Blood Res.
2019 Jun;54(2):114-119. 10.5045/br.2019.54.2.114.
Clinical significance of cell-free DNA as a prognostic biomarker in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Genetics, Faculty of Advanced Science and Technology, Tehran Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
- 2Medical Genetics, Department of Medical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Transplantation Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. mahmadvand@sina.tums.ac.ir
- 4Cell Therapy and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Research Center, Hematologic Malignancies Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 5Department of Medical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine, Ilam University of Medical Sciences, Ilam, Iran.
- KMID: 2451011
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2019.54.2.114
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has the potential to serve as a non-invasive prognostic biomarker in some types of neoplasia. The investigation of plasma concentration of cfDNA may reveal its use as a valuable biomarker for risk stratification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The present prognostic value of plasma cfDNA has not been widely confirmed in DLBCL subjects. Here, we evaluated cfDNA plasma concentration and assessed its potential prognostic value as an early DLBCL diagnostic tool.
METHODS
cfDNA concentrations in plasma samples from 40 patients with DLBCL during diagnosis and of 38 normal controls were determined with quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) for the multi-locus L1PA2 gene.
RESULTS
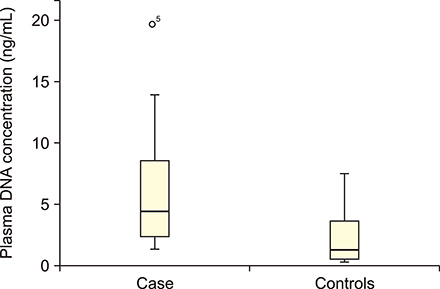
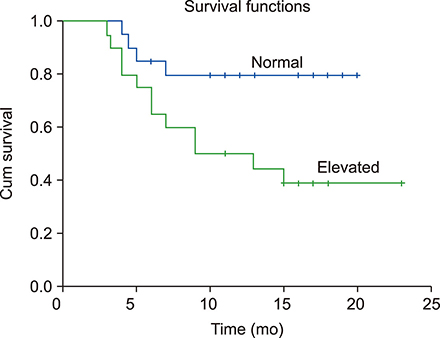
Statistically significant elevation in plasma cfDNA concentrations was observed in patients with DLBCL as compared to that in normal controls (P<0.05). A cutoff point of 2.071 ng/mL provided 82.5% sensitivity and 62.8% specificity and allowed successful discrimination of patients with DLBCL from normal controls (area under the curve=0.777; P=0.00003). Furthermore, patients with DLBCL showing higher concentrations of cfDNA had shorter overall survival (median, 9 mo; P=0.022) than those with lower cfDNA levels. In addition, elevated cfDNA concentration was significantly associated with age, B-symptoms, International Prognostic Index (IPI) score, and different stages of disease (all P<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Quantification of cfDNA with qPCR at the time of diagnosis may allow identification of patients with high cfDNA concentration, which correlates with aggressive clinical outcomes and adverse prognosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood. 2011; 117:5019–5032.
Article2. Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000; 403:503–511.
Article3. Schneider C, Pasqualucci L, Dalla-Favera R. Molecular pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2011; 28:167–177.
Article4. Koh W, Pan W, Gawad C, et al. Noninvasive in vivo monitoring of tissue-specific global gene expression in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111:7361–7366.
Article5. Stroun M, Anker P, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Maurice PA. Isolation and characterization of DNA from the plasma of cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987; 23:707–712.
Article6. Anker P, Mulcahy H, Chen XQ, Stroun M. Detection of circulating tumour DNA in the blood (plasma/serum) of cancer patients. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999; 18:65–73.7. Stroun M, Anker P. Circulating DNA in higher organisms cancer detection brings back to life an ignored phenomenon. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2005; 51:767–774.8. Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014; 6:224ra24.9. Rapisuwon S, Vietsch EE, Wellstein A. Circulating biomarkers to monitor cancer progression and treatment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016; 14:211–222.
Article10. Sozzi G, Conte D, Leon M, et al. Quantification of free circulating DNA as a diagnostic marker in lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:3902–3908.
Article11. Sozzi G, Conte D, Mariani L, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA in plasma at diagnosis and during follow-up of lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001; 61:4675–4678.12. Lecomte T, Berger A, Zinzindohoué F, et al. Detection of free-circulating tumor-associated DNA in plasma of colorectal cancer patients and its association with prognosis. Int J Cancer. 2002; 100:542–548.
Article13. Hohaus S, Giachelia M, Massini G, et al. Cell-free circulating DNA in Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:1408–1413.
Article14. Armand P, Oki Y, Neuberg DS, et al. Detection of circulating tumour DNA in patients with aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2013; 163:123–126.
Article15. Kurtz DM, Green MR, Bratman SV, et al. Noninvasive monitoring of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunoglobulin high-throughput sequencing. Blood. 2015; 125:3679–3687.
Article16. Rossi D, Diop F, Spaccarotella E, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma genotyping on the liquid biopsy. Blood. 2017; 129:1947–1957.
Article17. Bohers E, Viailly PJ, Becker S, et al. Non-invasive monitoring of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by cell-free DNA high-throughput targeted sequencing: analysis of a prospective cohort. Blood Cancer J. 2018; 8:74.
Article18. Roschewski M, Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, et al. Circulating tumour DNA and CT monitoring in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a correlative biomarker study. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:541–549.
Article19. Lo YM, Tein MS, Lau TK, et al. Quantitative analysis of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum: implications for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1998; 62:768–775.
Article20. Breitbach S, Tug S, Helmig S, et al. Direct quantification of cell-free, circulating DNA from unpurified plasma. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e87838.
Article21. Pfreundschuh M, Schubert J, Ziepert M, et al. Six versus eight cycles of bi-weekly CHOP-14 with or without rituximab in elderly patients with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphomas: a randomised controlled trial (RICOVER-60). Lancet Oncol. 2008; 9:105–116.22. Ahmadvand M, Eskandari M, Pashaiefar H, et al. Over expression of circulating miR-155 predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res. 2018; 70:45–48.
Article23. Pashaiefar H, Izadifard M, Yaghmaie M, et al. Low expression of long noncoding RNA IRAIN is associated with poor prognosis in non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia patients. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2018; 22:288–294.
Article24. Li M, Jia Y, Xu J, Cheng X, Xu C. Assessment of the circulating cell-free DNA marker association with diagnosis and prognostic prediction in patients with lymphoma: a single-center experience. Ann Hematol. 2017; 96:1343–1351.
Article25. Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Szpechcinski A. The impact of genetic markers on the diagnosis of lung cancer: a current perspective. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:1044–1051.
Article26. Ulivi P, Silvestrini R. Role of quantitative and qualitative characteristics of free circulating DNA in the management of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2013; 36:439–448.
Article27. Szpechcinski A, Struniawska R, Zaleska J, et al. Evaluation of fluorescence-based methods for total vs. amplifiable DNA quantification in plasma of lung cancer patients. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008; 59:675–681.28. Jung M, Klotzek S, Lewandowski M, Fleischhacker M, Jung K. Changes in concentration of DNA in serum and plasma during storage of blood samples. Clin Chem. 2003; 49:1028–1029.
Article29. Taback B, O’Day SJ, Hoon DS. Quantification of circulating DNA in the plasma and serum of cancer patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1022:17–24.
Article30. Szpechcinski A, Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Struniawski R, et al. Cell-free DNA levels in plasma of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and inflammatory lung disease. Br J Cancer. 2015; 113:476–483.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Expression of p16 in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Its Prognostic Implications
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Diffuse Plane Xanthoma Associated with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
- Inverse Psoriasis Developed in a Patient with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
- Primary Cutaneous T-cell/histiocyte-rich B-cell Lymphoma