Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2018 Jul;20(2):79-84. 10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.79.
Pulsatility of middle cerebral arteries is better correlated with white matter hyperintensities than aortic stiffening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leejuhun@hallym.or.kr
- 3Department of Neurology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2454709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.79
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pulsatility of cerebral arteries and aortic stiffness have been associated with white matter hyperintensities (WMH). We explored which is better correlated with the severity of WMH in a population with acute lacunar infarct.
METHODS
We included patients with acute small subcortical infarcts who underwent transcranial Doppler (TCD) and brachial ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV). Exclusion criteria were any stenosis or occlusion on major cerebral arteries on magnetic resonance angiography; poor temporal insonation windows; ankle brachial index < 0.9; and atrial fibrillation. We assessed the performance of the pulsatility index of bilateral middle cerebral arteries (PI-MCA) and baPWV for predicting moderate-to-severe WMH, defined as an Age Related White Matter Changes score > 5, and then sought to find independent predictors using binary logistic regression analysis.
RESULTS
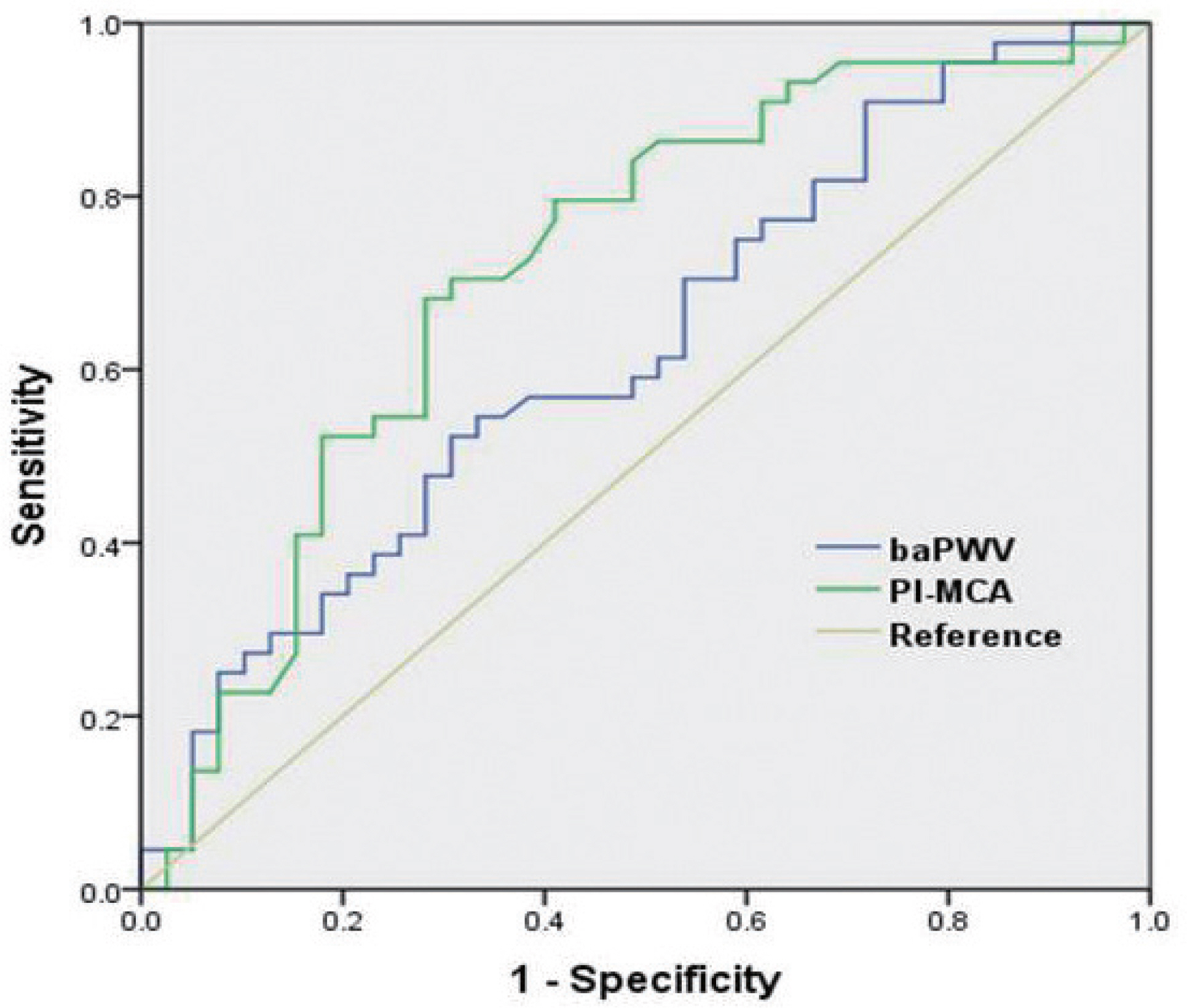
Eighty-three patients (56 males, mean age 61.5 ± 11.4) participated in the study. Univariate analysis showed old age and high PI-MCA were significantly correlated with moderate-to-severe WMH. However, baPWV was not associated with the severity of WMH. Multivariate analysis revealed old age (odds ratio per 1-year increase, 1.068; p = 0.044) and upper tertile of PI-MCA (odds ratio, 5.138; p = 0.049) were independently associated with moderate-to-severe WMH. Receiver-operating characteristics showed PI-MCA differentiated those with and without moderate-to-severe WMH with an area under the curve of 0.719.
CONCLUSIONS
PI-MCA derived from TCD was better correlated with the severity of WMH than baPWV in a population with lacunar infarction. Pulsatility of cerebral arteries may better predict cerebral small vessel disease than the aortic stiffness index.
MeSH Terms
-
Ankle
Ankle Brachial Index
Atrial Fibrillation
Cerebral Arteries
Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases
Constriction, Pathologic
Humans
Logistic Models
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Male
Middle Cerebral Artery*
Multivariate Analysis
Pulse Wave Analysis
Stroke, Lacunar
Ultrasonography, Doppler, Transcranial
Vascular Stiffness
White Matter*
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. O'Rourke MF, Staessen JA, Vlachopoulos C, Duprez D, Plante GE. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values. Am J Hypertens. 2002; 15:426–444.2. Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM. Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation. 1999; 99:2434–2439.
Article3. Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L, et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2001; 37:1236–1241.
Article4. Sugawara J, Hayashi K, Yokoi T, Cortez-Cooper MY, DeVan AE, Anton MA, et al. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: an index of central arterial stiffness? J Hum Hypertens. 2005; 19:401–406.
Article5. Legarth J, Thorup E. Characteristics of doppler blood-velocity waveforms in a cardiovascular in vitro model. i. the model and the influence of pulse rate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1989; 49:451–457.
Article6. Giller CA, Hodges K, Batjer HH. Transcranial doppler pulsatility in vasodilation and stenosis. J Neurosurg. 1990; 72:901–906.
Article7. Heliopoulos I, Artemis D, Vadikolias K, Tripsianis G, Piperidou C, Tsivgoulis G. Association of ultrasonographic parameters with subclinical white-matter hyperintensities in hypertensive patients. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2012; 2012:616572.
Article8. Mitchell GF, van Buchem MA, Sigurdsson S, Gotal JD, Jonsdottir MK, Kjartansson Ó, et al. Arterial stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility and brain structure and function: the age, gene/environ-ment susceptibility–Reykjavik study. Brain. 2011; 134(Pt 11):3398–3407.9. Kidwell CS, el-Saden S, Livshits Z, Martin NA, Glenn TC, Saver JL. Transcranial doppler pulsatility indices as a measure of diffuse small-vessel disease. J Neuroimaging. 2001; 11:229–235.
Article10. Mok V, Ding D, Fu J, Xiong Y, Chu WW, Wang D, et al. Transcranial doppler ultrasound for screening cerebral small vessel disease: a community study. Stroke. 2012; 43:2791–2793.11. Henskens LH, Kroon AA, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Gronenschild EH, Fuss-Lejeune MM, Hofman PA, et al. Increased aortic pulse wave velocity is associated with silent cerebral small-vessel disease in hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 2008; 52:1120–1126.
Article12. Kim DH, Choi JH, Moon JS, Kim HJ, Cha JK. Association between the severity of cerebral small vessel disease, pulsatility of cerebral arteries, and brachial ankle pulse wave velocity in patients with lacunar infarction. Eur Neurol. 2010; 64:247–252.
Article13. Xiong Y, Yang J, Wong A, Wong CH, Chan SS, Li HH, et al. Oper-ational definitions improve reliability of the age-related white matter changes scale. Eur J Neurol. 2011; 18:744–749.
Article14. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.15. Mitchell GF. Effects of central arterial aging on the structure and function of the peripheral vasculature: implications for end-or-gan damage. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008; 105:1652–1660.
Article16. de Riva N, Budohoski KP, Smielewski P, Kasprowicz M, Zweifel C, Steiner LA, et al. Transcranial doppler pulsatility index: what it is and what it isn't. Neurocrit Care. 2012; 17:58–66.
Article17. Webb AJ, Simoni M, Mazzucco S, Kuker W, Schulz U, Rothwell PM. Increased cerebral arterial pulsatility in patients with leukoarai-osis: arterial stiffness enhances transmission of aortic pulsatility. Stroke. 2012; 43:2631–2636.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Association of Low Blood Pressure with White Matter Hyperintensities in Elderly Individuals with Controlled Hypertension
- High Mean Platelet Volume Is Associated with Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities in Non-Stroke Individuals
- Arterial-Cardiac Interaction: The Concept and Implications
- Leukoaraiosis: Epidemiology, Imaging, Risk Factors, and Management of Age-Related Cerebral White Matter Hyperintensities
- Changes in Interictal Cerebral Blood Flow in Patients with Epilepsy