Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Apr;43(2):187-194. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.187.
Predictive Value of Pharyngeal Width at Rest (JOSCYL Width) for Aspiration in Elderly People
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. ohnsh@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2449001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.187
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To develop a new tool for aspiration risk prediction based on pharyngeal width at rest in older adults with symptoms of aspiration.
METHODS
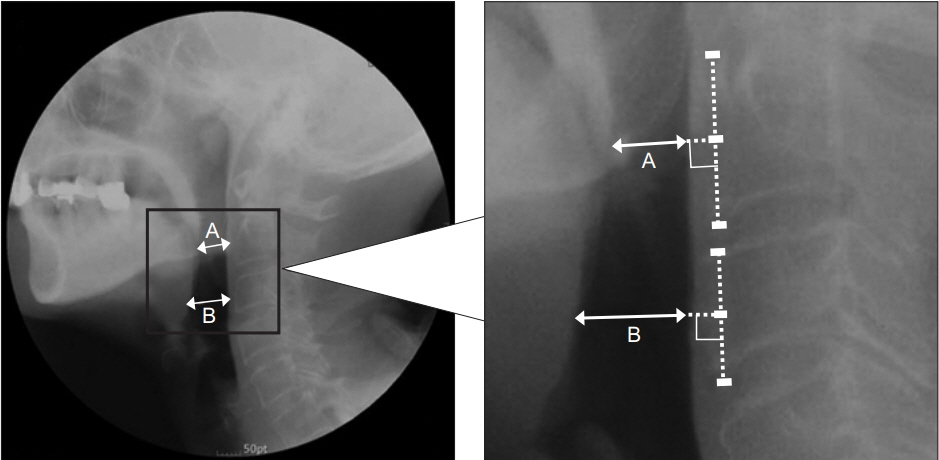
Lateral cervical spine roentgenograms were obtained from 33 older adult patients who complained of dysphagia and from 33 healthy, age-matched controls. Pharyngeal width at rest was measured at two points. We named the average of these two pharyngeal widths "˜JOSCYL Width', calculated "˜JOSCYL Scale', and compared these parameters between dysphagia and control groups. Correlations of individual JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale, with Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) and Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale (DOSS) scores were analyzed for the dysphagia group. To determine optimal cutoff points for predicting aspiration, a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed on JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale.
RESULTS
Both JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale of the dysphagia group were larger than those of the control group (p<0.001). The correlation between JOSCYL Width and severity of dysphagia was significant for the dysphagia group (PAS p=0.007; DOSS p=0.012). The correlation between JOSCYL Scale and the severity of dysphagia was also significant for the dysphagia group (PAS p=0.009; DOSS p=0.011). Optimal cutoffs for JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale for predicting aspiration were 20.0 mm and 5.9, respectively.
CONCLUSION
JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale can be new indicators for predicting aspiration in older adults. They are both precise and easy to use.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Changes in Pharyngeal Width Over Time as an Indicator of Dysphagia in Stroke Patients
Seungki Baek, Il Hwan Jung, Ho Young Lee, Jimin Song, Eunsil Cha, Kwang-Ik Jung, Woo-Kyoung Yoo, Suk Hoon Ohn
Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(3):203-209. doi: 10.5535/arm.19140.
Reference
-
1. Madhavan A, LaGorio LA, Crary MA, Dahl WJ, Carnaby GD. Prevalence of and risk factors for dysphagia in the community dwelling elderly: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging. 2016; 20:806–15.
Article2. Kikuchi R, Watabe N, Konno T, Mishina N, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. High incidence of silent aspiration in elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994; 150:251–3.
Article3. Buchholz DW. Neurogenic dysphagia: what is the cause when the cause is not obvious? Dysphagia. 1994; 9:245–55.
Article4. Robbins J, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster GB. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103:823–9.
Article5. Tracy JF, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Jacob P, Kobara M, Krugler C. Preliminary observations on the effects of age on oropharyngeal deglutition. Dysphagia. 1989; 4:90–4.
Article6. Smithard DG, O’Neill PA, Parks C, Morris J. Complications and outcome after acute stroke. Does dysphagia matter? Stroke. 1996; 27:1200–4.7. Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke. 2005; 36:2756–63.8. Chodzko-Zajko WJ, Ringel RL. Physiological aspects of aging. J Voice. 1987; 1:18–26.
Article9. Molfenter SM, Amin MR, Branski RC, Brumm JD, Hagiwara M, Roof SA, et al. Age-related changes in pharyngeal lumen size: a retrospective MRI analysis. Dysphagia. 2015; 30:321–7.
Article10. Sura L, Madhavan A, Carnaby G, Crary MA. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin Interv Aging. 2012; 7:287–98.11. Marik PE, Kaplan D. Aspiration pneumonia and dysphagia in the elderly. Chest. 2003; 124:328–36.
Article12. Edmiaston J, Connor LT, Loehr L, Nassief A. Validation of a dysphagia screening tool in acute stroke patients. Am J Crit Care. 2010; 19:357–64.
Article13. Leigh JH, Lim JY, Han MK, Bae HJ, Kim WS, Paik NJ. A prospective comparison between bedside swallowing screening test and videofluoroscopic swallowing study in post-stroke dysphagia. Brain Neurorehabil. 2016; 9(2):e7.
Article14. Park S, Lee JY, Jung H, Koh SE, Lee IS, Yoo KH, et al. Use of videofluoroscopic swallowing study in patients with aspiration pneumonia. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36:785–90.
Article15. Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971; 9:97–113.
Article16. Nicosia MA, Robbins J. The usefulness of the line spread test as a measure of liquid consistency. Dysphagia. 2007; 22:306–11.
Article17. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:677–82.
Article18. Eisenhuber E, Schima W, Schober E, Pokieser P, Stadler A, Scharitzer M, et al. Videofluoroscopic assessment of patients with dysphagia: pharyngeal retention is a predictive factor for aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 178:393–8.19. Jaffer NM, Ng E, Au FW, Steele CM. Fluoroscopic evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: anatomic, technical, and common etiologic factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 204:49–58.
Article20. Jones B. Radiologic evaluation of the dysphagic patient. Nutr Clin Pract. 1999; 14:S10–S12.
Article21. Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996; 11:93–8.
Article22. O’Neil KH, Purdy M, Falk J, Gallo L. The dysphagia outcome and severity scale. Dysphagia. 1999; 14:139–45.
Article23. Maeda K, Akagi J. Decreased tongue pressure is associated with sarcopenia and sarcopenic dysphagia in the elderly. Dysphagia. 2015; 30:80–7.
Article24. Feng X, Todd T, Lintzenich CR, Ding J, Carr JJ, Ge Y, et al. Aging-related geniohyoid muscle atrophy is related to aspiration status in healthy older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2013; 68:853–60.
Article25. Baba T, Goto T, Fujimoto K, Honda T, Yagi K, Nagao K, et al. Age-related changes in geniohyoid muscle morphology predict reduced swallowing function. J Oral Health Biosci. 2017; 30:18–25.26. Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Pharyngeal constriction in elderly dysphagic patients compared with young and elderly nondysphagic controls. Dysphagia. 2001; 16:272–8.
Article27. Stokely SL, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Leigh C, Molfenter SM, Steele CM. The relationship between pharyngeal constriction and post-swallow residue. Dysphagia. 2015; 30:349–56.
Article28. Mirzakhani H, Williams JN, Mello J, Joseph S, Meyer MJ, Waak K, et al. Muscle weakness predicts pharyngeal dysfunction and symptomatic aspiration in long-term ventilated patients. Anesthesiology. 2013; 119:389–97.
Article29. Kallman DA, Plato CC, Tobin JD. The role of muscle loss in the age-related decline of grip strength: crosssectional and longitudinal perspectives. J Gerontol. 1990; 45:M82–8.
Article30. Maeda K, Akagi J. Sarcopenia is an independent risk factor of dysphagia in hospitalized older people. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016; 16:515–21.
Article31. Zammit-Maempel I, Chapple CL, Leslie P. Radiation dose in videofluoroscopic swallow studies. Dysphagia. 2007; 22:13–5.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes in Pharyngeal Width Over Time as an Indicator of Dysphagia in Stroke Patients
- The effect of mesiodistal crown widths of anterior teeth on incisor relationship
- Improved Dysphagia After Decannulation of Tracheostomy in Patients With Brain Injuries
- Dosimetric Consideration of the Lung Block in the Mantle Field
- Relationship between mesiodistal width and enamel thickness in mandibular incisors