Yonsei Med J.
2012 Sep;53(5):999-1004.
Therapeutic Effects of Carbogen Inhalation and Lipo-Prostaglandin E1 in Sudden Hearing Loss
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ismoonmd@yuhs.ac
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Vascular disorders and viral infections are considered the main causes of sudden hearing loss (SHL), although its pathogenesis remain unclear. Treatments include carbogen inhalation and lipo-prostaglandin E1 (lipo-PGE1), both of which have circulation-enhancing effects. We investigated the effectiveness of carbogen inhalation and lipo-PGE1 in SHL.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
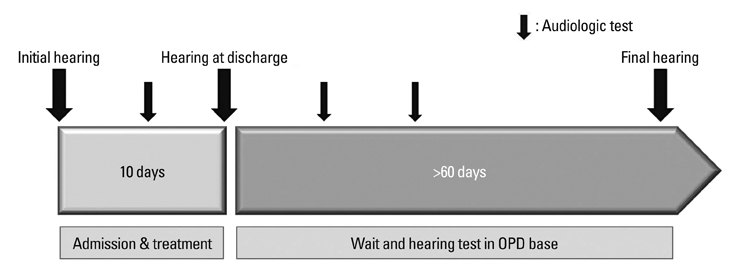
This retrospective review included 202 patients with idiopathic SHL who visited our clinic within 14 days of symptom onset between January 2006 and June 2010. All patients received oral prednisolone for 10 days. Of the 202 patients, 44 received no additional treatment, 106 received additional carbogen inhalation, and 52 received additional lipo-PGE1. Hearing improvement was measured using Siegel's criteria.
RESULTS
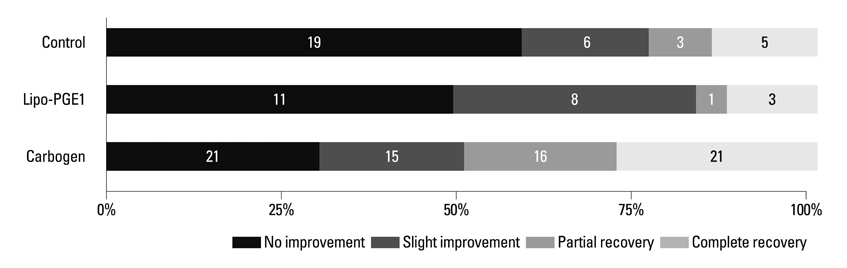
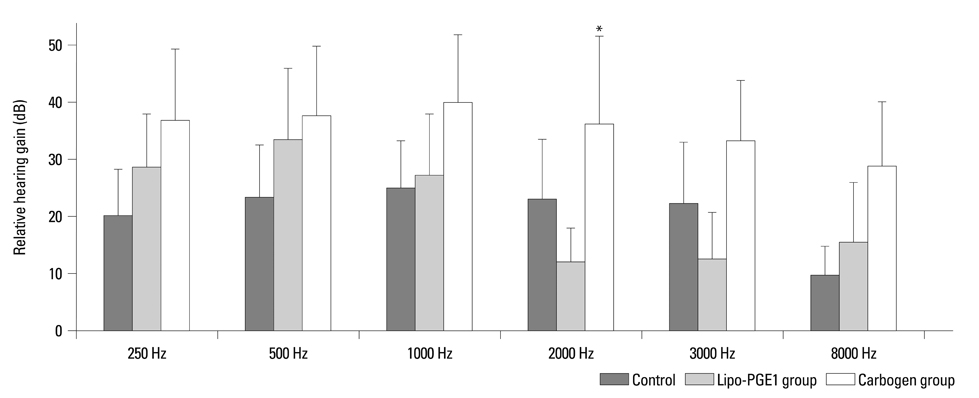
Overall recovery rates were 67.9% in the carbogen group, 53.8% in the lipo-PGE1 group, and 52.3% in the steroid-only control group (p=0.097). Limited to type 1 and type 2 categories of Sigels's criteria, the carbogen group had a significantly higher recovery rate (53.8%) than the lipo-PGE1 group (26.9%) and the steroid-only control group (38.6%) (p=0.005).
