Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Apr;48(2):621-631. 10.4143/crt.2015.220.
Conditional Survival and Associated Prognostic Factors in Patients with Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma after Radical Nephroureterectomy: A Retrospective Study at a Single Institution
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. randyku@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2454340
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.220
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the changes of conditional survival (CS) probabilities and to identify the prognostic parameters that significantly affect CS over time post-surgery in upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 330 patients were examined in the final analysis. Primary end point was conditional cancer-specific survival (CSS), overall survival (OS), and intravesical recurrence-free survival (IVRFS) after surgery. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for calculation of CS. Cox regression hazard ratio model was used to determine the predictors of CS.
RESULTS
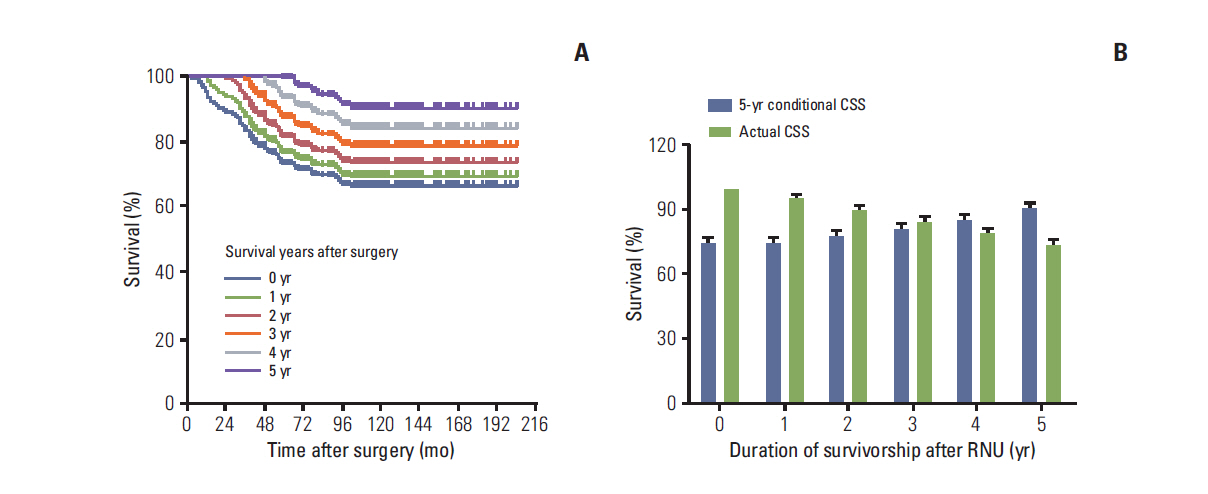
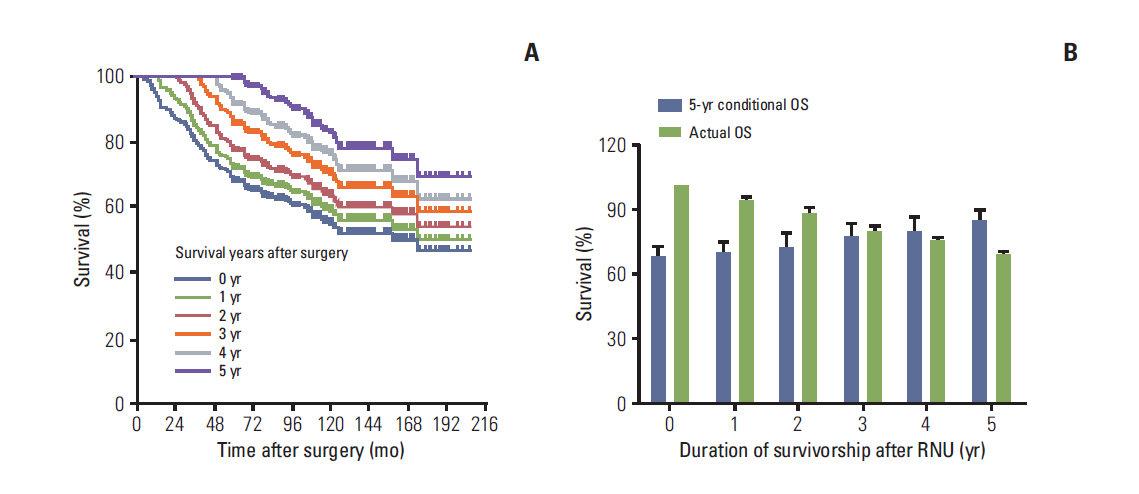
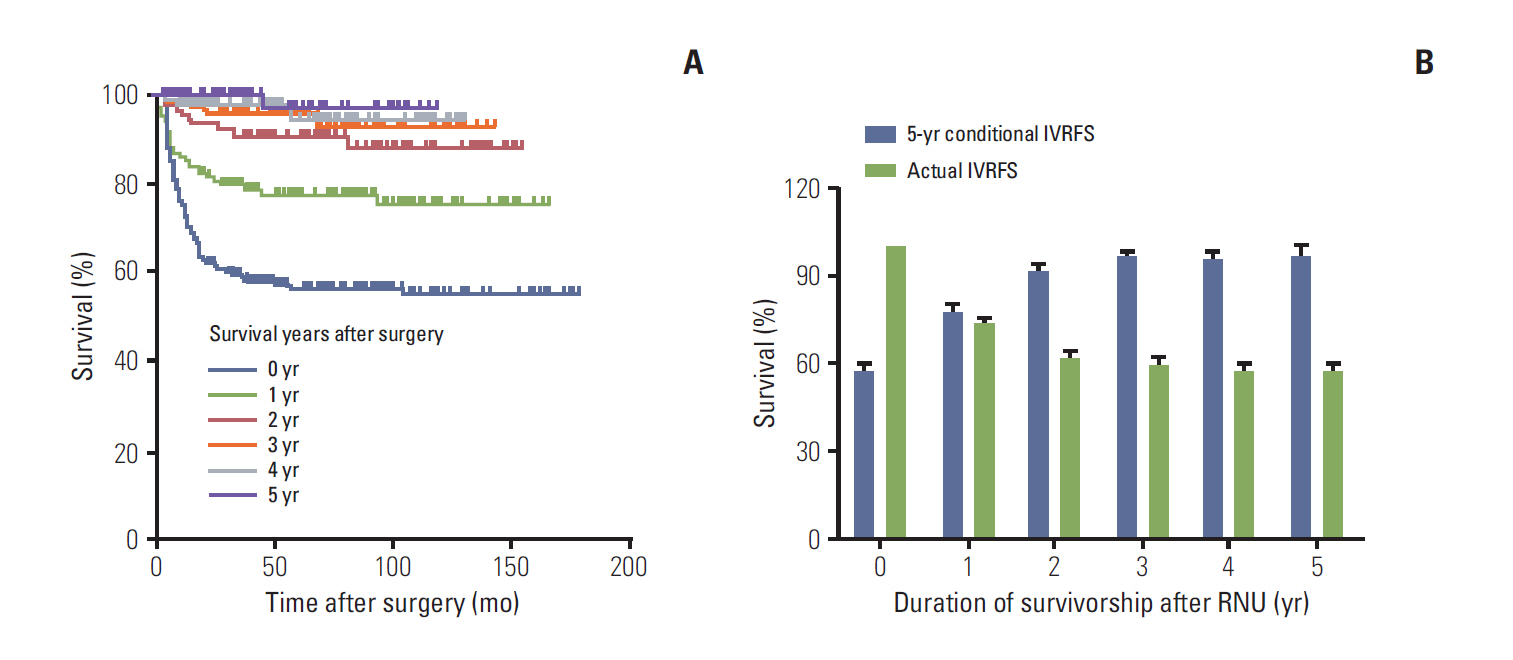
