Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Jun;52(2):140-142. 10.5115/acb.2019.52.2.140.
An anatomical study of the lingual nerve in the lower third molar area
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seattle Science Foundation, Seattle, WA, USA. joei@seattlesciencefoundation.org
- 2Dental and Oral Medical Center, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan.
- 3Division of Gross and Clinical Anatomy, Department of Anatomy, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan.
- 4Department of Anatomical Sciences, St. George's University, St. George's, Grenada, West Indies.
- KMID: 2451217
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2019.52.2.140
Abstract
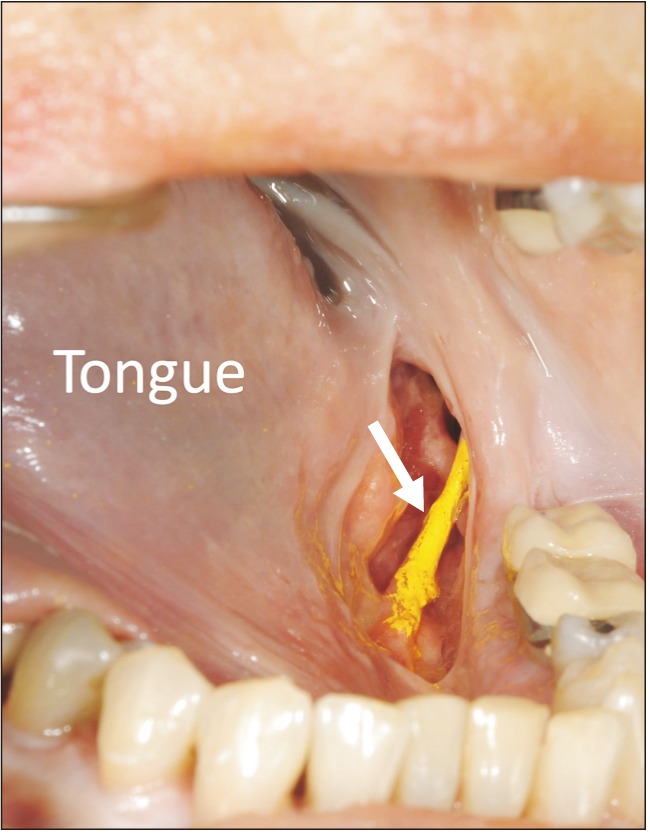
- The lingual nerve (LN) is a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, and its injury is one of the major complications during oral surgery. This study aims to investigate the anatomy of the LN in the lower third molar area. Twenty sides from ten fresh-frozen adult cadaveric Caucasian heads were examined to measure the diameter of the LN. The mean diameter of the LN was 2.20±0.37 mm (range, 1.61-2.95 mm). There were no statistically significant differences in the measurements between sexes, sides, or tooth status (dentulous or edentulous). Understanding the anatomical features of the LN is essential for performing any surgical procedure in the oral region.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A large sublingual glandular branch of the lingual nerve: a rare case report
Aaron Albuck, Yuto Haikata, Koichi Watanabe, R. Shane Tubbs, Joe Iwanaga
Anat Cell Biol. 2022;55(3):380-383. doi: 10.5115/acb.22.016.
Reference
-
1. Heasman PA, Beynon AD. Quantitative diameter analysis of lingual nerve axons in man. J Dent Res. 1986; 65:1016–1019. PMID: 3458751.2. Zur KB, Mu L, Sanders I. Distribution pattern of the human lingual nerve. Clin Anat. 2004; 17:88–92. PMID: 14974094.3. Iwanaga J, Watanabe K, Saga T, Tabira Y, Nakamura M, Fisahn C, Tubbs RS, Kusukawa J, Yamaki KI. Communicating branches between lingual and hypoglossal nerve: observation using Sihler's staining technique. Surg Radiol Anat. 2017; 39:741–745. PMID: 27913866.4. Behnia H, Kheradvar A, Shahrokhi M. An anatomic study of the lingual nerve in the third molar region. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 58:649–651. PMID: 10847287.5. Kiesselbach JE, Chamberlain JG. Clinical and anatomic observations on the relationship of the lingual nerve to the mandibular third molar region. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984; 42:565–567. PMID: 6590806.6. Pogrel MA, Renaut A, Schmidt B, Ammar A. The relationship of the lingual nerve to the mandibular third molar region: an anatomic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995; 53:1178–1181. PMID: 7562172.7. Kim SY, Hu KS, Chung IH, Lee EW, Kim HJ. Topographic anatomy of the lingual nerve and variations in communication pattern of the mandibular nerve branches. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004; 26:128–135. PMID: 14586562.8. Erdogmus S, Govsa F, Celik S. Anatomic position of the lingual nerve in the mandibular third molar region as potential risk factors for nerve palsy. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19:264–270. PMID: 18216699.9. Shimoo Y, Yamamoto M, Suzuki M, Yamauchi M, Kaketa A, Kasahara M, Serikawa M, Kitamura K, Matsunaga S, Abe S. Anatomic and histological study of lingual nerve and its clinical implications. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2017; 58:95–101. PMID: 28724864.10. Iwanaga J. The clinical view for dissection of the lingual nerve with application to minimizing iatrogenic injury. Clin Anat. 2017; 30:467–469. PMID: 28295613.11. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 41st ed. London: Elsevier Health Sciences;2015.12. Joo W, Funaki T, Yoshioka F, Rhoton AL Jr. Microsurgical anatomy of the infratemporal fossa. Clin Anat. 2013; 26:455–469. PMID: 23355316.13. Miloro M, Halkias LE, Slone HW, Chakeres DW. Assessment of the lingual nerve in the third molar region using magnetic resonance imaging. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:134–137. PMID: 9024349.14. Hölzle FW, Wolff KD. Anatomic position of the lingual nerve in the mandibular third molar region with special consideration of an atrophied mandibular crest: an anatomical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 30:333–338. PMID: 11518358.15. Morris CD, Rasmussen J, Throckmorton GS, Finn R. The anatomic basis of lingual nerve trauma associated with inferior alveolar block injections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:2833–2836. PMID: 20832156.16. Iwanaga J, Choi PJ, Vetter M, Patel M, Kikuta S, Oskouian RJ, Tubbs RS. Anatomical study of the lingual nerve and inferior alveolar nerve in the pterygomandibular space: complications of the inferior alveolar nerve block. Cureus. 2018; 10:e3109. PMID: 30338184.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mapping out the surgical anatomy of the lingual nerve: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Morphology and topography of the lingual nerve in Koreans
- Management and prevention of third molar surgery-related trigeminal nerve injury: time for a rethink
- Injury of submandibular gland and lingual nerve as complication third molar tooth extraction in mandible : a case report
- Analysis and evaluation of relative positions of mandibular third molar and mandibular canal impacts