CONCLUSION
Carbogen inhalation added to steroid was a more effective treatment than lipo-PGE1 added to steroid or steroid alone in patients with SHL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arts HA. Flint PW, editor. Sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Cummings Otolaryngology: head & neck surgery. 2010. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;2117–2130.
Article2. De Kleyn A. Sudden complete or partial loss of function of the octarus system in apparently normal person. Acta Otolaryngol. 1944. 32:407–429.3. Park MS. Rha KS, editor. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2009. 2nd ed. Seoul, Korea: Ilchokak;781–788.4. Lazarini PR, Camargo AC. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: etiopathogenic aspects. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2006. 72:554–561.
Article5. Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol. 1980. 106:772–776.
Article6. Cinamon U, Bendet E, Kronenberg J. Steroids, carbogen or placebo for sudden hearing loss: a prospective double-blind study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2001. 258:477–480.
Article7. Kanzaki J, Taiji H, Ogawa K. Evaluation of hearing recovery and efficacy of steroid treatment in sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1988. 456:31–36.
Article8. Moon IS, Lee JD, Kim J, Hong SJ, Lee WS. Intratympanic dexamethasone is an effective method as a salvage treatment in refractory sudden hearing loss. Otol Neurotol. 2011. 32:1432–1436.
Article9. Stokroos RJ, Albers FW, Tenvergert EM. Antiviral treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Acta Otolaryngol. 1998. 118:488–495.
Article10. Shea JJ, Kitabchi AE. Management of fluctuant hearing loss. Arch Otolaryngol. 1973. 97:118–124.
Article11. Zhuo XL, Wang Y, Zhuo WL, Zhang XY. Is the application of prostaglandin E1 effective for the treatment of sudden hearing loss? An evidence-based meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2008. 36:467–470.
Article12. Ahn JH, Kim MR, Kim HC. Therapeutic effect of lipoprostaglandin E1 on sudden hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005. 26:245–248.
Article13. Moon IS, Kim J, Lee SY, Choi HS, Lee WS. How long should the sudden hearing loss patients be followed after early steroid combination therapy? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009. 266:1391–1395.
Article14. Westerlaken BO, Stokroos RJ, Dhooge IJ, Wit HP, Albers FW. Treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with antiviral therapy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003. 112:993–1000.
Article15. Karetova D, Bultas J, Vondracek V, Aschermann M. Alprostadil: modes of actions in peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Am J Ther. 1997. 4:359–363.16. Ferreira SH, Vane JR. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967. 216:868–873.
Article17. Hoshi K, Mizushima Y, Kiyokawa S, Yanagawa A. Prostaglandin E1 incorporated in lipid microspheres in the treatment of peripheral vascular diseases and diabetic neuropathy. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1986. 12:681–685.18. Kallinen J, Didier A, Miller JM, Nuttall A, Grénman R. The effect of CO2- and O2-gas mixtures on laser Doppler measured cochlear and skin blood flow in guinea pigs. Hear Res. 1991. 55:255–262.
Article19. Fisch U, Murata K, Hossli G. Measurement of oxygen tension in human perilymph. Acta Otolaryngol. 1976. 81:278–282.
Article20. Kallinen J, Laurikainen E, Laippala P, Grénman R. Sudden deafness: a comparison of anticoagulant therapy and carbogen inhalation therapy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997. 106:22–26.
Article21. Nishimura T, Nario K, Hosoi H. Effects of intravenous administration of prostaglandin E(1) and lipo-prostaglandin E(1) on cochlear blood flow in guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2002. 259:253–256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Study for Combined Therapeutic Effects of Lipoprostaglandin E1 with Carbogen Inhalation on Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Comparative Analysis of the Combined Therapeutic Effects of Lipoprostaglandin E1 on Sudden Idiopathic Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Effects of Carbogen Inhalation and Stellate Ganglion Block in the Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Analysis of Therapeutic Effects of Lipo-Prostaglandin E1 for Treatment of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- A Comparative Study on the Treatment Effect of Lipo-Prostagladin with Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Patients