UTUC patients who had already survived 5 years after radical nephroureterectomy had a more favorable CS probability in all given survivorships compared to those with shorter survival times. Patients with unfavorable pathologic features showed a higher increment of 5-year conditional CSS and OS compared to their counterparts. For 5-year conditional CSS, several factors, including high-grade tumor, lymphovascular invasion, and tumor location showed significant association with risk elevation over time. Only age remained as a predictor of 5-year conditional OS with increased risk in all given survivorships. For 5-year IVRFS, no variables remained as significant predictive factors over time after surgery.
CONCLUSION
Our study provides valuable information for practical survival estimation and relevant prognostic factors for patients with UTUC after surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Munoz JJ, Ellison LM. Upper tract urothelial neoplasms: incidence and survival during the last 2 decades. J Urol. 2000; 164:1523–5.
Article2. Margulis V, Shariat SF, Matin SF, Kamat AM, Zigeuner R, Kikuchi E, et al. Outcomes of radical nephroureterectomy: a series from the Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Collaboration. Cancer. 2009; 115:1224–33.
Article3. Raman JD, Messer J, Sielatycki JA, Hollenbeak CS. Incidence and survival of patients with carcinoma of the ureter and renal pelvis in the USA, 1973-2005. BJU Int. 2011; 107:1059–64.
