Yonsei Med J.
2015 May;56(3):719-725. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.719.
Prevalence of Vitiligo and Associated Comorbidities in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Severance Hospital, Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. oddung93@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Dermatology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dermatology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Dermatology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Dermatology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Dermatology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Bundang, Korea.
- 8Whiteline Skin Clinic, Changwon, Korea.
- 9Department of Dermatology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University Graduate School of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 10Department of Dermatology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 11Department of Dermatology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Department of Dermatology, School of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea.
- 13Korea Institute of Vitiligo Research & Drs. Woo and Hann's Skin Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 14Department of Dermatology, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. cjpark777smp@gmail.com
- KMID: 2450346
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.3.719
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Vitiligo prevalence and its associated comorbidities rate have been reported variably among different populations. We aimed to determine the prevalence of vitiligo in Korea along with the baseline rate of comorbidities and compared the risks to the general population using hospital visit information of the total population in Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We assessed demographic characteristics of vitiligo patients in Korean population from 2009 to 2011 in a nationwide data from Health Insurance Review Assessment Service. Patients who had at least one visit to Korea's primary, secondary, or tertiary referral hospitals with International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification diagnosis code for vitiligo were identified. As a supplementary study, comorbidities associated with vitiligo were selected for further review to calculate relative risks compared to the general population.
RESULTS
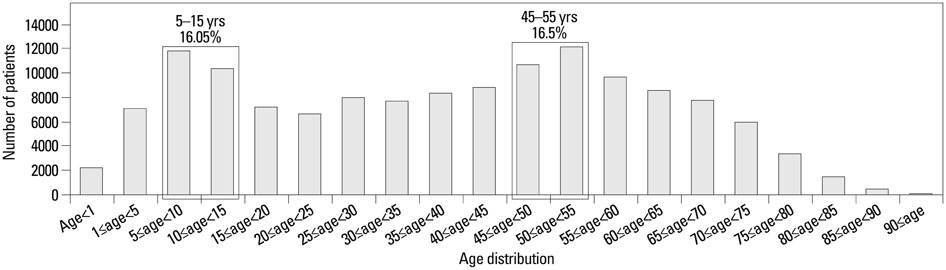
The annual prevalence of vitiligo determined by hospital-visiting rate in Korea was 0.12% to 0.13% over a three year period. In sync with other previous epidemiological studies, there was bimodal distribution among the age groups and no difference between genders. Also, vitiligo in Korean population was associated with various autoimmune/non-autoimmune diseases such as thyroiditis, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis.
CONCLUSION
This study was by far the most comprehensive review on prevalence of vitiligo using a data of total population in Korea. The prevalence is within a range of those reported in previous literatures, and increased risk of comorbidities such as thyroid diseases and psoriasis in vitiligo might aid clinicians in the initial work up of vitiligo patients and concurrent follow ups.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The MARCOPOLO Study of Ustekinumab Utilization and Efficacy in a Real-World Setting: Treatment of Patients with Plaque Psoriasis in Asia-Pacific Countries
Sang Woong Youn, Tsen-Fang Tsai, Colin Theng, Siew-Eng Choon, Benny E. Wiryadi, Antonio Pires, Weihao Tan, Min-Geol Lee,
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(2):222-231. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.2.222.Psoriasis, Vitiligo and Crohn's Disease Co-Existing in a Single Patient: A Variant Type of Multiple Autoimmune Syndrome?
Sul Hee Lee, Ye Seul Kim, Hyun Ju Kim, Young Lip Park
Ann Dermatol. 2017;29(6):782-785. doi: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.6.782.
Reference
-
1. Sheth VM, Guo Y, Qureshi AA. Comorbidities associated with vitiligo: a ten-year retrospective study. Dermatology. 2013; 227:311–315.
Article2. Taïeb A, Picardo M;. The definition and assessment of vitiligo: a consensus report of the Vitiligo European Task Force. Pigment Cell Res. 2007; 20:27–35.
Article3. Shah H, Mehta A, Astik B. Clinical and sociodemographic study of vitiligo. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008; 74:701.
Article4. Krüger C, Schallreuter KU. A review of the worldwide prevalence of vitiligo in children/adolescents and adults. Int J Dermatol. 2012; 51:1206–1212.
Article5. Park SY, Youn JI, Lim SD. A clinical study of 217 cases of vitiligo. Korean J Dermatol. 1981; 19:145–152.6. Taïeb A, Picardo M. Epidemiology, definitions and classification. In : Picardo M, Taïeb A, editors. Vitiligo. Berlin: Springer;2010. p. 13–24.7. Song YJ. The South Korean Health Care System. JMAJ. 2009; 52:206–209.8. Lee YK, Ha YC, Park C, Yoo JJ, Shin CS, Koo KH. Bisphosphonate use and increased incidence of subtrochanteric fracture in South Korea: results from the National Claim Registry. Osteoporos Int. 2013; 24:707–711.
Article9. Park SJ, Choi NK, Park KH, Woo SJ. Five year nationwide incidence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment requiring surgery in Korea. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e80174.
Article10. Lee YK, Jang S, Jang S, Lee HJ, Park C, Ha YC, et al. Mortality after vertebral fracture in Korea: analysis of the National Claim Registry. Osteoporos Int. 2012; 23:1859–1865.11. Korean Statistical Information Service. Summary of Census Population. accessed on 2013 December 23. Available at: http://www.kosis.kr.12. Furue M, Yamazaki S, Jimbow K, Tsuchida T, Amagai M, Tanaka T, et al. Prevalence of dermatological disorders in Japan: a nationwide, cross-sectional, seasonal, multicenter, hospital-based study. J Dermatol. 2011; 38:310–320.
Article13. Lu T, Gao T, Wang A, Jin Y, Li Q, Li C. Vitiligo prevalence study in Shaanxi Province, China. Int J Dermatol. 2007; 46:47–51.
Article14. Zhao B. Clinical Dermatology. 3rd ed. Nanjing: Jiangsu Scientific Press;2001.15. Xu YY, Ye DQ, Tong ZC, Hao JH, Jin J, Shen SF, et al. An epidemiological survey for four skin diseases in Anhui. Chin J Dermatol. 2002; 35:406–407.16. Hann SK, Nordlund JJ. A Monograph on the Basic and Clinical Science. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd.;2000.17. Yu HJ, Park KC, Ahn JS, Lim JG, Kwon TE, Koh WS, et al. Clinical study of vitiligo. Korean J Dermatol. 1998; 36:1037–1042.18. Narita T, Oiso N, Fukai K, Kabashima K, Kawada A, Suzuki T. Generalized vitiligo and associated autoimmune diseases in Japanese patients and their families. Allergol Int. 2011; 60:505–508.
Article19. Silverberg JI, Silverberg NB. Association between vitiligo and atopic disorders: a pilot study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013; 149:983–986.
Article20. Sawchuk M, Spano F, Loo WJ, Guenther L. The coexistence of psoriasis and vitiligo: a review. J Cutan Med Surg. 2012; 16:300–305.
Article21. Youn JI. Psoriasis in Korean. Korean J Dermatol. 2012; 50:387–402.22. Tsai TF, Wang TS, Hung ST, Tsai PI, Schenkel B, Zhang M, et al. Epidemiology and comorbidities of psoriasis patients in a national database in Taiwan. J Dermatol Sci. 2011; 63:40–46.
Article23. Zhu KJ, Lv YM, Yin XY, Wang ZX, Sun LD, He SM, et al. Psoriasis regression analysis of MHC loci identifies shared genetic variants with vitiligo. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e23089.
Article24. Bassiouny DA, Shaker O. Role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of vitiligo. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011; 36:292–297.
Article25. Basak PY, Adiloglu AK, Ceyhan AM, Tas T, Akkaya VB. The role of helper and regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 60:256–260.
Article26. Jin Y, Mailloux CM, Gowan K, Riccardi SL, LaBerge G, Bennett DC, et al. NALP1 in vitiligo-associated multiple autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:1216–1225.
Article27. Spritz RA. Shared genetic relationships underlying generalized vitiligo and autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid. 2010; 20:745–754.
Article