Korean J Radiol.
2019 Aug;20(8):1275-1284. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0615.
Fully Automatic Segmentation of Acute Ischemic Lesions on Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Using Convolutional Neural Networks: Comparison with Conventional Algorithms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Convergence Medicine, Biomedical Engineering Research Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dynamics79@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2453077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0615
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To develop algorithms using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for automatic segmentation of acute ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and compare them with conventional algorithms, including a thresholding-based segmentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
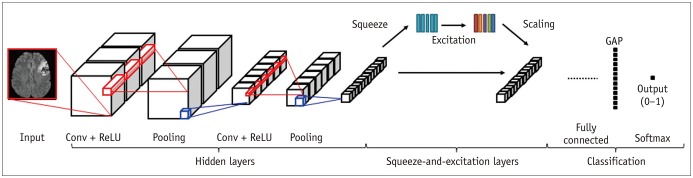
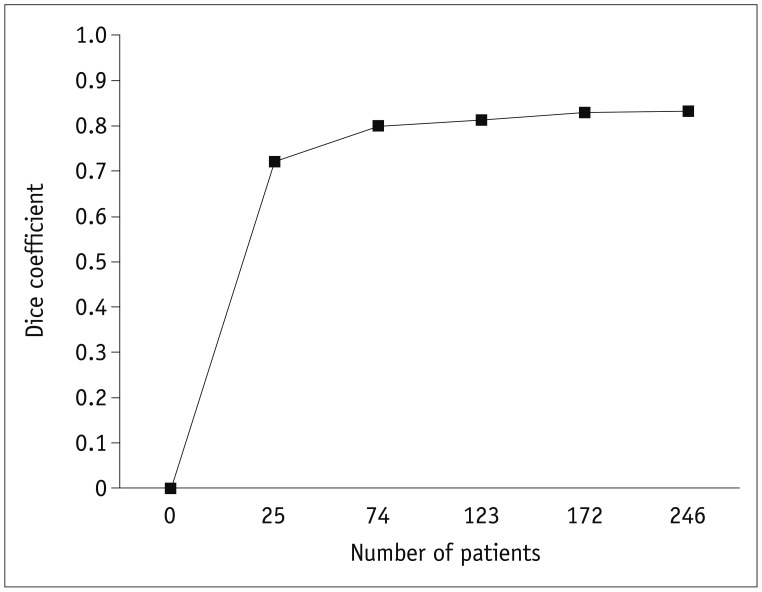
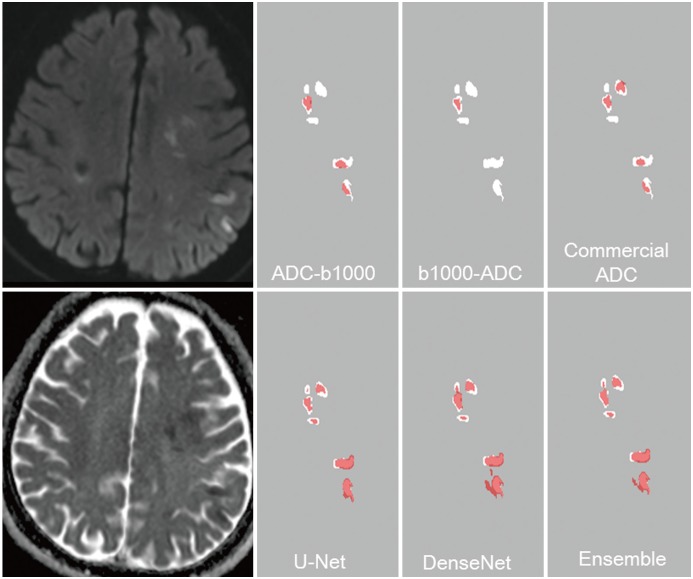
Between September 2005 and August 2015, 429 patients presenting with acute cerebral ischemia (training:validation:test set = 246:89:94) were retrospectively enrolled in this study, which was performed under Institutional Review Board approval. Ground truth segmentations for acute ischemic lesions on DWI were manually drawn under the consensus of two expert radiologists. CNN algorithms were developed using two-dimensional U-Net with squeeze-and-excitation blocks (U-Net) and a DenseNet with squeeze-and-excitation blocks (DenseNet) with squeeze-and-excitation operations for automatic segmentation of acute ischemic lesions on DWI. The CNN algorithms were compared with conventional algorithms based on DWI and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) signal intensity. The performances of the algorithms were assessed using the Dice index with 5-fold cross-validation. The Dice indices were analyzed according to infarct volumes (< 10 mL, ≥ 10 mL), number of infarcts (≤ 5, 6-10, ≥ 11), and b-value of 1000 (b1000) signal intensities (< 50, 50-100, > 100), time intervals to DWI, and DWI protocols.
RESULTS
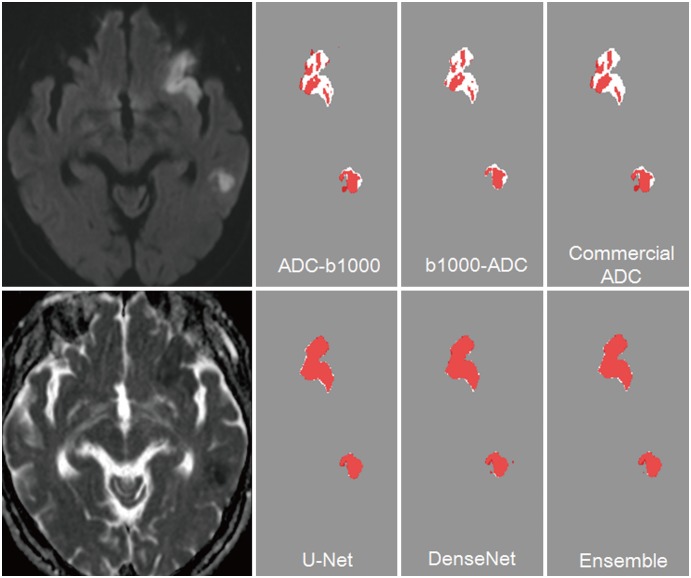
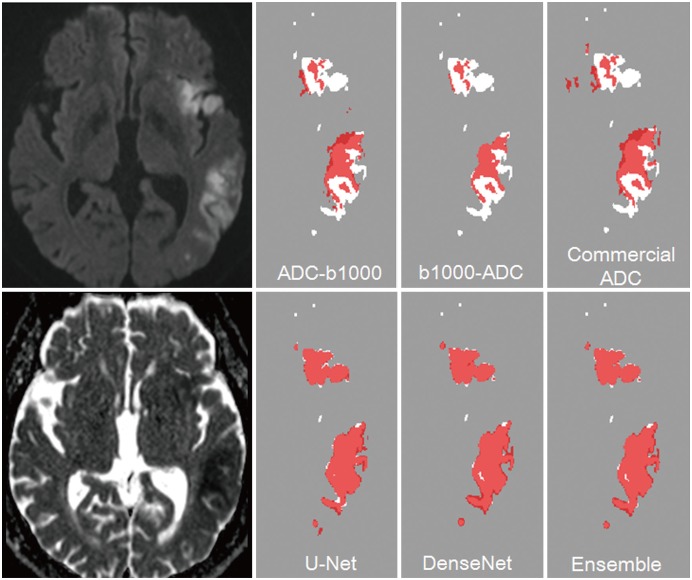
The CNN algorithms were significantly superior to conventional algorithms (p < 0.001). Dice indices for the CNN algorithms were 0.85 for U-Net and DenseNet and 0.86 for an ensemble of U-Net and DenseNet, while the indices were 0.58 for ADC-b1000 and b1000-ADC and 0.52 for the commercial ADC algorithm. The Dice indices for small and large lesions, respectively, were 0.81 and 0.88 with U-Net, 0.80 and 0.88 with DenseNet, and 0.82 and 0.89 with the ensemble of U-Net and DenseNet. The CNN algorithms showed significant differences in Dice indices according to infarct volumes (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
The CNN algorithm for automatic segmentation of acute ischemic lesions on DWI achieved Dice indices greater than or equal to 0.85 and showed superior performance to conventional algorithms.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Proposed Protocols for Artificial Intelligence Imaging Database in Acute Stroke Imaging
Minjae Kim, Seung Chai Jung, Soo Chin Kim, Bum Joon Kim, Woo-Keun Seo, Byungjun Kim
Neurointervention. 2023;18(3):149-158. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2023.00339.
Reference
-
1. Wheeler HM, Mlynash M, Inoue M, Tipirneni A, Liggins J, Zaharchuk G, et al. DEFUSE 2 Investigators. Early diffusion-weighted imaging and perfusion-weighted imaging lesion volumes forecast final infarct size in DEFUSE 2. Stroke. 2013; 44:681–685. PMID: 23390119.
Article2. Muir KW, Buchan A, von Kummer R, Rother J, Baron JC. Imaging of acute stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:755–768. PMID: 16914404.
Article3. Chen L, Bentley P, Rueckert D. Fully automatic acute ischemic lesion segmentation in DWI using convolutional neural networks. Neuroimage Clin. 2017; 15:633–643. PMID: 28664034.
Article4. Mah YH, Jager R, Kennard C, Husain M, Nachev P. A new method for automated high-dimensional lesion segmentation evaluated in vascular injury and applied to the human occipital lobe. Cortex. 2014; 56:51–63. PMID: 23347558.
Article5. Boldsen JK, Engedal TS, Pedraza S, Cho TH, Thomalla G, Nighoghossian N, et al. Better diffusion segmentation in acute ischemic stroke through automatic tree learning anomaly segmentation. Front Neuroinform. 2018; 12:21. PMID: 29910721.
Article6. Straka M, Albers GW, Bammer R. Real-time diffusion-perfusion mismatch analysis in acute stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 32:1024–1037. PMID: 21031505.
Article7. Forbes F, Doyle S, Garcia-Lorenzo D, Barillot C, Dojat M. Adaptive weighted fusion of multiple MR sequences for brain lesion segmentation. In : 2010 IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro; 2010 April 14–17; Rotterdam, Netherlands.8. Charoensuk W, Covavisaruch N, Lerdlum S, Likitjaroen Y. Acute stroke brain infarct segmentation in DWI images. Int J Pharm Med Biol Sci. 2015; 4:115–122.9. Prakash KNB, Gupta V, Bilello M, Beauchamp NJ, Nowinski WL. Identification, segmentation, and image property study of acute infarcts in diffusion-weighted images by using a probabilistic neural network and adaptive Gaussian mixture model. Acad Radiol. 2006; 13:1474–1484. PMID: 17138115.10. Mohd Saad N, Noor NSM, Abdullah AR, Muda S, Muda AF, Abdul Rahman NNS. Automated stroke lesion detection and diagnosis system. In : International MultiConference of engineers and computer scientists; 2017 March 15–17; Hong Kong, China.11. Maier O, Wilms M, von der Gablentz J, Krämer UM, Münte TF, Handels H. Extra tree forests for sub-acute ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in MR sequences. J Neurosci Methods. 2015; 240:89–100. PMID: 25448384.
Article12. Peng Y, Zhang X, Hu Q. Segmentation of hyper-acute ischemic infarcts from diffusion weighted imaging based on support vector machine. Journal of Computer and Communications. 2015; 3:152–157.
Article13. Nag MK, Koley S, China D, Sadhu AK, Balaji R, Ghosh S, et al. Computer-assisted delineation of cerebral infarct from diffusion-weighted MRI using Gaussian mixture model. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017; 12:539–552. PMID: 28070776.
Article14. Warach S, Chien D, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR. Fast magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging of acute human stroke. Neurology. 1992; 42:1717–1723. PMID: 1513459.
Article15. van Everdingen KJ, van der Grond J, Kappelle LJ, Ramos LMP, Mali WPTM. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in acute stroke. Stroke. 1998; 29:1783–1790. PMID: 9731595.
Article16. Purushotham A, Campbell BC, Straka M, Mlynash M, Olivot JM, Bammer R, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient threshold for delineation of ischemic core. Int J Stroke. 2015; 10:348–353. PMID: 23802548.
Article17. Ogata T, Christensen S, Nagakane Y, Ma H, Campbell BC, Churilov L, et al. EPITHET and DEFUSE Investigators. The effects of alteplase 3 to 6 hours after stroke in the EPITHET-DEFUSE combined dataset: post hoc case-control study. Stroke. 2013; 44:87–89. PMID: 23250996.18. Lee JG, Jun S, Cho YW, Lee H, Kim GB, Seo JB, et al. Deep learning in medical imaging: general overview. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:570–584. PMID: 28670152.
Article19. Woo I, Lee AR, Lee H, Choi K, Kang DW, Jung SC, et al. Sementic segmentation with squeeze-and-excitation block: application to infarct segmentation in DWI. In : NIPS 2017: the thirty-first annual conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; 2017 December 4–9; Long Beach, CA, USA.20. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In : 18th Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Interventions (MICCAI); 2015 October 5–9; Munich, Germany.21. Jégou S, Drozdzal M, Vazquez D, Romero A, Bengio Y. The one hundred layers tiramisu: fully convolutional DenseNets for semantic segmentation. In : IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW); 2017 July 21–26; Honolulu, HI, USA.22. Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In : IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR); 2018 June 18–22; Salt Lake City, UT, USA.23. Nair V, Hinton GE. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In : 27th international conference on international conference on machine learning; 2010 June 21–24; Haifa, Israel.24. Shinohara RT, Sweeney EM, Goldsmith J, Shiee N, Mateen FJ, Calabresi PA, et al. Australian Imaging Biomarkers Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Statistical normalization techniques for magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage Clin. 2014; 6:9–19. PMID: 25379412.
Article25. Noh H, Hong S, Han B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In : IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV); 2015 December 7–13; Santiago, Chile.26. Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. Densely connected convolutional networks. In : IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR); 2017 July 21–26; Honolulu, HI, USA.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reversal of a Large Ischemic Lesion with Low Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value by Rapid Spontaneous Recanalization
- An Overview of Deep Learning Algorithms and Their Applications in Neuropsychiatry
- Deep learning for prediction of mechanism in acute ischemic stroke using brain diffusion magnetic resonance image
- Perfusion MR Imaging in Patients with Acute Cerebral Infarction:Comparison with T2-Weighted and Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
- The Usefulness of Diffusion: Weighted Magnetic Resonance Image in the Diagnosis of Neonatal Seizure