Article4. Roupret M, Babjuk M, Comperat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester R, Burger M, et al. European guidelines on upper tract urothelial carcinomas: 2013 update. Eur Urol. 2013; 63:1059–71.5. Audenet F, Yates DR, Cussenot O, Roupret M. The role of chemotherapy in the treatment of urothelial cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract (UUT-UCC). Urol Oncol. 2013; 31:407–13.
Article6. Birtle AJ, Lewis R, Johnson M, Hall E; POUT Trial Management Group (TMG). Time to define an international standard of postoperative care for resected upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma (TCC): opening of the peri-operative chemotherapy versus surveillance in upper tract urothelial cancer (POUT) Trial. BJU Int. 2012; 110:919–21.7. Chromecki TF, Bensalah K, Remzi M, Verhoest G, Cha EK, Scherr DS, et al. Prognostic factors for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 2011; 8:440–7.
Article8. Sun M, Abdo A, Abdollah F, Schmitges J, Thuret R, Jeldres C, et al. Management of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010; 10:1955–65.
Article9. Baade PD, Youlden DR, Chambers SK. When do I know I am cured? Using conditional estimates to provide better information about cancer survival prospects. Med J Aust. 2011; 194:73–7.
Article10. Ploussard G, Xylinas E, Lotan Y, Novara G, Margulis V, Roupret M, et al. Conditional survival after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:803–12.
Article11. Skuladottir H, Olsen JH. Conditional survival of patients with the four major histologic subgroups of lung cancer in Denmark. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:3035–40.
Article12. Merrill RM, Hunter BD. Conditional survival among cancer patients in the United States. Oncologist. 2010; 15:873–82.
Article13. Bianchi M, Becker A, Hansen J, Trinh QD, Tian Z, Abdollah F, et al. Conditional survival after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma (RCC): changes in future survival probability over time. BJU Int. 2013; 111:E283–9.
Article14. Ploussard G, Shariat SF, Dragomir A, Kluth LA, Xylinas E, Masson-Lecomte A, et al. Conditional survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: evidence for a patient changing risk profile over time. Eur Urol. 2014; 66:361–70.
Article15. Ku JH, Moon KC, Jung JH, Jeong SH, Kwak C, Kim HH. External validation of an online nomogram in patients undergoing radical nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:1130–6.
Article16. Taweemonkongsap T, Nualyong C, Amornvesukit T, Leewansangtong S, Srinualnad S, Chaiyaprasithi B, et al. Outcomes of surgical treatment for upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma: comparison of retroperitoneoscopic and open nephroureterectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 2008; 6:3.
Article17. Sobin L, Gospodarowicz M, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell;2009. p. 258–61.18. Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. World Health Organisation classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Press;2004. p. 89–158.19. Henson DE, Ries LA. On the estimation of survival. Semin Surg Oncol. 1994; 10:2–6.
Article20. Zabor EC, Gonen M, Chapman PB, Panageas KS. Dynamic prognostication using conditional survival estimates. Cancer. 2013; 119:3589–92.
Article21. Margulis V, Youssef RF, Karakiewicz PI, Lotan Y, Wood CG, Zigeuner R, et al. Preoperative multivariable prognostic model for prediction of nonorgan confined urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol. 2010; 184:453–8.
Article22. Lughezzani G, Burger M, Margulis V, Matin SF, Novara G, Roupret M, et al. Prognostic factors in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas: a comprehensive review of the current literature. Eur Urol. 2012; 62:100–14.
Article23. Shariat SF, Favaretto RL, Gupta A, Fritsche HM, Matsumoto K, Kassouf W, et al. Gender differences in radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma. World J Urol. 2011; 29:481–6.
Article24. Ehdaie B, Chromecki TF, Lee RK, Lotan Y, Margulis V, Karakiewicz PI, et al. Obesity adversely impacts disease specific outcomes in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. J Urol. 2011; 186:66–72.
Article25. Ng CK, Shariat SF, Lucas SM, Bagrodia A, Lotan Y, Scherr DS, et al. Does the presence of hydronephrosis on preoperative axial CT imaging predict worse outcomes for patients undergoing nephroureterectomy for upper-tract urothelial carcinoma? Urol Oncol. 2011; 29:27–32.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Urothelial Tumors of the Upper Urinary Tract: Multiplicity and Prognostic Variables
- Identification of Significant Prognostic Tissue Markers Associated with Survival in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Patients Treated with Radical Nephroureterectomy: A Retrospective Immunohistochemical Analysis Using Tissue Microarray
- Prognostic Factors in Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Upper Urinary Tract after Radical Nephroureterectomy
- Single Early Intravesical Instillation of Epirubicin for Preventing Bladder Recurrence after Nephroureterectomy in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
- The Characteristics of Recurrent Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma after Radical Nephroureterectomy without Bladder Cuff Excision