Kosin Med J.
2019 Jun;34(1):38-46. 10.7180/kmj.2019.34.1.38.
Comparative Study of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion MR Images between Warthin's Tumor and Malignant Parotid Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Cancer center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Otrhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. chawonjae@gmail.com
- KMID: 2451774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2019.34.1.38
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To identify diagnostically meaningful differences between Warthin's tumor and malignant masses in the parotid gland by dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR imaging.
METHODS
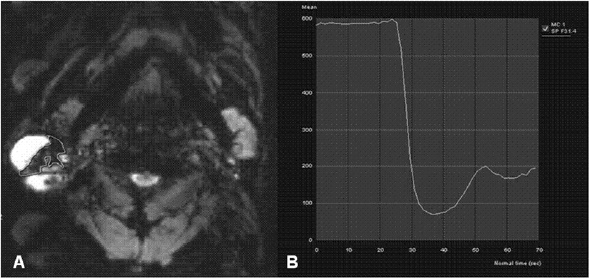
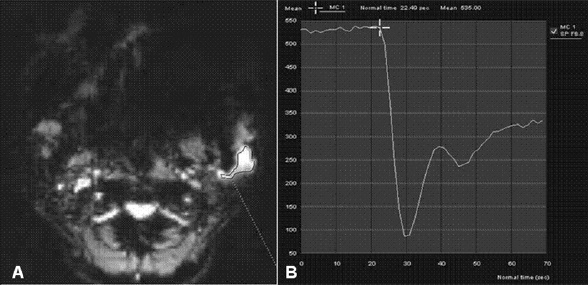
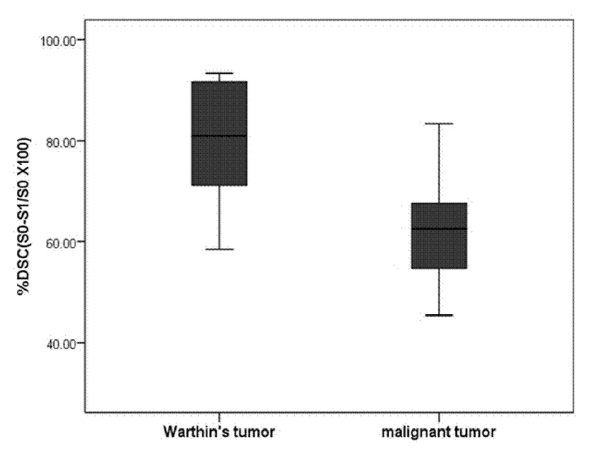
Eleven malignant parotid tumors and 9 Warthin's tumors were included. MR imaging was performed on all patients. Signal intensity time curves of tumors were obtained by DSC MR imaging and dynamic susceptibility contrast percentages (DSC%) were calculated.
RESULTS
No significant difference was observed between malignant tumors and Warthin's tumors (P = 0.437), although DSC% values tended to be higher for Warthin's tumors.
CONCLUSIONS
Warthin's tumor tended to have higher DSC% values than malignant parotid tumors, but this difference was not significantly different.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seifert G, Sobin L. Histological typing of salivary gland tumours. 2nd ed. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag;1991.2. Das DK, Petkar MA, Al-Mane NM, Sheikh ZA, Mallik MK, Anim JT. Role of fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of swellings in the salivary gland regions: A study of 712 cases. Med Princ Pract. 2004; 13:95–106.
Article3. Saade Rami E, Diana M, Bell EYH. Benign neoplasms of the salivary glands. Cummings Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. p. 1238–1257.4. Yousem DM, Gad K, Tufano RP. Resectability issues with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:2024–2036.5. Batsakis JG. Carcinoma ex papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum. Malignant Warthin's tumor. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1987; 96:234–235.6. Yabuuchi H, Fukuya T, Tajima T, Hachitanda Y, Tomita K, Koga M. Salivary gland tumors: diagnostic value of gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 2003; 226:345–354.
Article7. Eida S, Ohki M, Sumi M, Yamada T, Nakamura T. MR factor analysis: Improved technology for the assessment of 2D dynamic structures of benign and malignant salivary gland tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 27:1256–1262.
Article8. Hisatomi M, Asaumi J, Yanagi Y, Unetsubo T, Maki Y, Murakami J, et al. Diagnostic value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the salivary gland tumors. Oral Oncol. 2007; 43:940–947.
Article9. Kato H, Kanematsu M, Watanabe H, Kajita K. Mizuta K, Aoki M, et al. Perfusion imaging of parotid gland tumours : usefulness of arterial spin labeling for differentiating Warthin's tumours. Eur Radiol. 2015; 25:3247–3254.
Article10. Razek AA, Elsorogy LG, Soliman NY, Nada N. Dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MR imaging in distinguishing malignant from benign head and neck tumors: A pilot study. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 77:73–79.
Article11. Abdel Razek AA, Samir S, Ashmalla GA. Characterization of parotid tumors with dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2017; 41:131–136.
Article12. Jahng GH, Li KL, Ostergaard L, Calamante F. Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging: A comprehensive update on principles and techniques. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:554–577.
Article13. Swanson SD. MR Methods to Measure Cerebral perfusion. MR imaging in white matter diseases of the brain and spinal cord. 2005. p. 83–91.14. Mangla R, Kolar B, Zhu T, Zhong J, Almast J, Ekholm S. Percentage signal recovery derived from MR dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging is useful to differentiate common enhancing malignant lesions of the brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1004–1010.
Article15. Kuhl CK, Bieling H, Gieseke J, Ebel T, Mielcarek P, Far F, et al. Breast Neoplasms: T2* susceptibility-contrast, first-pass perfusion MR imaging. Radiology. 1997; 202:87–95.
Article16. Alibek S, Zenk J, Bozzato A, Lell M, Grunewald M, Anders K, et al. The value of dynamic MRI studies in parotid tumors. Acad Radiol. 2007; 14:701–710.
Article17. Wolf RL, Detre JA. Clinical neuroimaging using arterial spin-labeled perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Neurotherapeutics. 2007; 4:346–359.
Article18. Xu Z, Rong F, Yu T, Chen Y, Gao Q, Zhou T, et al. Pleomorphic adenoma versus Warthin tumor of the parotid gland: Diagnostic value of CT perfusion imaging and its pathologic explanation. J Tumor. 2016; 4:419–425.19. Schimdt RL, Hall BJ, Wilson AR, Layfield LJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology for parotid gland lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 136:45–59.
Article20. Donovan DT, Conley JJ. Capsular significance in parotid tumor surgery: reality and myths of lateral lobectomy. Laryngoscope. 1984; 94:324–329.21. Eveson JW, Cawson RA. Salivary gland tumours. A review of 2410 cases with particular reference to histological types, site, age and sex distribution. J Pathol. 1985; 146:51–58.
Article22. Ebbs SR, Webb AJ. Adenolymphoma of the parotid: aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Br J Surg. 1986; 73:627–630.
Article23. Browne RF, Golding SJ, Watt-Smith SR. The role of MRI in facial swelling due to presumed salivary gland disease. Br J Radiol. 2001; 74:127–133.
Article24. Yabuuchi H, Fukuya T, Tajima T, Hachitanda Y, Tomita K, Koga M. Salivary gland tumors: diagnostic value of gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 2003; 226:345–354.
Article25. Ikeda M, Motoori K, Hanazawa T, Nagai Y, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, et al. Warthin Tumor of the Parotid Gland: Diagnostic Value of MR Imaging with Histopathologic Correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1256–1262.26. García-Pérez AI, López-Beltrán EA, Klüner P, Luque J, Ballesteros P, Cerdán S. Molecular crowding and viscosity as determinants of translational diffusion of metabolites in subcellular organelles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999; 362:329–338.
Article27. Donahue KM, Krouwer HG, Rand SD, Pathak AP, Marszalkowski CS, Censky SC, et al. Utility of simultaneously acquired gradient-echo and spinecho cerebral blood volume and morphology maps in brain tumor patients. Magn Reson Med. 2000; 43:845–853.
Article28. Uematsu H, Maeda M, Sadato N, Matsuda T, Ishimori Y, Koshimoto Y, et al. Blood volume of gliomas determined by double-echo dynamic perfusion-weighted MR imaging: A preliminary study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1915–1919.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral Warthin tumor of the parotid gland: A case report
- Warthin's Tumor of the Parotid Gland: CT and MR Features
- Perfusion Imaging of the Brain Using Z-Score and Dynamic Images Obtained by Subtracting Images from before and after Contrast Injection
- Effect of Smoking to Warthin's Tumor of Parotid Gland
- Three Cases of Multifocal Warthin's Tumor