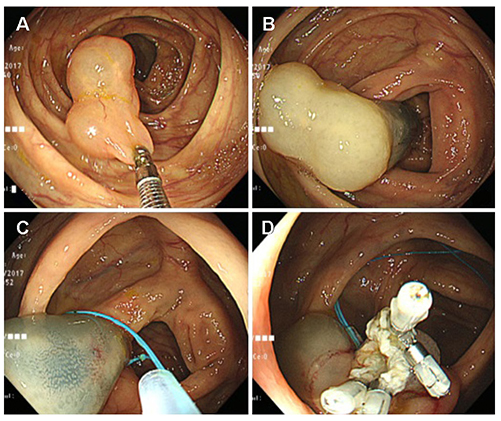
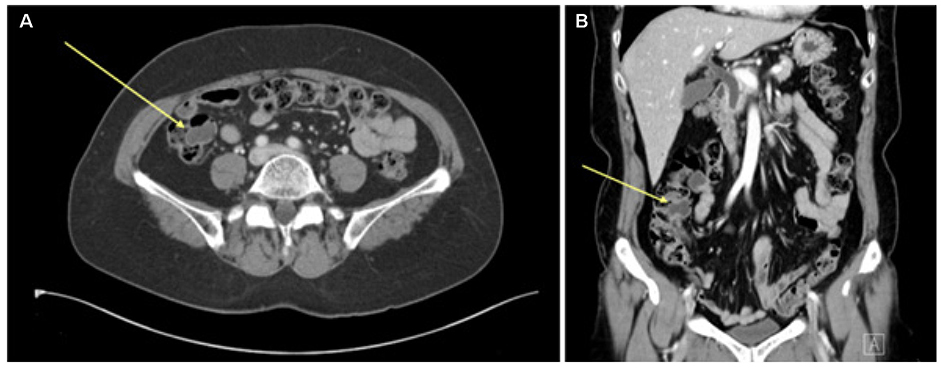
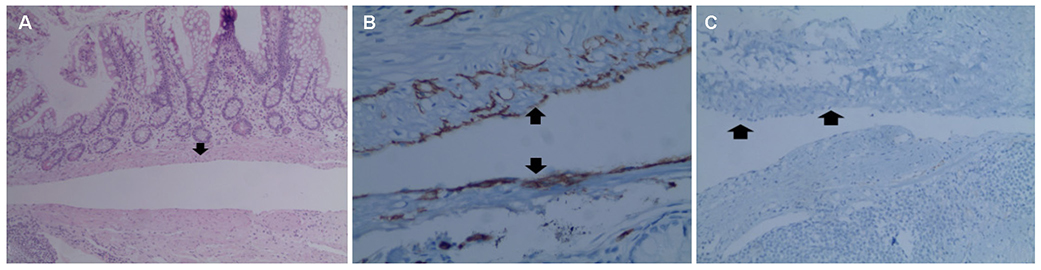
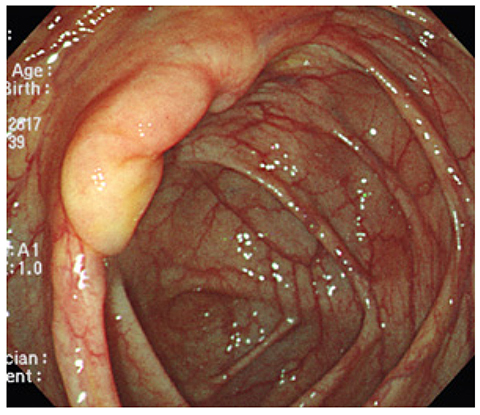
Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Jun;73(6):370-372. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.6.370.
Endoscopic Resection of Colonic Vascular Ectasia Mimicking as a Pedunculated Polypoid Lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. schlp@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Anatomic Pathology, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2454100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.6.370
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tada Y, Okamura S, Okita Y, et al. Vascular ectasia of the colon treated by argon plasma coagulation: report of a case. Dig Endosc. 2001; 13:37–40.
Article2. Koziara FJ, Brodmerkel GJ, Boylan JJ, Ciambotti GF, Agrawal RM. Bleeding from polypoid colonic arteriovenous malformations. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:584–586.3. Yu BH, Shin SJ, Lee KW, et al. A large polypoid vascular ectasia removed by using a polypectomy with a detachable snare in an asymptomatic patient. Ann Coloproctol. 2013; 29:31–33.
Article4. Lin IT, Chang WH, Shih SC, et al. Successful endoscopic polypectomy for colonic vascular ectasia presenting as pedunculated polypoid lesion. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:Suppl 1. E253–E254.
Article5. Boley SJ, Sammartano R, Adams A, DiBiase A, Kleinhaus S, Sprayregen S. On the nature and etiology of vascular ectasias of the colon. Degenerative lesions of aging. Gastroenterology. 1977; 72(4 Pt 1):650–660.6. Kim JW, Oh HC, Kim MK, Kim JG. Polypoid vascular and lymphatic malformation of the duodenum: a case report. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2010; 19:85–88.7. Roberts PL, Schoetz DJ Jr, Coller JA. Vascular ectasia. Diagnosis and treatment by colonoscopy. Am Surg. 1988; 54:56–59.8. Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Mohamadnejad M, Malekzadeh R, Tavangar SM. Images of interest. Gastrointestinal: polypoid arteriovenous malformation of the colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 19:1419.9. Gong EJ, Kim DH, Jung HY, et al. An arteriovenous malformation in the jejunum mimicking a gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2014; 63:42–46.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Large Polypoid Vascular Ectasia Removed by Using a Polypectomy With a Detachable Snare in an Asymptomatic Patient
- A Case of Colonic Cavernous Hemangioma Misdiagnosed as a Pedunculated Polyp
- A case report of an unexpected colonic polyp: cavernous hemangioma
- Cecal Polypoid Arteriovenous Malformations Removed by Endoscopic Biopsy
- A large and pedunculated inflammatory pseudotumor with pseudosarcomatous change of the cecum mimicking a malignant polyp: a case report and literature review