J Rhinol.
2019 May;26(1):32-37. 10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.32.
The Effect of Long-Term Follow up on Outcome of Pediatric Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Dankook University, College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. jihunmo@gmail.com
- KMID: 2449026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.32
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Chronic pediatric sinusitis continues to be a challenging problem to otolaryngologists and has been reported to show worse prognosis than that of adults. However, most studies were performed with short-term follow-up. In this study, we aimed to assess the clinical outcome of pediatric endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) with a longer follow-up and to determine the effect of age on postoperative outcome.
SUBJECTS AND METHOD
A retrospective analysis was performed on pediatric patients than 15 years with ESS younger from 2005 to 2014 in a tertiary referral hospital. All patients completed a questionnaire regarding symptoms before to from 1 to 9 years after surgery. Telephone survey was performed to evaluate symptoms including nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, PND, and headache at 1 to 9 years after surgery.
RESULTS
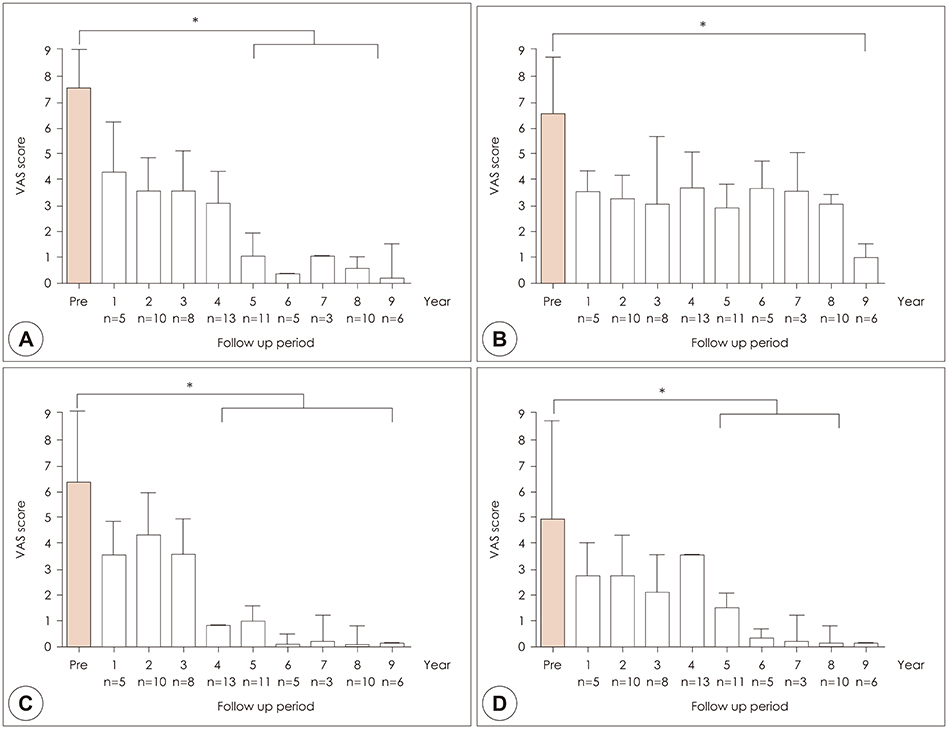
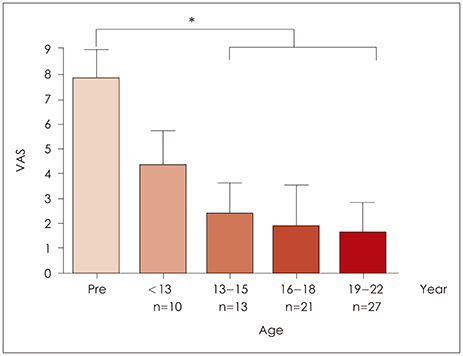
Seventy-one pediatric patients with bilateral chronic sinusitis were treated with ESS. They showed gradual symptom improvement from 5 year after surgery for the following: nasal obstruction (p=0.032), PND (p=0.005), and headache (p=0.048). However, there was improvement in rhinorrhea after 9 years (p=0.042). In addition, when analyzed in terms of age, the outcome was poor in children younger than 13 years (p=0.003) compared with the older age group. Multivariate analysis showed that preoperative nasal obstruction was dependent on AR, and postoperative symptoms were dependent on presence of AR and involuntary smoking. Nasal discharge was dependent on presence of AR and involuntary smoking preoperatively and postoperatively. These suggest the importance of AR and involuntary smoking as risk factors for prognosis.
CONCLUSION
Chronic pediatric sinusitis showed gradual improvement after ESS and should be more carefully monitored on a long-term basis. We should keep in mind that long-term follow-up is needed for pediatric ESS cases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ramadan HH. Surgical management of chronic sinusitis in children. The Laryngoscope. 2004; 114(12):2103–2109.
Article2. Manning S. Surgical intervention for sinusitis in children. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 2001; 1(3):289–296.
Article3. Kim BC, Lee JW, Kim YT, Oh JH, Kim HJ. Anatomic variations of the paranasal sinus in children with chronic sinusitis. Korean Journal of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. 2005; 48(6):729–734.4. Lee JY, Lee SW. Influence of age on the surgical outcome after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. The Laryngoscope. 2007; 117(6):1084–1089.
Article5. Poole MD. Pediatric endoscopic sinus surgery: the conservative view. Ear Nose Throat J. 1994; 73(4):221–227.
Article6. Ramadan HH. Adenoidectomy vs endoscopic sinus surgery for the treatment of pediatric sinusitis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999; 125(11):1208–1211.
Article7. Hebert RL 2nd, Bent JP 3rd. Meta-analysis of outcomes of pediatric functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 1998; 108(6):796–799.
Article8. Lusk RP, Bothwell MR, Piccirillo J. Long-term follow-up for children treated with surgical intervention for chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2006; 116(12):2099–2107.
Article9. Ramadan HH. Relation of age to outcome after endoscopic sinus surgery in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 129(2):175–177.
Article10. Tsukidate T, Haruna S, Fukami S, Nakajima I, Konno W, Moriyama H. Long-term evaluation after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic pediatric sinusitis with polyps. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012; 39(6):583–587.
Article11. Senior BA, Kennedy DW, Tanabodee J, Kroger H, Hassab M, Lanza D. Long-term results of functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope. 1998; 108(2):151–157.
Article12. Rudnick EF, Mitchell RB. Improvements in quality of life in children after surgical therapy for sinonasal disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 134(5):737–740.
Article13. Costa Carvalho BT, Nagao AT, Arslanian C, Carneiro Sampaio MM, Naspitz CK, Sorensen RU, et al. Immunological evaluation of allergic respiratory children with recurrent sinusitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005; 16(6):534–538.
Article14. Song HM, Yu MS, Park HW, Chung YS, Lee BJ, Jang YJ. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of endoscopic sinus surgery in pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2006; 49(2):168–173.15. Kim HY, Dhong HJ, Chung SK, Chung YJ, Min JY. Prognostic factors of pediatric endoscopic sinus surgery. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 69(11):1535–1539.
Article16. Watelet JB, Annicq B, van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Objective outcome after functional endoscopic sinus surgery: prediction factors. Laryngoscope. 2004; 114(6):1092–1097.
Article17. Lee SH, Park CY, Lee KC. Recurrence Rates of Nasal Polyps after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in regards to Underlying Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. J Rhinol. 2007; 14(2):106–109.18. Lee JS, Jang ES, Maeng JW, Ko I, Kim HY, Kim JY. The Effect of Smoking on Outcome in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. J Rhinol. 2009; 16(2):91–94.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-Term Outcomes of Transnasal Endoscopic Marsupialization through Middle, Inferior Meatal Antrostomy or Extended Middle Meatal Antrostomy in Maxillary Sinus Mucoceles
- Clinical Study of Surgical Treatment for Frontal Sinus Disease: Osteoplastic Frontal Sinus Surgery versus Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- Radical Endoscopic Antrum Surgery for the Treatment of Pediatric Sinusitis
- Effect of Pediatric Endoscopic Sinus Surgery with Antrochoanal Polyps on Sinus Growth
- The Effect of Smoking on Outcome in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery