J Neurocrit Care.
2023 Dec;16(2):85-93. 10.18700/jnc.230039.
Deep learning for prediction of mechanism in acute ischemic stroke using brain diffusion magnetic resonance image
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Public Health, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center, Icheon Hospital, Icheon, Korea
- 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea
- 5Department of Neurology, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu, Korea
- 6Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Neurology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- KMID: 2549485
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.230039
Abstract
- Background
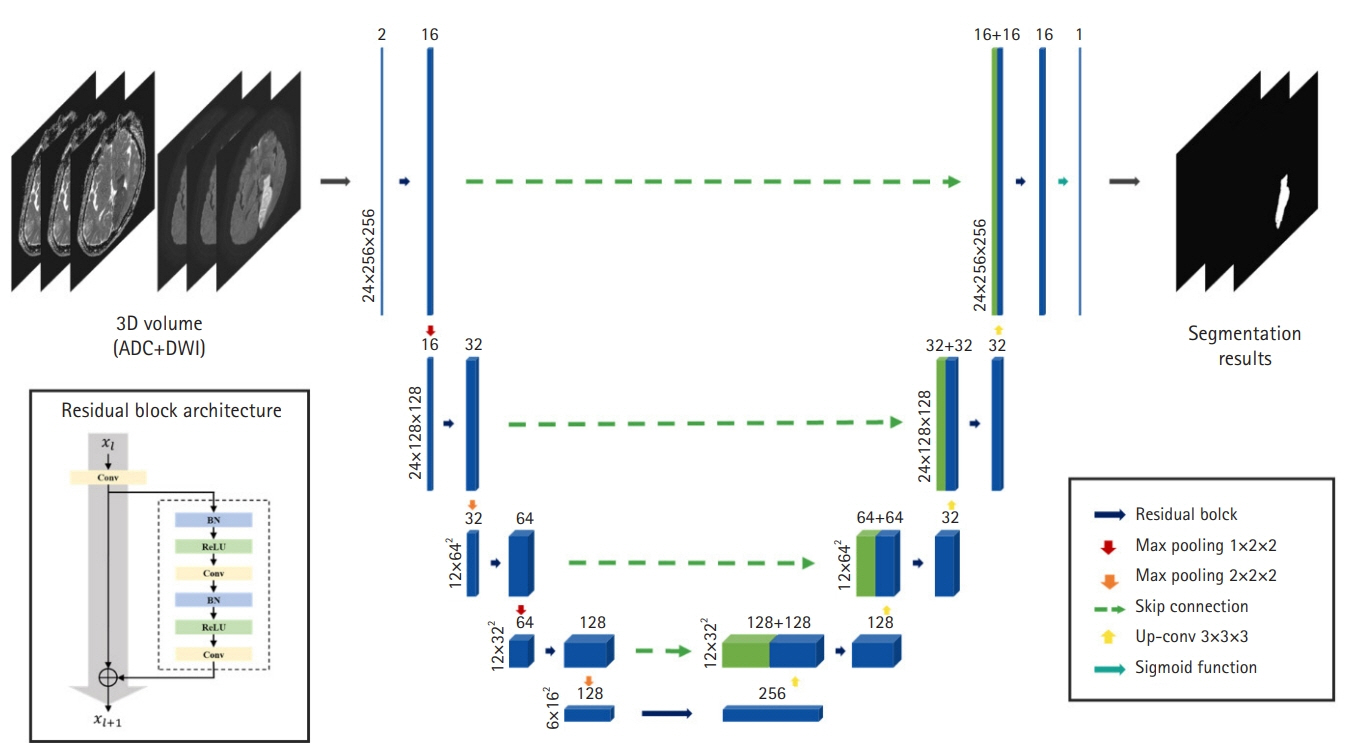
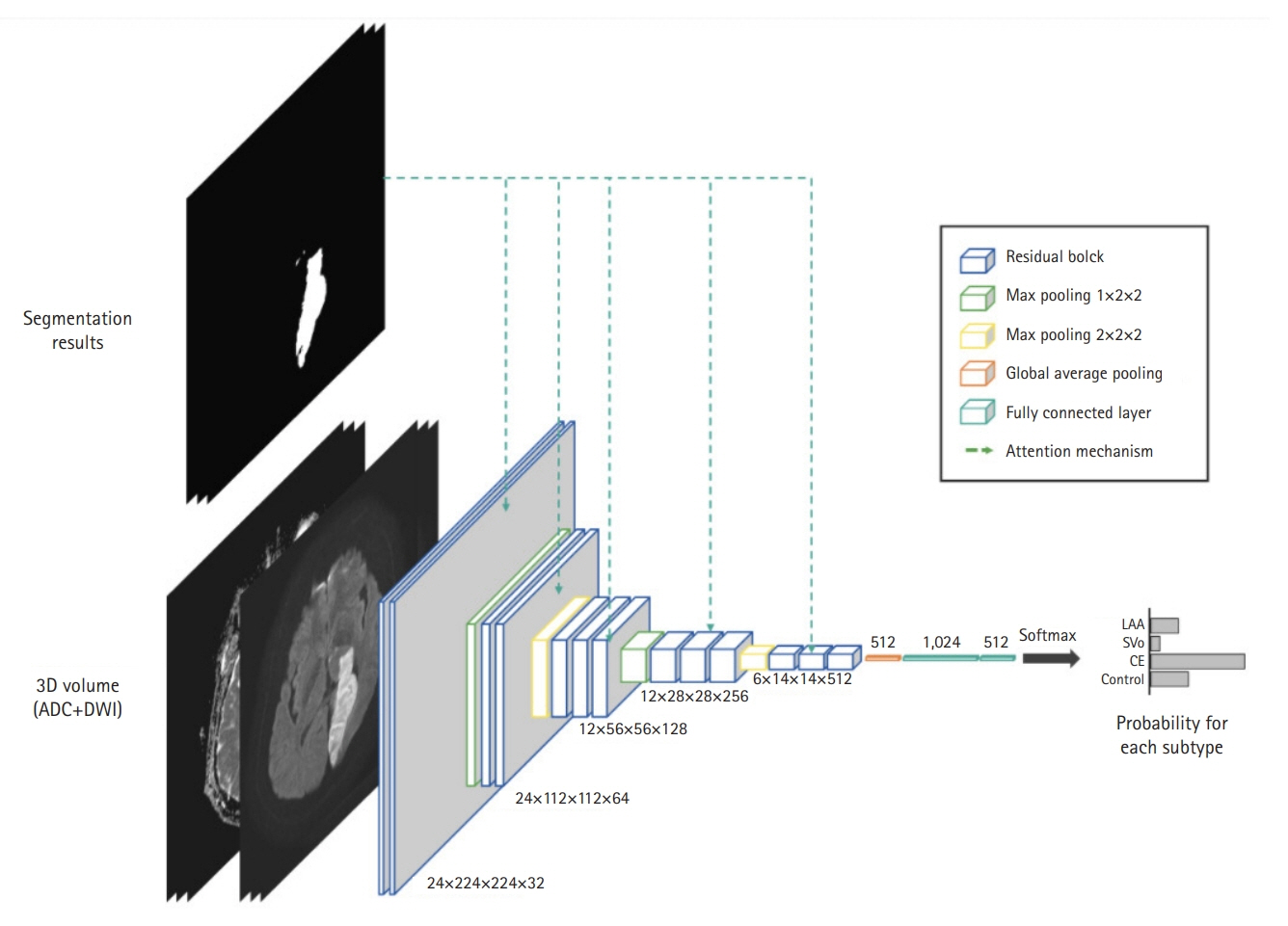
Acute ischemic stroke is a disease with multiple etiologies. Therefore, identifying the mechanism of acute ischemic stroke is fundamental to its treatment and secondary prevention. The Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment classification is currently the most widely used system, but it often has a limitations of classifying unknown causes and inadequate inter-rater reliability. Therefore, we attempted to develop a three-dimensional (3D)-convolutional neural network (CNN)-based algorithm for stroke lesion segmentation and subtype classification using only the diffusion and apparent diffusion coefficient information of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Methods
This study included 2,251 patients with acute ischemic stroke who visited our hospital between February 2013 and July 2019.
Results
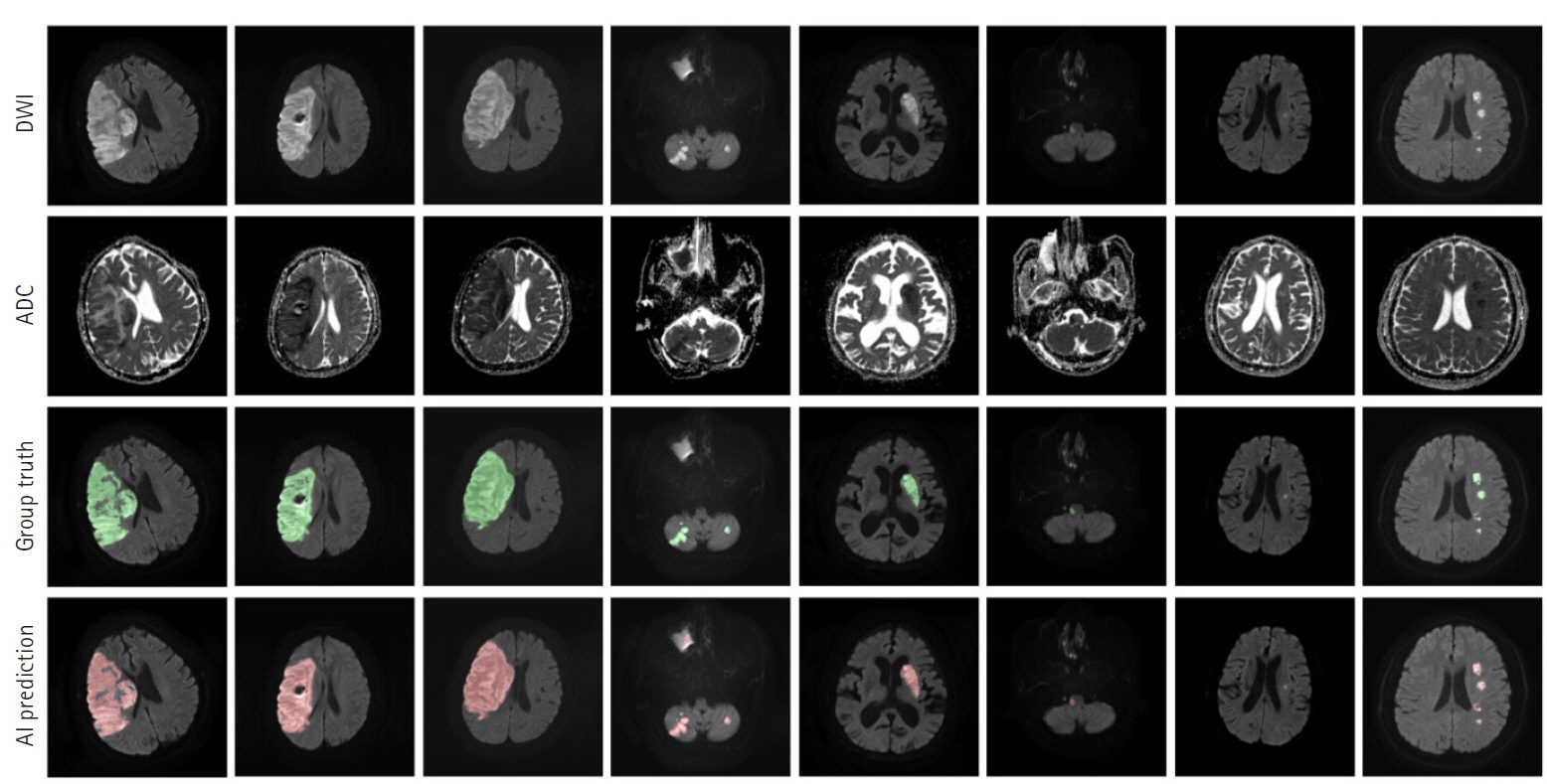
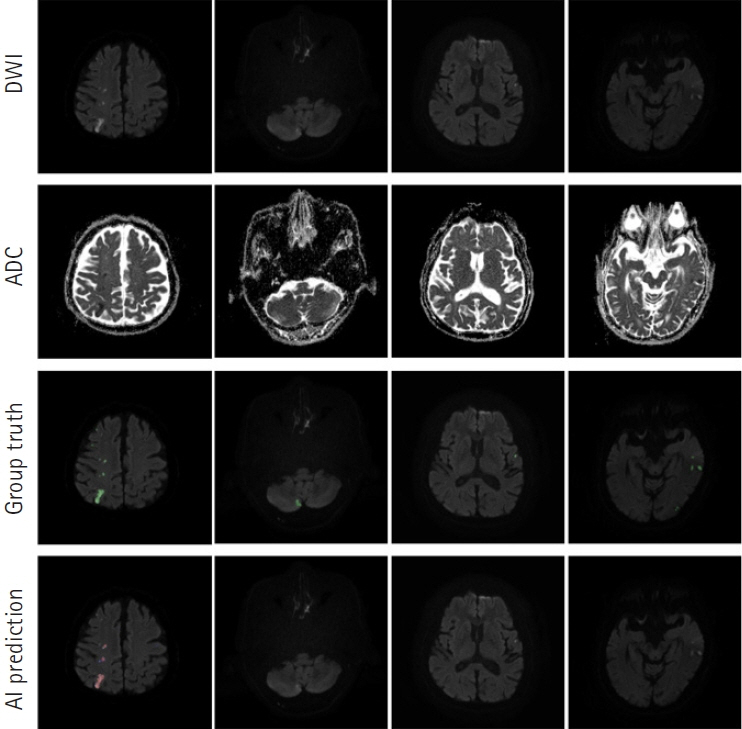
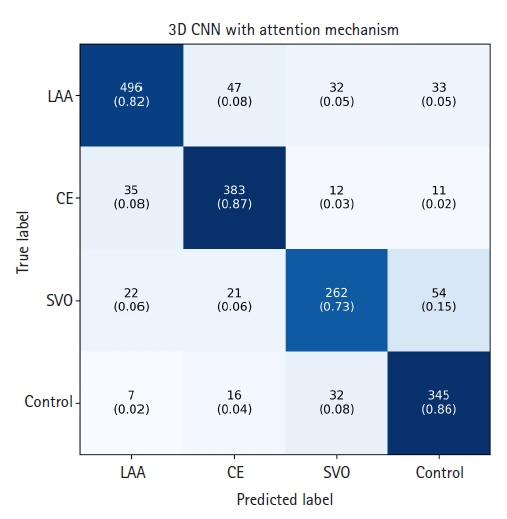
The segmentation model for lesion segmentation in the training set achieved a Dice score of 0.843±0.009. The subtype classification model achieved an average accuracy of 81.9%, with accuracies of 81.6% for large artery atherosclerosis, 86.8% for cardioembolism, 72.9% for small vessel occlusion, and 86.3% for control.
Conclusion
We developed a model to predict the mechanism of cerebral infarction using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging, which has great potential for identifying diffusion lesion segmentation and stroke subtype classification. As deep learning systems are gradually developing, they are becoming useful in clinical practice and applications.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Deep Learning-Based Automatic Classification of Ischemic Stroke Subtype Using Diffusion-Weighted Images
Wi-Sun Ryu, Dawid Schellingerhout, Hoyoun Lee, Keon-Joo Lee, Chi Kyung Kim, Beom Joon Kim, Jong-Won Chung, Jae-Sung Lim, Joon-Tae Kim, Dae-Hyun Kim, Jae-Kwan Cha, Leonard Sunwoo, Dongmin Kim, Sang-Il Suh, Oh Young Bang, Hee-Joon Bae, Dong-Eog Kim
J Stroke. 2024;26(2):300-311. doi: 10.5853/jos.2024.00535.
Reference
-
1. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.2. Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Caplan LR, Donnan GA, Hennerici MG. Classification of stroke subtypes. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009; 27:493–501.3. Meschia JF, Barrett KM, Chukwudelunzu F, Brown WM, Case LD, Kissela BM, et al. Interobserver agreement in the trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment classification of stroke based on retrospective medical record review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006; 15:266–72.4. Goldstein LB, Jones MR, Matchar DB, Edwards LJ, Hoff J, Chilukuri V, et al. Improving the reliability of stroke subgroup classification using the Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) criteria. Stroke. 2001; 32:1091–8.5. Ko Y, Lee S, Chung JW, Han MK, Park JM, Kang K, et al. MRI-based algorithm for acute ischemic stroke subtype classification. J Stroke. 2014; 16:161–72.6. Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B, Wielopolski P, Edelman RR. Acute human stroke studied by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1995; 37:231–41.7. Lansberg MG, Thijs VN, O'Brien MW, Ali JO, de Crespigny AJ, Tong DC, et al. Evolution of apparent diffusion coefficient, diffusion-weighted, and T2-weighted signal intensity of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:637–44.8. Wessels T, Wessels C, Ellsiepen A, Reuter I, Trittmacher S, Stolz E, et al. Contribution of diffusion-weighted imaging in determination of stroke etiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:35–9.9. Kang DW, Chalela JA, Ezzeddine MA, Warach S. Association of ischemic lesion patterns on early diffusion-weighted imaging with TOAST stroke subtypes. Arch Neurol. 2003; 60:1730–4.10. Wu O, Winzeck S, Giese AK, Hancock BL, Etherton MR, Bouts MJ, et al. Big data approaches to phenotyping acute ischemic stroke using automated lesion segmentation of multi-center magnetic resonance imaging data. Stroke. 2019; 50:1734–41.11. Lee H, Lee EJ, Ham S, Lee HB, Lee JS, Kwon SU, et al. Machine learning approach to identify stroke within 4.5 hours. Stroke. 2020; 51:860–6.12. Boldsen JK, Engedal TS, Pedraza S, Cho TH, Thomalla G, Nighoghossian N, et al. Better diffusion segmentation in acute ischemic stroke through automatic tree learning anomaly segmentation. Front Neuroinform. 2018; 12:21.13. Yu Y, Xie Y, Thamm T, Gong E, Ouyang J, Huang C, et al. Use of deep learning to predict final ischemic stroke lesions from initial magnetic resonance imaging. JAMA Netw Open. 2020; 3:e200772.14. Do LN, Baek BH, Kim SK, Yang HJ, Park I, Yoon W. Automatic assessment of ASPECTS using diffusion-weighted imaging in acute ischemic stroke using recurrent residual convolutional neural network. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020; 10:803.15. Woo I, Lee A, Jung SC, Lee H, Kim N, Cho SJ, et al. Fully automatic segmentation of acute ischemic lesions on diffusion-weighted imaging using convolutional neural networks: comparison with conventional algorithms. Korean J Radiol. 2019; 20:1275–84.16. Kim YC, Lee JE, Yu I, Song HN, Baek IY, Seong JK, et al. Evaluation of diffusion lesion volume measurements in acute ischemic stroke using encoder-decoder convolutional network. Stroke. 2019; 50:1444–51.17. Hui H, Zhang X, Li F, Mei X, Guo Y. A partitioning-stacking prediction fusion network based on an improved attention u-net for stroke lesion segmentation. IEEE Access. 2020; 8:47419–32.18. Zhang R, Zhao L, Lou W, Abrigo JM, Mok VC, Chu WC, et al. Automatic segmentation of acute ischemic stroke from DWI using 3-D fully convolutional DenseNets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2018; 37:2149–60.19. Liu X, Yang H, Qi K, Dong P, Liu Q, Liu X, et al. MSDF-net: Multi-scale deep fusion network for stroke lesion segmentation. IEEE Access. 2019; 7:178486–95.20. Zhang L, Song R, Wang Y, Zhu C, Liu J, Yang J, et al. Ischemic stroke lesion segmentation using multi-plane information fusion. IEEE Access. 2020; 8:45715–25.21. Liu L, Wu FX, Wang J. Efficient multi-kernel dcnn with pixel dropout for stroke mri segmentation. Neurocomputing. 2019; 350:117–27.22. Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA. fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In : 2016 fourth international conference on 3D vision (3DV); 2016. Stanford, CA, USA.23. Bang OY, Chung JW, Son JP, Ryu WS, Kim DE, Seo WK, et al. Multimodal MRI-based triage for acute stroke therapy: challenges and progress. Front Neurol. 2018; 9:586.24. Fung SH, Roccatagliata L, Gonzalez RG, Schaefer PW. MR diffusion imaging in ischemic stroke. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2011; 21:345–77.25. Lee LJ, Kidwell CS, Alger J, Starkman S, Saver JL. Impact on stroke subtype diagnosis of early diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography. Stroke. 2000; 31:1081–9.26. Ay H, Furie KL, Singhal A, Smith WS, Sorensen AG, Koroshetz WJ. An evidence-based causative classification system for acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2005; 58:688–97.27. Ay H, Benner T, Arsava EM, Furie KL, Singhal AB, Jensen MB, et al. A computerized algorithm for etiologic classification of ischemic stroke: the Causative Classification of Stroke System. Stroke. 2007; 38:2979–84.28. Hart RG, Catanese L, Perera KS, Ntaios G, Connolly SJ. Embolic stroke of undetermined source: a systematic review and clinical update. Stroke. 2017; 48:867–72.29. Hart RG, Diener HC, Coutts SB, Easton JD, Granger CB, O'Donnell MJ, et al. Embolic strokes of undetermined source: the case for a new clinical construct. Lancet Neurol. 2014; 13:429–38.30. Healey JS, Gladstone DJ, Swaminathan B, Eckstein J, Mundl H, Epstein AE, et al. Recurrent stroke with rivaroxaban compared with aspirin according to predictors of atrial fibrillation: secondary analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019; 76:764–73.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Applications of diffusion-weighted imaging in diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of acute ischemic stroke
- Use of Machine Learning in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Narrative Review
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Guided by Stroke MRI
- Silent New Brain Lesions: Innocent Bystander or Guilty Party?
- Clinical Features of Patients with False Negative Diffusion-weighted MR Findings in Acute Ischemic Stroke