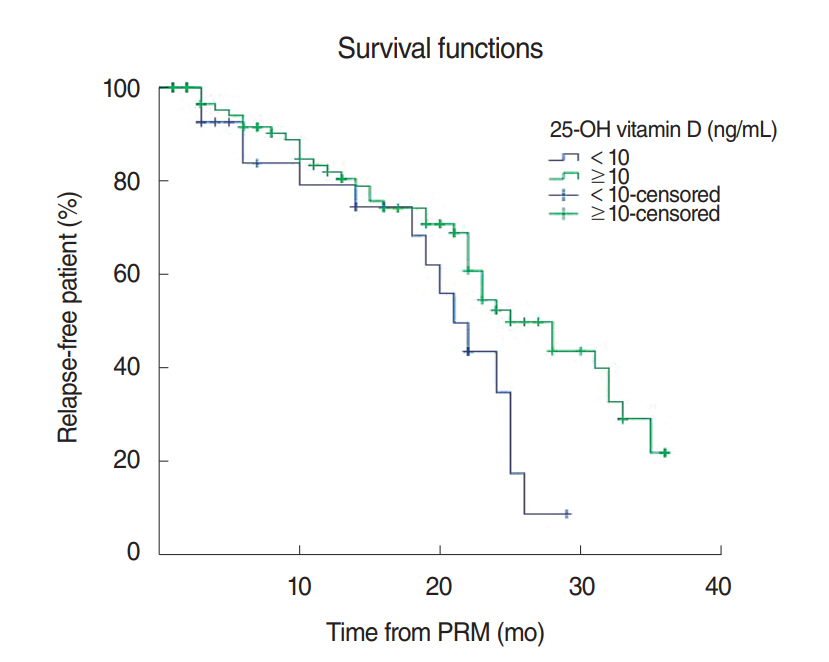
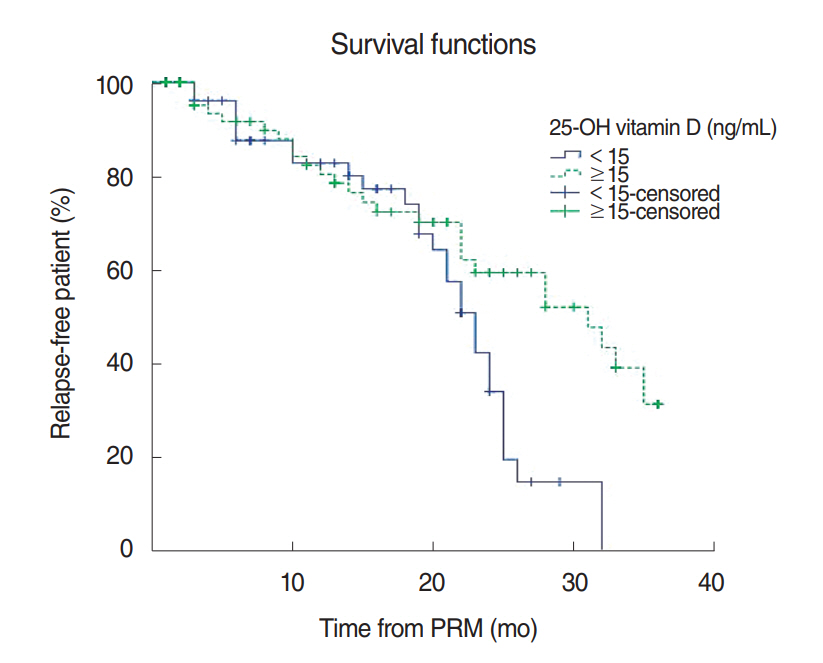
The recurrence rates obtained with Kaplan-Meier estimates were 18% and 50% at 12 months and 24 months, respectively. When the patients were divided into groups with vitamin D concentrations of <10 ng/mL and ≥10 ng/mL and the recurrence rates of the groups were compared, the difference was statistically significant (P=0.040). In addition, when the patients were divided into groups with vitamin D concentrations of <15 ng/mL and ≥15 ng/mL and the recurrence rates of the groups were compared, the difference was statistically quite significant (P=0.017). In a Cox regression model, variables such as age, sex, the types and locations of semicircular canals, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and 25-hydroxy vitamin D did not significantly affect recurrence.
CONCLUSION
The present study investigated the recurrence rates of BPPV in patients for a long time without limiting the sex, age, or locations of semicircular canals and it could be seen that serum vitamin D concentrations significantly affected the recurrence of BPPV.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tanimoto H, Doi K, Nishikawa T, Nibu K. Risk factors for recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008; Dec. 37(6):832–5.2. Sakaida M, Takeuchi K, Ishinaga H, Adachi M, Majima Y. Long-term outcome of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology. 2003; May. 60(9):1532–4.
Article3. Brandt T, Huppert D, Hecht J, Karch C, Strupp M. Benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo: a long-term follow-up (6-17 years) of 125 patients. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; Feb. 126(2):160–3.
Article4. De Stefano A, Dispenza F, Suarez H, Perez-Fernandez N, Manrique-Huarte R, Ban JH, et al. A multicenter observational study on the role of comorbidities in the recurrent episodes of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2014; Feb. 41(1):31–6.
Article5. Rhim GI. Serum vitamin D and recurrent benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2016; Oct. 1(6):150–3.
Article6. Lundberg YW, Zhao X, Yamoah EN. Assembly of the otoconia complex to the macular sensory epithelium of the vestibule. Brain Res. 2006; May. 1091(1):47–57.
Article7. Vibert D, Kompis M, Hausler R. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in older women may be related to osteoporosis and osteopenia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003; Oct. 112(10):885–9.
Article8. Yamanaka T, Shirota S, Sawai Y, Murai T, Fujita N, Hosoi H. Osteoporosis as a risk factor for the recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope. 2013; Nov. 123(11):2813–6.
Article9. Jeong SH, Choi SH, Kim JY, Koo JW, Kim HJ, Kim JS. Osteopenia and osteoporosis in idiopathic benign positional vertigo. Neurology. 2009; Mar. 72(12):1069–76.
Article10. Jeong SH, Kim JS, Shin JW, Kim S, Lee H, Lee AY, et al. Decreased serum vitamin D in idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J Neurol. 2013; Mar. 260(3):832–8.
Article11. Talaat HS, Abuhadied G, Talaat AS, Abdelaal MS. Low bone mineral density and vitamin D deficiency in patients with benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; Sep. 272(9):2249–53.
Article12. Buki B, Ecker M, Junger H, Lundberg YW. Vitamin D deficiency and benign paroxysmal positioning vertigo. Med Hypotheses. 2013; Feb. 80(2):201–4.13. von Brevern M, Bertholon P, Brandt T, Fife T, Imai T, Nuti D, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res. 2015; 25(3-4):105–17.
Article14. Kansu L, Avci S, Yilmaz I, Ozluoglu LN. Long-term follow-up of patients with posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010; Sep. 130(9):1009–12.
Article15. Perez P, Franco V, Cuesta P, Aldama P, Alvarez MJ, Mendez JC. Recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otol Neurotol. 2012; Apr. 33(3):437–43.16. Kim SY, Han SH, Kim YH, Park MH. Clinical features of recurrence and osteoporotic changes in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017; Apr. 44(2):156–61.
Article17. Dawson-Hughes B, Harris SS, Krall EA, Dallal GE. Effect of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone density in men and women 65 years of age or older. N Engl J Med. 1997; Sep. 337(10):670–6.
Article18. Mosekilde L. Vitamin D and the elderly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2005; Mar. 62(3):265–81.
Article19. Talaat HS, Kabel AM, Khaliel LH, Abuhadied G, El-Naga HA, Talaat AS. Reduction of recurrence rate of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo by treatment of severe vitamin D deficiency. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016; Jun. 43(3):237–41.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-Term Results of Posterior Semicircular Occlusion for Intractable Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Positional Dizziness and Vertigo without Nystagmus and Orthostatic Hypotension
- Diagnosis of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Extremely Long Latency Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Model Experiment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo