J Neurocrit Care.
2019 Jun;12(1):1-8. 10.18700/jnc.190079.
Generalized periodic discharges with triphasic morphology
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Cincinnati Medical Center, University of Cincinnati Gardner Neuroscience Institute, Cincinnati, OH, USA. foremabo@ucmail.uc.edu
- 2Division of Neurocritical Care, University of Cincinnati Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA.
- KMID: 2452821
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.190079
Abstract
- Generalized periodic discharges (GPDs) with triphasic morphology are an electroencephalographic (EEG) pattern traditionally associated with encephalopathy and coma, although they have been observed in a wide array of neurological disorders. The clinical significance of these waveforms and their relationship to seizures and prognosis has been debated, and differentiation between interictal patterns, patterns associated with seizures, and patterns representing nonconvulsive status epilepticus can at times be a challenge. The most established literature suggests that GPDs, including those with triphasic morphology, are associated with the development of electrographic seizures, but that in the absence of clinical information, distinguishing waveforms based on morphology alone may not be clinically useful. Recent work has advocated for a more proactive approach in evaluating GPDs with triphasic morphology. Further studies of nonsedating antiseizure drugs in patients with GPDs with triphasic morphology that incorporate continuous EEG monitoring will be useful in tailoring therapy to optimize long-term clinical outcomes and recovery.
MeSH Terms
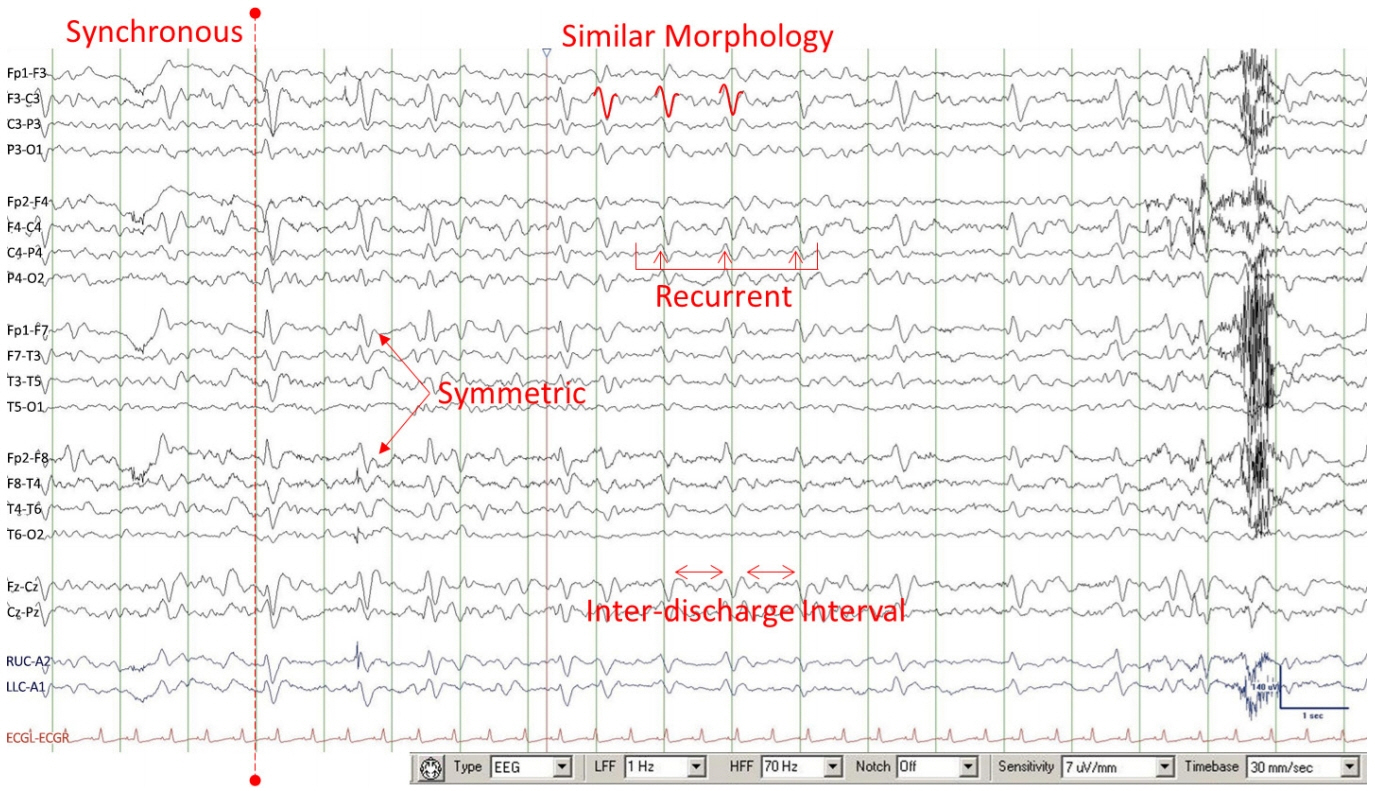
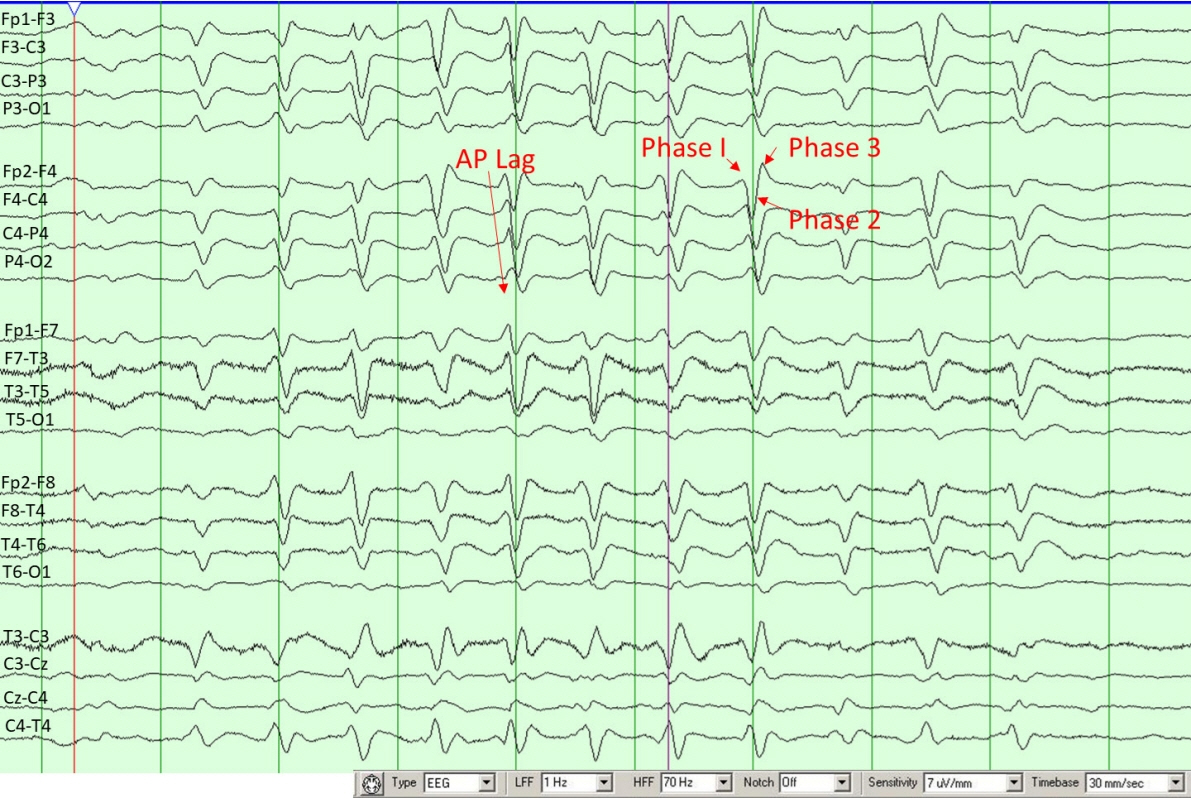
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cefepime-induced neurotoxicity
Se-Jin Lee
J Neurocrit Care. 2019;12(2):74-84. doi: 10.18700/jnc.190109.
Reference
-
1. Hirsch LJ, LaRoche SM, Gaspard N, Gerard E, Svoronos A, Herman ST, et al. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society's standardized critical care EEG terminology: 2012 version. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 30:1–27.2. Gloor P, Kalabay O, Giard N. The electroencephalogram in diffuse encephalopathies: electroencephalographic correlates of grey and white matter lesions. Brain. 1968; 91:779–802.
Article3. van Putten MJ, Hofmeijer J. Generalized periodic discharges: pathophysiology and clinical considerations. Epilepsy Behav. 2015; 49:228–33.
Article4. Foreman B, Claassen J, Abou Khaled K, Jirsch J, Alschuler DM, Wittman J, et al. Generalized periodic discharges in the critically ill: a case-control study of 200 patients. Neurology. 2012; 79:1951–60.
Article5. Sully KE, Husain AM. Generalized periodic discharges: a topical review. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2018; 35:199–207.6. Adams RD, Foley JM. The neurological disorder associated with liver disease. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1953; 32:198–237.7. Bickford RG, Butt HR. Hepatic coma: the electroencephalographic pattern. J Clin Invest. 1955; 34:790–9.
Article8. Karnaze DS, Bickford RG. Triphasic waves: a reassessment of their significance. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1984; 57:193–8.
Article9. Bahamon-Dussan JE, Celesia GG, Grigg-Damberger MM. Prognostic significance of EEG triphasic waves in patients with altered state of consciousness. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1989; 6:313–9.
Article10. Brenner RP. The interpretation of the EEG in stupor and coma. Neurologist. 2005; 11:271–84.
Article11. Sundaram MB, Blume WT. Triphasic waves: clinical correlates and morphology. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987; 14:136–40.
Article12. Hormes JT, Benarroch EE, Rodriguez M, Klass DW. Periodic sharp waves in baclofen-induced encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1988; 45:814–5.
Article13. Neufeld MY. Periodic triphasic waves in levodopa-induced encephalopathy. Neurology. 1992; 42:444–6.
Article14. Kemperman CJ, Notermans SL. Creutzfeld-Jacob like syndrome due to lithium toxicity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989; 52:291.
Article15. Wengs WJ, Talwar D, Bernard J. Ifosfamide-induced nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Arch Neurol. 1993; 50:1104–5.
Article16. Drake ME, Erwin CW. Triphasic EEG discharges in metrizamide encephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984; 47:324–5.
Article17. Aguglia U, Gambardella A, Oliveri RL, Lavano A, Quattrone A. Nonmetabolic causes of triphasic waves: a reappraisal. Clin Electroencephalogr. 1990; 21:120–5.
Article18. Kwon OY, Jung KY, Park KJ, Kang JK, Shon YM, Lee IK, et al. Source localization of triphasic waves: implications for the pathophysiological mechanism. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2007; 38:161–7.
Article19. Sutter R, Stevens RD, Kaplan PW. Significance of triphasic waves in patients with acute encephalopathy: a nine-year cohort study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 124:1952–8.
Article20. Gaspard N, Hirsch LJ, LaRoche SM, Hahn CD, Westover MB; Critical Care EEG Monitoring Research Consortium. Interrater agreement for critical care EEG terminology. Epilepsia. 2014; 55:1366–73.
Article21. Young GB, McLachlan RS, Kreeft JH, Demelo JD. An electroencephalographic classification for coma. Can J Neurol Sci. 1997; 24:320–5.
Article22. Foreman B, Mahulikar A, Tadi P, Claassen J, Szaflarski J, Halford JJ, et al. Generalized periodic discharges and 'triphasic waves': a blinded evaluation of inter-rater agreement and clinical significance. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016; 127:1073–80.
Article23. Alkhachroum AM, Al-Abri H, Sachdeva A, Maturu S, Waldron J, Wang H, et al. Generalized periodic discharges with and without triphasic morphology. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2018; 35:144–50.
Article24. Kaplan PW. EEG criteria for nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2007; 48 Suppl 8:39–41.
Article25. Boulanger JM, Deacon C, Lécuyer D, Gosselin S, Reiher J. Triphasic waves versus nonconvulsive status epilepticus: EEG distinction. Can J Neurol Sci. 2006; 33:175–80.
Article26. Kaya D, Bingol CA. Significance of atypical triphasic waves for diagnosing nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Epilepsy Behav. 2007; 11:567–77.
Article27. Trinka E, Leitinger M. Which EEG patterns in coma are nonconvulsive status epilepticus? Epilepsy Behav. 2015; 49:203–22.
Article28. Rodriguez Ruiz A, Vlachy J, Lee JW, Gilmore EJ, Ayer T, Haider HA, et al. Association of periodic and rhythmic electroencephalographic patterns with seizures in critically ill patients. JAMA Neurol. 2017; 74:181–8.
Article29. Husain AM, Mebust KA, Radtke RA. Generalized periodic epileptiform discharges: etiologies, relationship to status epilepticus, and prognosis. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1999; 16:51–8.
Article30. Fong MWK, Gaspard N, Hirsch LJ. Generalized periodic discharges with and without triphasic morphology. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2019; 36:173–4.
Article31. Bauer G, Trinka E, Kaplan PW. EEG patterns in hypoxic encephalopathies (post-cardiac arrest syndrome): fluctuations, transitions, and reactions. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2013; 30:477–89.32. Ruijter BJ, van Putten MJ, Hofmeijer J. Generalized epileptiform discharges in postanoxic encephalopathy: quantitative characterization in relation to outcome. Epilepsia. 2015; 56:1845–54.
Article33. Gilmore EJ, Gaspard N, Choi HA, Cohen E, Burkart KM, Chong DH, et al. Acute brain failure in severe sepsis: a prospective study in the medical intensive care unit utilizing continuous EEG monitoring. Intensive Care Med. 2015; 41:686–94.
Article34. Rossetti AO, Oddo M, Liaudet L, Kaplan PW. Predictors of awakening from postanoxic status epilepticus after therapeutic hypothermia. Neurology. 2009; 72:744–9.
Article35. Ruijter BJ, van Putten MJ, Horn J, Blans MJ, Beishuizen A, van Rootselaar AF, et al. Treatment of electroencephalographic status epilepticus after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (TELSTAR): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014; 15:433.
Article36. O'Rourke D, Chen PM, Gaspard N, Foreman B, McClain L, Karakis I, et al. Response rates to anticonvulsant trials in patients with triphasic-wave EEG patterns of uncertain significance. Neurocrit Care. 2016; 24:233–9.37. Bermeo-Ovalle A. Triphasic waves: swinging the pendulum back in this diagnostic dilemma. Epilepsy Curr. 2017; 17:40–2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cefepime-induced neurotoxicity
- A Case of Baclofen-induced Encephalopathy
- A Comatose Patient with Continuous Generalized 3 Hz Spike-and-Wave Discharges after Cardiac Arrest
- Significance of Triphasic Waves in Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Fixed and dilated pupils by pupillometer in lateralized periodic discharges: a case report in the neurocritical care unit