Ann Surg Treat Res.
2019 Jun;96(6):313-318. 10.4174/astr.2019.96.6.313.
Outcome of ClosureFAST radiofrequency ablation for large-diameter incompetent great saphenous vein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul Metropolitan Government - Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. sboy5240@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2447956
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2019.96.6.313
Abstract
- PURPOSE
There is limited data on the outcomes of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for large diameter saphenous veins. This study aimed to determine whether the large-diameter great saphenous vein (GSV) affected closure rate, complications, and clinical and quality of life (QoL) improvement.
METHODS
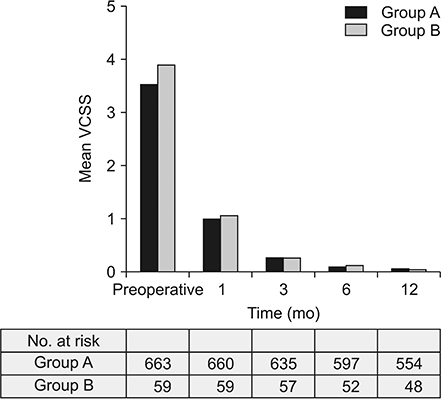
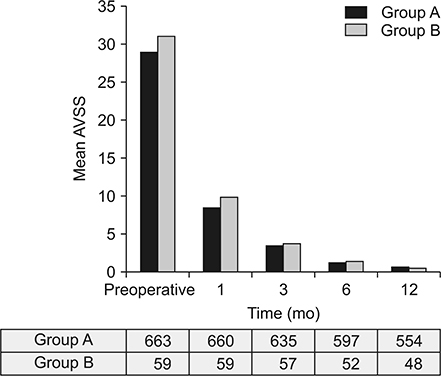
From January 2012 to September 2016, a total of 722 limbs were treated with ClosureFAST RFA in a single center. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to the vein diameter measured 3 cm below the saphenofemoral junction (group A ≤ 12 mm, group B > 12 mm). Vein closure was evaluated with duplex scan at 3-5 days, 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. The incidence of complications, improvements in symptoms (measured by the Venous Clinical Severity Score [VCSS]) and QoL (measured by the Aberdeen Varicose Vein Symptom Severity Score [AVSS]) were evaluated.
RESULTS
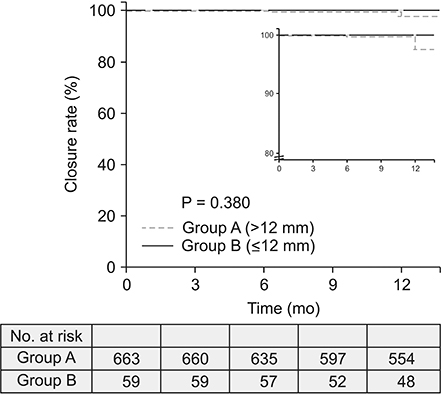
Groups consisted of 663 GSVs in group A (mean diameter, 6.00 ± 1.74 mm) and 59 in group B (mean diameter, 13.17 ± 1.28 mm). Vein closure rates at 12 months were 98.9% in group A and 100% in group B (P = 0.428). There was no significant difference in the incidence of complications. Both groups showed marked improvements in the VCSS and the AVSS with no significant differences.
CONCLUSION
For large-diameter veins, RFA showed comparable outcomes in terms of closure rate, complications, clinical and QoL improvements.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Proebstle TM, Alm J, Dimitri S, Rasmussen L, Whiteley M, Lawson J, et al. The European multicenter cohort study on cyanoacrylate embolization of refluxing great saphenous veins. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2015; 3:2–7.
Article2. Hoggan BL, Cameron AL, Maddern GJ. Systematic review of endovenous laser therapy versus surgery for the treatment of saphenous varicose veins. Ann Vasc Surg. 2009; 23:277–287.
Article3. Luebke T, Brunkwall J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of endovenous radiofrequency obliteration, endovenous laser therapy, and foam sclerotherapy for primary varicosis. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2008; 49:213–233.4. Luebke T, Gawenda M, Heckenkamp J, Brunkwall J. Meta-analysis of endovenous radiofrequency obliteration of the great saphenous vein in primary varicosis. J Endovasc Ther. 2008; 15:213–223.
Article5. Sun JJ, Chowdhury MM, Sadat U, Hayes PD, Tang TY. Mechanochemical ablation for treatment of truncal venous insufficiency: a review of the current literature. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:1422–1431.
Article6. Rasmussen LH, Lawaetz M, Bjoern L, Vennits B, Blemings A, Eklof B. Randomized clinical trial comparing endovenous laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation, foam sclerotherapy and surgical stripping for great saphenous varicose veins. Br J Surg. 2011; 98:1079–1087.
Article7. Nordon IM, Hinchliffe RJ, Brar R, Moxey P, Black SA, Thompson MM, et al. A prospective double-blind randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency versus laser treatment of the great saphenous vein in patients with varicose veins. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:876–881.
Article8. Lurie F, Creton D, Eklof B, Kabnick LS, Kistner RL, Pichot O, et al. Prospective randomized study of endovenous radiofrequency obliteration (closure procedure) versus ligation and stripping in a selected patient population (EVOLVeS Study). J Vasc Surg. 2003; 38:207–214.
Article9. Nicolini P. Closure Group. Treatment of primary varicose veins by endovenous obliteration with the VNUS closure system: results of a prospective multicentre study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005; 29:433–439.
Article10. Calcagno D, Rossi JA, Ha C. Effect of saphenous vein diameter on closure rate with ClosureFAST radiofrequency catheter. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2009; 43:567–570.
Article11. Shaidakov EV, Grigorian AG, Iliukhin EA, Bulatov VL, Gal'chenko MI. Analysis of efficacy of radiofrequency obliteration with due regard for the target vein's diameter. Angiol Sosud Khir. 2014; 20:87–94.12. Cabrero Fernandez M, Martinez Lopez I, Hernandez Mateo MM, Marques de Marino P, Cernuda Artero I, Serrano Hernando FJ. Prospective study of safety and effectiveness in the use of radiofrequency ablation for incompetent great saphenous vein ≥12 mm. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017; 5:810–816.13. Rutherford RB, Padberg FT Jr, Comerota AJ, Kistner RL, Meissner MH, Moneta GL. Venous severity scoring: an adjunct to venous outcome assessment. J Vasc Surg. 2000; 31:1307–1312.
Article14. Garratt AM, Macdonald LM, Ruta DA, Russell IT, Buckingham JK, Krukowski ZH. Towards measurement of outcome for patients with varicose veins. Qual Health Care. 1993; 2:5–10.
Article15. De Maeseneer M, Pichot O, Cavezzi A, Earnshaw J, van Rij A, Lurie F, et al. Duplex ultrasound investigation of the veins of the lower limbs after treatment for varicose veins - UIP consensus document. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; 42:89–102.
Article16. Chan YC, Law Y, Cheung GC, Cheng SW. Predictors of recanalization for incompetent great saphenous veins treated with cyanoacrylate glue. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 28:665–671.
Article17. Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA. Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14(9 Pt 2):S199–S202.
Article18. Keo HH, Baumann F, Diehm N, Regli C, Staub D. Rivaroxaban versus fondaparinux for thromboprophylaxis after endovenous laser ablation. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2017; 5:817–823.
Article19. Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, Eklof BG, Gillespie DL, Gloviczki ML, et al. The care of patients with varicose veins and associated chronic venous diseases: clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum. J Vasc Surg. 2011; 53:5 Suppl. 2S–48S.
Article20. Proebstle TM, Vago B, Alm J, Gockeritz O, Lebard C, Pichot O. Treatment of the incompetent great saphenous vein by endovenous radiofrequency powered segmental thermal ablation: first clinical experience. J Vasc Surg. 2008; 47:151–156.
Article21. Creton D, Pichot O, Sessa C, Proebstle TM. ClosureFast Europe Group. Radiofrequency-powered segmental thermal obliteration carried out with the ClosureFast procedure: results at 1 year. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010; 24:360–366.
Article22. Medical Advisory Secretariat. Endovascular radiofrequency ablation for varicose veins: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011; 11:1–93.23. Marsh P, Price BA, Holdstock J, Harrison C, Whiteley MS. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after venous thermoablation techniques: rates of endovenous heat-induced thrombosis (EHIT) and classical DVT after radiofrequency and endovenous laser ablation in a single centre. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010; 40:521–527.
Article24. Proebstle TM, Alm J, Gockeritz O, Wenzel C, Noppeney T, Lebard C, et al. Three-year European follow-up of endovenous radiofrequency-powered segmental thermal ablation of the great saphenous vein with or without treatment of calf varicosities. J Vasc Surg. 2011; 54:146–152.
Article25. Merchant RF, Pichot O. Closure Study Group. Long-term outcomes of endovenous radiofrequency obliteration of saphenous reflux as a treatment for superficial venous insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2005; 42:502–509.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful use of VenaSeal system for the treatment of large great saphenous vein of 2.84-cm diameter
- The Early Results of Endovenous Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Flush High Ligation for Patients with Varicose Veins
- Effect of Diameter of Saphenous Vein on Stump Length after Radiofrequency Ablation for Varicose Vein
- The occlusion rate and patterns of saphenous vein after radiofrequency ablation
- My Experience and Comprehension of Flebogrif®, a New Modality of Mechanochemical Ablation for Incompetent Saphenous Veins – What’s Different from ClariVein®?