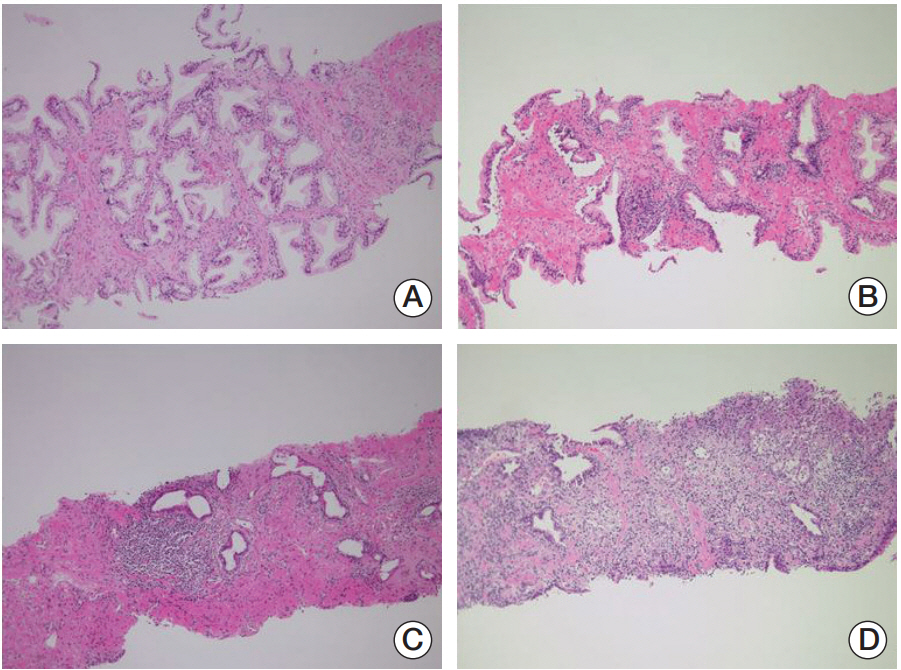
Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Jul;51(3):910-918. 10.4143/crt.2018.314.
Retrospective Study of the Significant Predictive Role of Inflammatory Degree in Initial and Repeat Prostate Biopsy Specimens for Detecting Prostate Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Center for Prostate Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. uroonco@ncc.re.kr
- 2Biostatistics Collaboration Unit, Research Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Center for Prostate Cancer, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. thymus@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2454283
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.314
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to determine whether histologic inflammation (HI) in initial and repeat prostate biopsy specimens was significantly associated with the detection of prostate cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between 2005 and 2017, the clinicopathological records of patients with high prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels who underwent initial and repeat prostate biopsies were retrospectively reviewed. The presence of HI and its degree in each biopsied specimen were interpreted by one uropathologist with 20 years of experience. The association between HI and cancer diagnosis was statistically assessed, with p < 0.05 considered significant, and the cancer and non-cancer groups were compared.
RESULTS
Among the 522 patients with a median PSA levels of 6.5 ng/dL, including 258 (49.4%) whose cancer was diagnosed following repeat biopsy, the median degrees of HI in the initial and repeat biopsies were 25.0% and 41.7%, respectively. Furthermore, 211 (40.4%) and 247 (47.3%) patients had HI (> 0%) on biopsied specimens, respectively. Comparison of the cancer and noncancer groups revealed that a greater rate of HI specimens in the initial biopsy was associated with fewer prostate cancer diagnoses following repeat biopsy (p < 0.001). Other comparisons between the cancer and non-cancer groups showed that the cancer group had a significantly higher rate of hypertension, whereas those non-cancer group had a significantly higher rate of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
A finding of a lesser degree of HI in the initial and a greater degree of HI in the repeat biopsied specimens was associated with the higher probability of cancer diagnosis in patients with high PSA levels.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Constantinou J, Feneley MR. PSA testing: an evolving relationship with prostate cancer screening. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2006; 9:6–13.
Article2. Blute ML Jr, Abel EJ, Downs TM, Kelcz F, Jarrard DF. Addressing the need for repeat prostate biopsy: new technology and approaches. Nat Rev Urol. 2015; 12:435–44.
Article3. Mohammed AA. Biomarkers in prostate cancer: new era and prospective. Med Oncol. 2014; 31:140.
Article4. Yli-Hemminki TH, Laurila M, Auvinen A, Maattanen L, Huhtala H, Tammela TL, et al. Histological inflammation and risk of subsequent prostate cancer among men with initially elevated serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) concentration in the Finnish prostate cancer screening trial. BJU Int. 2013; 112:735–41.
Article5. De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Xu J, Gronberg H, Drake CG, et al. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7:256–69.
Article6. Mahmud S, Franco E, Aprikian A. Prostate cancer and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2004; 90:93–9.
Article7. De Marzo AM, Marchi VL, Epstein JI, Nelson WG. Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate: implications for prostatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1999; 155:1985–92.8. Amara S, Tiriveedhi V. Inflammatory role of high salt level in tumor microenvironment (review). Int J Oncol. 2017; 50:1477–81.
Article9. Liu S, Sun JY, Ren LP, Chen K, Xu B. Propofol attenuates intermittent hypoxia induced up-regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in microglia through inhibiting the activation of NF-Bkappa/p38 MAPK signalling. Folia Neuropathol. 2017; 55:124–31.10. Fassi Fehri L, Mak TN, Laube B, Brinkmann V, Ogilvie LA, Mollenkopf H, et al. Prevalence of Propionibacterium acnes in diseased prostates and its inflammatory and transforming activity on prostate epithelial cells. Int J Med Microbiol. 2011; 301:69–78.
Article11. Huang TR, Wang GC, Zhang HM, Peng B. Differential research of inflammatory and related mediators in BPH, histological prostatitis and PCa. Andrologia. [Epub 2018 Feb 14]. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12974.
Article12. Romagny S, Bouaouiche S, Lucchi G, Ducoroy P, Bertoldo JB, Terenzi H, et al. S-Nitrosylation of cIAP1 switches cancer cell fate from TNFalpha/TNFR1-mediated cell survival to cell death. Cancer Res. 2018; 78:1948–57.13. Billis A. Prostatic atrophy: clinicopathological significance. Int Braz J Urol. 2010; 36:401–9.
Article14. Vasavada SR, Dobbs RW, Kajdacsy-Balla AA, Abern MR, Moreira DM. Inflammation on prostate needle biopsy is associated with lower prostate cancer risk: a meta-analysis. J Urol. 2018; 199:1174–81.
Article15. Busby JE, Evans CP. Determining variables for repeat prostate biopsy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2004; 7:93–8.
Article16. Scattoni V, Maccagnano C, Capitanio U, Gallina A, Briganti A, Montorsi F. Random biopsy: when, how many and where to take the cores? World J Urol. 2014; 32:859–69.
Article17. Ukimura O, Coleman JA, de la Taille A, Emberton M, Epstein JI, Freedland SJ, et al. Contemporary role of systematic prostate biopsies: indications, techniques, and implications for patient care. Eur Urol. 2013; 63:214–30.
Article18. Futterer JJ, Briganti A, De Visschere P, Emberton M, Giannarini G, Kirkham A, et al. Can clinically significant prostate cancer be detected with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging? A systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol. 2015; 68:1045–53.19. Mortezavi A, Marzendorfer O, Donati OF, Rizzi G, Rupp NJ, Wettstein MS, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and fusion guided targeted biopsy evaluated by transperineal template saturation prostate biopsy for the detection and characterization of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2018; 200:309–18.
Article20. Djavan B, Waldert M, Zlotta A, Dobronski P, Seitz C, Remzi M, et al. Safety and morbidity of first and repeat transrectal ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsies: results of a prospective European prostate cancer detection study. J Urol. 2001; 166:856–60.
Article21. Rosenkrantz AB, Taneja SS. Radiologist, be aware: ten pitfalls that confound the interpretation of multiparametric prostate MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014; 202:109–20.
Article22. Pal RP, Ahmad R, Trecartan S, Voss J, Ahmed S, Bazo A, et al. A single center evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging against transperineal prostate mapping biopsy: an analysis of men with benign histology and insignificant cancer following transrectal ultrasound biopsy. J Urol. 2018; 200:302–8.
Article23. Schouten MG, van der Leest M, Pokorny M, Hoogenboom M, Barentsz JO, Thompson LC, et al. Why and where do we miss significant prostate cancer with multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging followed by magnetic resonance-guided and transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy in biopsy-naive men? Eur Urol. 2017; 71:896–903.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Predictive Factors of Prostatic Cancer Detection on Repeat Prostate Biopsy
- Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
- Role of Prostate-Specific Antigen Change Ratio at Initial Biopsy as a Novel Decision-Making Marker for Repeat Prostate Biopsy
- Clinical Predictive Factors in Patients with Prostate Cancer Diagnosed by Repeat Prostate Biopsy
- Role of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer for Patients with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Serum PSA 4-10ng/ml with a Negative Repeat Transrectal Needle Biopsy of Prostat