J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Apr;24(2):342-345. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.342.
Cecal Polypoid Arteriovenous Malformations Removed by Endoscopic Biopsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunyoung@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1779143
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.2.342
Abstract
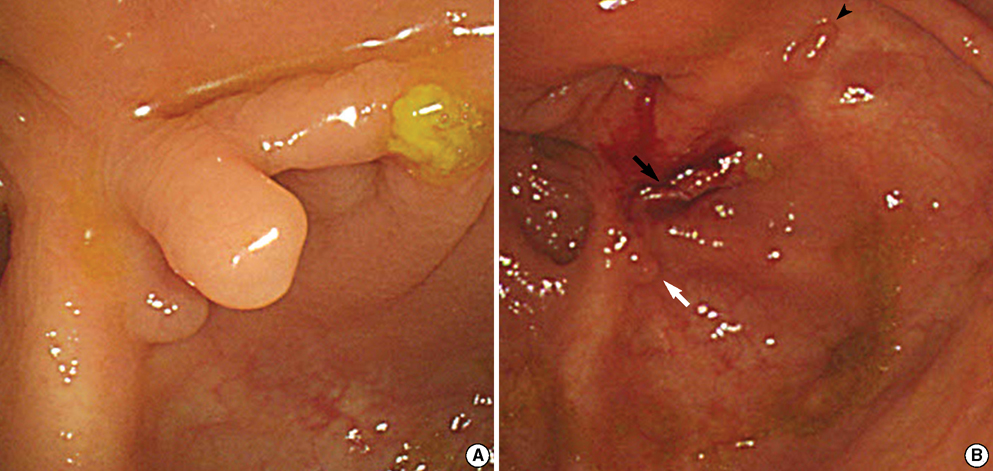
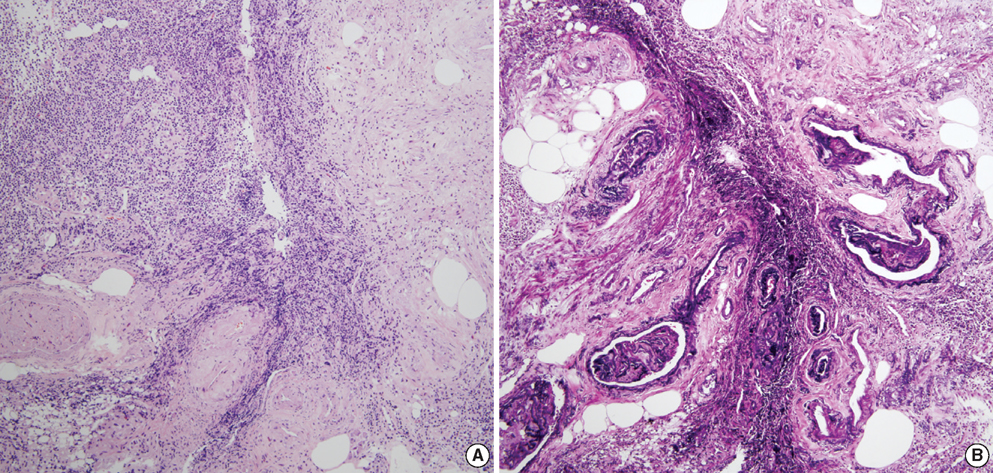
- Colonic arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is one of the causes of lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Unlike small vascular ectasia or angiodysplasia, colonic AVM tends to be solitary, large in size, and identified endoscopically as flat or elevated bright red lesion. Herein, we report a case of non-solitary and small cecal AVMs which were removed by endoscopic biopsy. A 66-yr-old woman was referred for routine gastrointestinal cancer screening. She was suffering from diabetes, hypertension, end-stage renal disease, and anemia of chronic disease. On colonoscopic finding, three semi-pedunculated polyps, less than 5 mm in size, were noticed near to the appendiceal orifice. Since the lesions revealed normal-looking epithelium with converging folds on the cecal base, lesions were diagnosed as inflammatory polyps on gross finding. Three biopsies were taken from each lesion. Bleeding from the biopsied site ceased spontaneously. Histopathologic evaluation demonstrated intramucosal hemorrhage and dilated submucosal vessels which were consistent with polypoid colonic AVMs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Polypoid Arteriovenous Malformation Presenting with Jejunojejunal Intussusceptions in an Adult
Doo-Ho Lim, Ji Yong Ahn, Myeongsook Seo, Ji Hyun Yun, Tae Hyung Kim, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Jin-Ho Kim, Young Soo Park
Clin Endosc. 2014;47(6):575-578. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.6.575.
Reference
-
1. Vernava AM 3rd, Moore BA, Longo WE, Johnson FE. Lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997. 40:846–858.
Article2. Koziara FJ, Brodmerkel GJ, Boylan JJ, Ciambotti GF, Agrawal RM. Bleeding from polypoid colonic arteriovenous malformations. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996. 91:584–586.3. Park ER, Yang SK, Jung SA, Shim KN, Jung HY, Kim HR, Hong WS, Min YI. A case of pedunculated arteriovenous malformation presenting with massive hematochezia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 51:96–97.
Article4. D'Arienzo A, Manguso F, D'Armiento FP, Bennato R, Somma P, Pisani A, Panarese A, Mazzacca G. Colonoscopic removal of a polypoid arteriovenous malformation. Dig Liver Dis. 2001. 33:435–437.5. McKevitt EC, Attwell AJ, Davis JE, Yoshida EM. Diminutive but dangerous: a case of a polypoid rectal arteriovenous malformation. Endoscopy. 2002. 34:429.
Article6. Maeng L, Choi KY, Lee A, Kang CS, Kim KM. Polypoid arteriovenous malformation of colon mimicking inflammatory fibroid polyp. J Gastroenterol. 2004. 39:575–578.
Article7. Nasseri-Moghaddam A, Mohamadnejad M, Malekzadeh R, Tavangar SM. Gastrointestinal polypoid arteriovenous malformation of the colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 19:1419.
Article8. Ji JS, Choi KY, Lee BI, Kim BW, Choi H, Cho SH, Chung WC, Lee IS, Lee KM, Chae HS, Chung IS, Kim KM. A large polypoid arteriovenous malformation of the colon treated with a detachable snare: case report and review of literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005. 62:172–175.
Article9. Boley SJ, Sammartano R, Adams A, DiBiase A, Kleinhaus S, Sprayregen S. On the nature and etiology of vascular ectasias of the colon: degenerative lesions of aging. Gastroenterology. 1977. 72:650–660.10. Kim HJ, Jung JK, Suh YM, Kim KS, Kim H. Bleeding from Dieulafoy's vascular malformation of the proximal ileum. Korean J Pathol. 1999. 33:1207–1210.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Polypoid Arteriovenous Malformation Treated by Polypectomy with Detachable Snare
- Polypoid Arteriovenous Malformation Presenting with Jejunojejunal Intussusceptions in an Adult
- A Case of Acquired Multiple Arteriovenous Malformations on the Scalp in the Patient of Liver Cirrhosis
- 3 Cases of Surgically Treated Arteriovenous Malformations of the Brain
- Two Stage Operation for Large Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation