Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 Jul;11(4):508-518. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.4.508.
Efficacy and Safety of Benralizumab for Korean Patients With Severe, Uncontrolled Eosinophilic Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, College of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
- 7AstraZeneca, Gaithersburg, MD, USA.
- KMID: 2448753
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.4.508
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In the Phase III SIROCCO trial (NCT01928771), benralizumab significantly reduced asthma exacerbations and improved lung function and symptoms for patients with severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma. The aim of this subgroup analysis was to evaluate efficacy and safety of benralizumab for Korean patients in SIROCCO.
METHODS
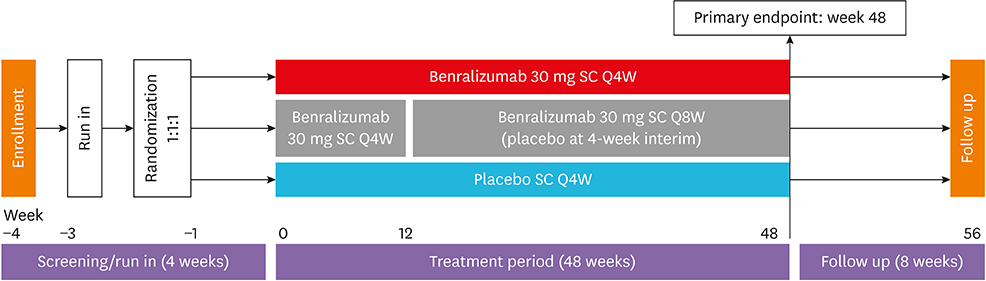
SIROCCO was a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial of 1,204 patients aged 12-75 years with severe asthma uncontrolled by high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids/long-acting β2-agonists (ICS/LABA). Patients received benralizumab 30 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or every 8 weeks (Q8W; first 3 doses Q4W) or placebo Q4W for 48 weeks. The primary analysis population comprised patients with blood eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL. This subgroup analysis evaluated Korean patients from this group.
RESULTS
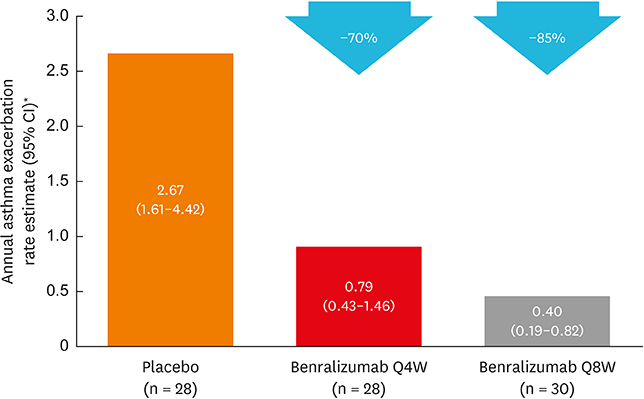
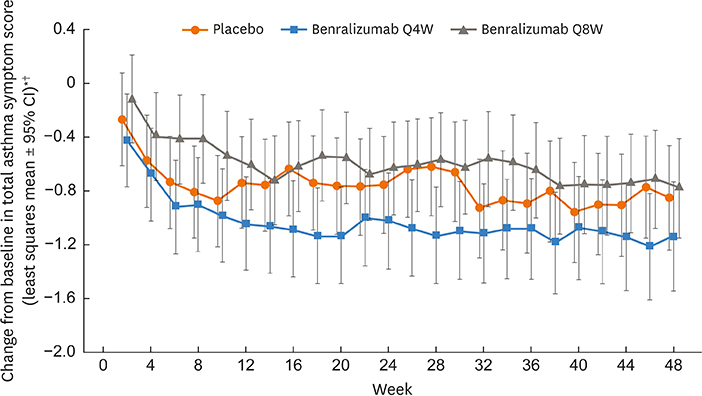
Of 122 Korean patients randomized, 86 had blood eosinophil counts ≥ 300 cells/µL. Benralizumab reduced the annual asthma exacerbation rate by 70% (Q4W: rate estimate 0.79, rate ratio 0.30 [95% confidence interval {CI}, 0.13-0.65], nominal P = 0.003; n = 28) and 85% (Q8W: rate estimate 0.40, rate ratio 0.15 [95% CI, 0.06-0.36], nominal P < 0.001; n = 30) vs. placebo (rate estimate 2.67, n = 28). Prebronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second was increased with benralizumab treatment by 0.270 L (Q4W: 95% CI, 0.039-0.500, nominal P = 0.023; n = 28) and 0.362 L (Q8W: 95% CI, 0.143-0.582, nominal P = 0.002; n = 30) vs. placebo (n = 27). Total asthma symptom score was similar for patients receiving either benralizumab Q4W (−0.27 [95% CI, −0.83 to 0.30], nominal P = 0.356; n = 27) or benralizumab Q8W (0.10 [95% CI, −0.44 to 0.65], nominal P = 0.708; n = 30) vs. placebo (n = 28). Drug-related adverse events were experienced by 2%, 8%, and 5% of patients in the placebo, benralizumab Q4W, and benralizumab Q8W arms.
CONCLUSIONS
Benralizumab reduced annual asthma exacerbation rates, increased lung function, and was well-tolerated by Korean patients with severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Biological treatments for severe asthma
Hyun Jung Jin
Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):262-268. doi: 10.12701/yujm.2020.00647.
Reference
-
1. To T, Stanojevic S, Moores G, Gershon AS, Bateman ED, Cruz AA, et al. Global asthma prevalence in adults: findings from the cross-sectional world health survey. BMC Public Health. 2012; 12:204.
Article2. Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, Bush A, Castro M, Sterk PJ, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. Eur Respir J. 2014; 43:343–373.3. Kim BK, Kim JY, Kang MK, Yang MS, Park HW, Min KU, et al. Allergies are still on the rise? A 6-year nationwide population-based study in Korea. Allergol Int. 2016; 65:186–191.
Article4. Kim DK, Park YB, Oh YM, Jung KS, Yoo JH, Yoo KH, et al. Korean asthma guideline 2014: summary of major updates to the Korean asthma guideline 2014. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2016; 79:111–120.
Article5. Peters SP, Ferguson G, Deniz Y, Reisner C. Uncontrolled asthma: a review of the prevalence, disease burden and options for treatment. Respir Med. 2006; 100:1139–1151.
Article6. AstraZeneca. Fasenra™ (benralizumab) prescribing information [Internet]. Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca;2017. cited 2018 Jan 10. Available from: https://www.azpicentral.com/fasenra/fasenra_pi.pdf#page=1.7. AstraZeneca. Fasenra™ (benralizumab) summary of product characteristics [Internet]. Södertälje: AstraZeneca;2018. cited 2018 Mar 13. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/health/documents/community-register/2018/20180108139598/anx_139598_en.pdf.8. AstraZeneca. Fasenra receives approval in Japan [Internet]. Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca;2018. cited 2018 Jan 19. Available from: https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2018/fasenra-recieves-approval-in-japan-19012018.html.9. AstraZeneca. Fasenra® (benralizumab) product monograph [Internet]. Mississauga: AstraZeneca Canada Inc.;2018. cited 2018 May 24. Available from: https://www.astrazeneca.ca/content/dam/az-ca/downloads/productinformation/fasenra-product-monograph-en.pdf.10. Pavord ID. Eosinophilic phenotypes of airway disease. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013; 10:Suppl. S143–S149.
Article11. Price D, Wilson AM, Chisholm A, Rigazio A, Burden A, Thomas M, et al. Predicting frequent asthma exacerbations using blood eosinophil count and other patient data routinely available in clinical practice. J Asthma Allergy. 2016; 9:1–12.12. Talini D, Novelli F, Bacci E, Bartoli M, Cianchetti S, Costa F, et al. Sputum eosinophilia is a determinant of FEV1 decline in occupational asthma: results of an observational study. BMJ Open. 2015; 5:e005748.
Article13. Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, Peng L, Andersson CK, Damschroder MM, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1344–1353.e2.14. Pham TH, Damera G, Newbold P, Ranade K. Reductions in eosinophil biomarkers by benralizumab in patients with asthma. Respir Med. 2016; 111:21–29.
Article15. Bleecker ER, FitzGerald JM, Chanez P, Papi A, Weinstein SF, Barker P, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab for patients with severe asthma uncontrolled with high-dosage inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting β2-agonists (SIROCCO): a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016; 388:2115–2127.16. FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Nair P, Korn S, Ohta K, Lommatzsch M, et al. Benralizumab, an anti-interleukin-5 receptor α monoclonal antibody, as add-on treatment for patients with severe, uncontrolled, eosinophilic asthma (CALIMA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016; 388:2128–2141.
Article17. Nair P, Wenzel S, Rabe KF, Bourdin A, Lugogo NL, Kuna P, et al. Oral glucocorticoid-sparing effect of benralizumab in severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:2448–2458.
Article18. Park HS, Kim MK, Imai N, Nakanishi T, Adachi M, Ohta K, et al. A phase 2a study of benralizumab for patients with eosinophilic asthma in South Korea and Japan. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2016; 169:135–145.
Article19. Ohta K, Adachi M, Tohda Y, Kamei T, Kato M, Mark Fitzgerald J, et al. Efficacy and safety of benralizumab in Japanese patients with severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic asthma. Allergol Int. 2018; 67:266–272.
Article20. Goldman M, Hirsch I, Zangrilli JG, Newbold P, Xu X. The association between blood eosinophil count and benralizumab efficacy for patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma: subanalyses of the Phase III SIROCCO and CALIMA studies. Curr Med Res Opin. 2017; 33:1605–1613.
Article21. FitzGerald JM, Bleecker ER, Menzies-Gow A, Zangrilli JG, Hirsch I, Metcalfe P, et al. Predictors of enhanced response with benralizumab for patients with severe asthma: pooled analysis of the SIROCCO and CALIMA studies. Lancet Respir Med. 2018; 6:51–64.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Eosinophils and childhood asthma
- Treatment of Severe Asthma
- Distinct functions of eosinophils in severe asthma with type 2 phenotype: clinical implications
- A pediatric case of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis accompanied by heart failure mimicking an asthma attack
- Clinical and Pathophysiological Characteristics of Severe Asthma