Blood Res.
2019 Jun;54(2):151-153. 10.5045/br.2019.54.2.151.
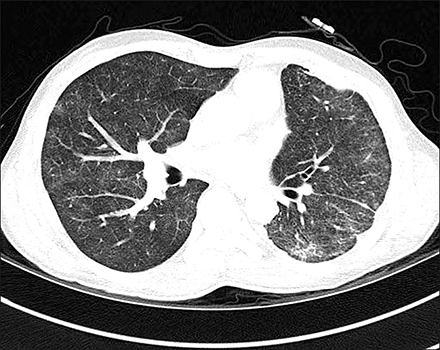
First case report of latent tuberculosis reactivation complicating treatment with nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Busan, Korea. hs52silver@gmail.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2451018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2019.54.2.151
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Reinwald M, Boch T, Hofmann WK, Buchheidt D. Risk of infectious complications in hemato-oncological patients treated with kinase inhibitors. Biomark Insights. 2016; 10:Suppl 3. 55–68.
Article2. Daniels JM, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Janssen JJ, Postmus PE, van Altena R. Tuberculosis complicating imatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia. Eur Respir J. 2009; 33:670–672.
Article3. Kang BW, Lee SJ, Moon JH, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia patient manifesting fatal hepatitis B virus reactivation during treatment with imatinib rescued by liver transplantation: case report and literature review. Int J Hematol. 2009; 90:383–387.
Article4. Mattiuzzi GN, Cortes JE, Talpaz M, et al. Development of Varicella-Zoster virus infection in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia treated with imatinib mesylate. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:976–980.5. García-Muñoz R, Galar A, Moreno C, et al. Parvovirus B19 acute infection and a reactivation of cytomegalovirus and herpesvirus 6 in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient during treatment with dasatinib (BMS-354825). Leuk Lymphoma. 2007; 48:2461–2464.
Article6. Senn L, Kovacsovics T, Tarr PE, Meylan P. Peritoneal tuberculosis after imatinib therapy. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:312–313.
Article7. Seggewiss R, Loré K, Greiner E, et al. Imatinib inhibits T-cell receptor-mediated T-cell proliferation and activation in a dose-dependent manner. Blood. 2005; 105:2473–2479.
Article8. Chen J, Schmitt A, Chen B, et al. Nilotinib hampers the proliferation and function of CD8+ T lymphocytes through inhibition of T cell receptor signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2008; 12:2107–2118.
Article9. Fei F, Yu Y, Schmitt A, et al. Dasatinib exerts an immunosuppressive effect on CD8+ T cells specific for viral and leukemia antigens. Exp Hematol. 2008; 36:1297–1308.
Article10. de Lavallade H, Khoder A, Hart M, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors impair B-cell immune responses in CML through off-target inhibition of kinases important for cell signaling. Blood. 2013; 122:227–238.
Article11. Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2251–2259.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nilotinib-Induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis during the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Metformin enhances the cytotoxic effect of nilotinib and overcomes nilotinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
- Treatment-free remission after discontinuation of imatinib, dasatinib, and nilotinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
- A Case Report of Multiple Capillary Hemangioma in a Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patient Taking Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- A Case of Leukemia Cutis in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Evolving into An Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia