Arch Hand Microsurg.
2019 Jun;24(2):183-188. 10.12790/ahm.2019.24.2.183.
Revisiting the Cross-Leg Flap: A Degraded or Still Useful Method?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pshero2@naver.com
- KMID: 2448053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2019.24.2.183
Abstract
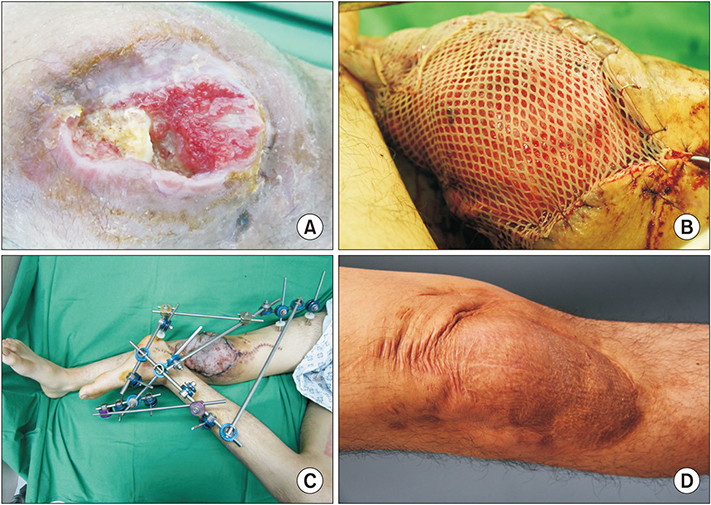
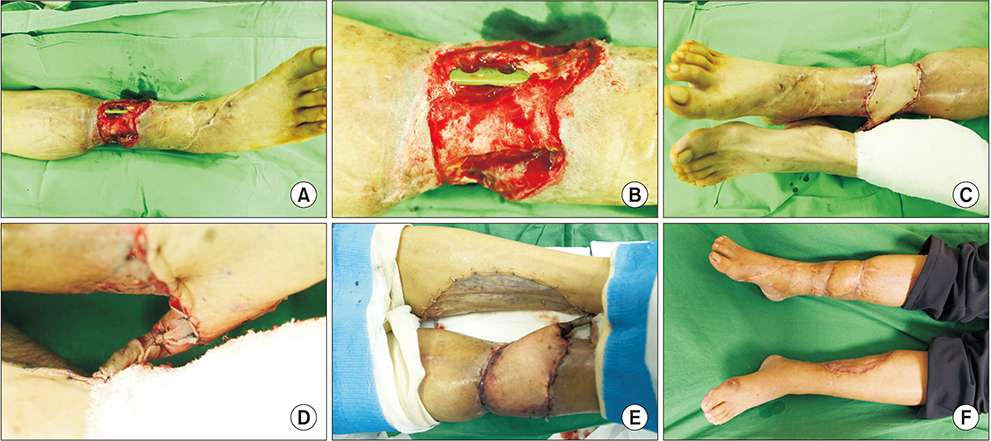
- Since the development of microsurgery, the cross-leg flap has not been a preferred method of lower extremity reconstruction. However, it is being used in several centers and has shown favorable results. This report presents our experience in treating lower extremity injuries using the cross-leg flap. We studied three patients with lower extremity defect who underwent cross-leg flap surgery. As there was no proper perforator for local flap or recipient vessel for free flap in the ipsilateral leg, two underwent the posterior tibial artery island cross-leg flap and one had the latissimus dorsi free flap, wherein the recipient vessels comprised the contralateral posterior tibial vessels. All procedures were successful without any severe complications. We recommend that cross-leg flaps be considered not only in cases of multiple vessel injuries or when no other options are available but also in cases of broad trauma or where scar tissue is present around the defect.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Basile A, Stopponi M, Loreti A, Minniti de Simeonibus AU. Heel coverage using a distally based sural artery fasciocutaneous cross-leg flap: report of a small series. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2008; 47:112–117.
Article2. Almeida MF, da Costa PR, Okawa RY. Reverse-flow island sural flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 109:583–591.
Article3. Goel P, Badash I, Gould DJ, Landau MJ, Carey JN. Options for covering large soft tissue defects in the setting of trauma. Curr Trauma Rep. 2018; 4:316–325.
Article4. Griffin JR, Thornton JF. Lower extremity reconstruction. In : Kenkel JM, editor. Selected readings in plastic surgery. Dallas: Selected Readings in Plastic Surgery, Inc.;2009. p. 1–57.5. Stark RB. The cross-leg flap procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946). 1952; 9:173–204.
Article6. Heller L, Levin LS. Lower extremity microsurgical reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001; 108:1029–1041. quiz 1042.
Article7. Lu L, Liu A, Zhu L, Zhang J, Zhu X, Jiang H. Cross-leg flaps: our preferred alternative to free flaps in the treatment of complex traumatic lower extremity wounds. J Am Coll Surg. 2013; 217:461–471.
Article8. Lai CS, Lin SD, Chou CK, Cheng YM. Use of a cross-leg free muscle flap to reconstruct an extensive burn wound involving a lower extremity. Burns. 1991; 17:510–513.
Article9. Manrique OJ, Bishop SN, Ciudad P, et al. Lower extremity limb salvage with cross leg pedicle flap, cross leg Free flap, and cross leg vascular cable bridge Flap. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2018; 34:522–529.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neovascularization in the "Cross-Leg Fashioned" Muscular Free Flap
- Cross-Leg Flap Imobilized with External Fixator Brace
- Use of the cross-leg distally based sural artery flap for the reconstruction of complex lower extremity defects
- Reconstruction of Lower Extremity Soft Tissue Defect using Cross-leg Free Flap
- Cross-Leg Achilles Tendon Reconstruction Using a Composite Flap of Dorsalis Pedis and Tendon Strips of the Extensor Digitorum Longus in a Vascular Compromised Wound