Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2019 May;12(2):163-168. 10.21053/ceo.2018.00899.
Hyperbilirubinemia and Follow-up Auditory Brainstem Responses in Preterm Infants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, College of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jychoi@yuhs.ac, jsjung@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2447424
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.00899
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
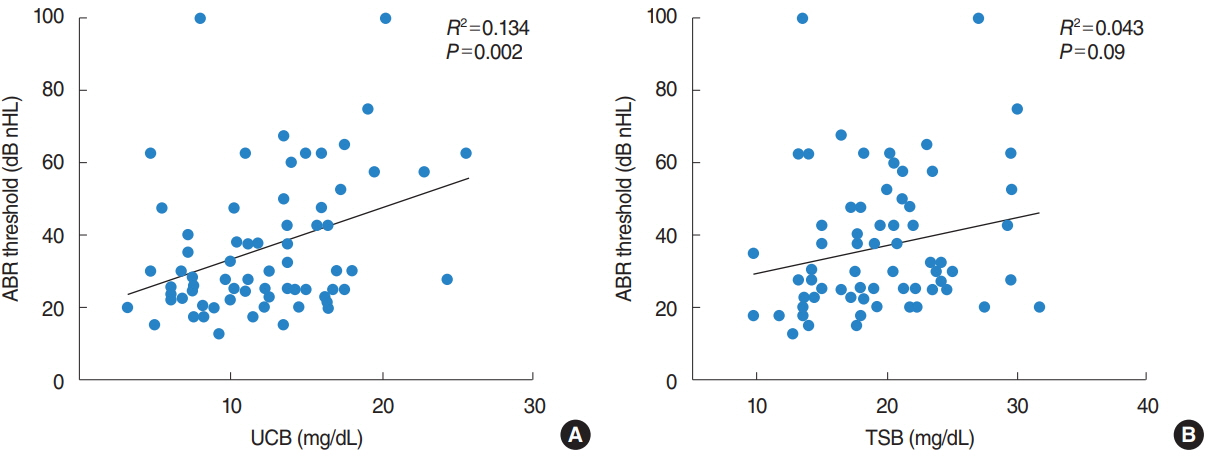
.: Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is considered one of the most common causative factors of hearing loss. Preterm infants are more vulnerable to neuronal damage caused by hyperbilirubinemia. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of hyperbilirubinemia on hearing threshold and auditory pathway in preterm infants by serial auditory brainstem response (ABR). In addition, we evaluate the usefulness of the unconjugated bilirubin (UCB) level compared with total serum bilirubin (TSB) on bilirubin-induced hearing loss.
METHODS
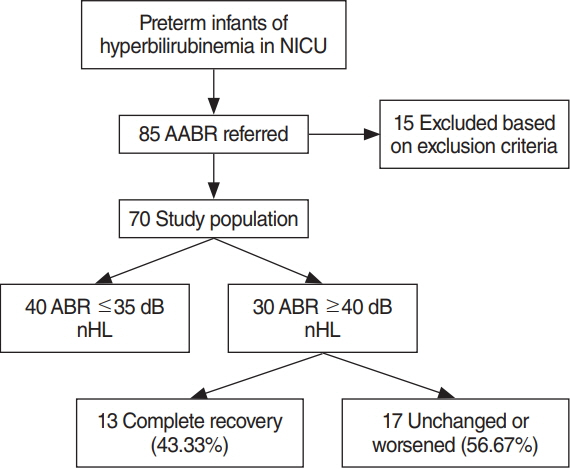
.: This study was conducted on 70 preterm infants with hyperbilirubinemia who failed universal newborn hearing screening by automated ABR. The diagnostic ABR was performed within 3 months after birth. Follow-up ABR was conducted in patients with abnormal results (30 cases). TSB and UCB concentration were compared according to hearing threshold by ABR.
RESULTS
.: The initial and maximal measured UCB concentration for the preterm infants of diagnostic ABR ≥40 dB nHL group (n=30) were statistically higher compared with ABR ≤35 dB nHL group (n=40) (P=0.031 and P=0.003, respectively). In follow-up ABR examination, 13 of the ABR ≥40 dB nHL group showed complete recovery, but 17 had no change or worsened. There was no difference in bilirubin level between the recovery group and non-recovery group.
CONCLUSION
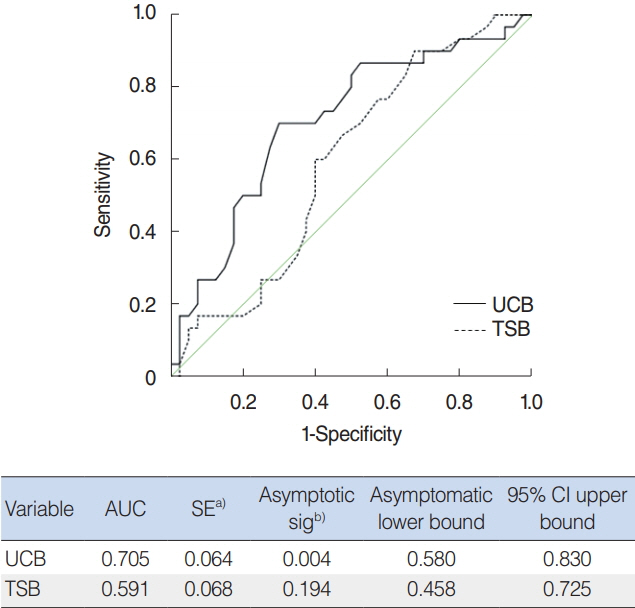
.: UCB is a better predictor of bilirubin-induced hearing loss than TSB in preterm infants as evaluated by serial ABR. Serial ABR testing can be a useful, noninvasive methods to evaluate early reversible bilirubin-induced hearing loss in preterm infants.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahlfors CE, Parker AE. Unbound bilirubin concentration is associated with abnormal automated auditory brainstem response for jaundiced newborns. Pediatrics. 2008; May. 121(5):976–8.
Article2. Mazeiras G, Roze JC, Ancel PY, Caillaux G, Frondas-Chauty A, Denizot S, et al. Hyperbilirubinemia and neurodevelopmental outcome of very low birthweight infants: results from the LIFT cohort. PLoS One. 2012; 7(1):e30900.
Article3. Shapiro SM, Nakamura H. Bilirubin and the auditory system. J Perinatol. 2001; Dec. 21 Suppl 1:S52–5.
Article4. Ye HB, Shi HB, Wang J, Ding DL, Yu DZ, Chen ZN, et al. Bilirubin induces auditory neuropathy in neonatal guinea pigs via auditory nerve fiber damage. J Neurosci Res. 2012; Nov. 90(11):2201–13.
Article5. Jiang ZD, Wilkinson AR. Impaired function of the auditory brainstem in term neonates with hyperbilirubinemia. Brain Dev. 2014; Mar. 36(3):212–8.
Article6. Shapiro SM. Bilirubin toxicity in the developing nervous system. Pediatr Neurol. 2003; Nov. 29(5):410–21.
Article7. van Imhoff DE, Dijk PH, Hulzebos CV; BARTrial Study Group; Netherlands Neonatal Research Network. Uniform treatment thresholds for hyperbilirubinemia in preterm infants: background and synopsis of a national guideline. Early Hum Dev. 2011; Aug. 87(8):521–5.
Article8. Bhutani VK, Stevenson DK. The need for technologies to prevent bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction syndrome. Semin Perinatol. 2011; Jun. 35(3):97–100.
Article9. Kim MH, Yoon JJ, Sher J, Brown AK. Lack of predictive indices in kernicterus: a comparison of clinical and pathologic factors in infants with or without kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1980; Dec. 66(6):852–8.
Article10. Turkel SB, Guttenberg ME, Moynes DR, Hodgman JE. Lack of identifiable risk factors for kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1980; Oct. 66(4):502–6.
Article11. O’Shea TM, Dillard RG, Klinepeter KL, Goldstein DJ. Serum bilirubin levels, intracranial hemorrhage, and the risk of developmental problems in very low birth weight neonates. Pediatrics. 1992; Dec. 90(6):888–92.12. Amin SB, Ahlfors C, Orlando MS, Dalzell LE, Merle KS, Guillet R. Bilirubin and serial auditory brainstem responses in premature infants. Pediatrics. 2001; Apr. 107(4):664–70.
Article13. Nakamura H, Lee Y. Microdetermination of unbound bilirubin in icteric newborn sera: an enzymatic method employing peroxidase and glucose oxidase. Clin Chim Acta. 1977; Sep. 79(2):411–7.14. Wennberg RP, Ahlfors CE, Bhutani VK, Johnson LH, Shapiro SM. Toward understanding kernicterus: a challenge to improve the management of jaundiced newborns. Pediatrics. 2006; Feb. 117(2):474–85.
Article15. Cashore WJ. The neurotoxicity of bilirubin. Clin Perinatol. 1990; Jun. 17(2):437–47.
Article16. Hansen TW. Bilirubin in the brain: distribution and effects on neurophysiological and neurochemical processes. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1994; Aug. 33(8):452–9.17. Rhine WD, Schmitter SP, Yu AC, Eng LF, Stevenson DK. Bilirubin toxicity and differentiation of cultured astrocytes. J Perinatol. 1999; Apr-May. 19(3):206–11.
Article18. Saluja S, Agarwal A, Kler N, Amin S. Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder in late preterm and term infants with severe jaundice. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; Nov. 74(11):1292–7.
Article19. Rance G. Auditory neuropathy/dys-synchrony and its perceptual consequences. Trends Amplif. 2005; 9(1):1–43.
Article20. American Academy of Pediatrics; Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007; Oct. 120(4):898–921.21. Holster IL, Hoeve LJ, Wieringa MH, Willis-Lorrier RM, de Gier HH. Evaluation of hearing loss after failed neonatal hearing screening. J Pediatr. 2009; Nov. 155(5):646–50.
Article22. Shapiro SM, Popelka GR. Auditory impairment in infants at risk for bilirubin-induced neurologic dysfunction. Semin Perinatol. 2011; Jun. 35(3):162–70.
Article23. Amin SB. Clinical assessment of bilirubin-induced neurotoxicity in premature infants. Semin Perinatol. 2004; Oct. 28(5):340–7.
Article24. Nakamura H, Takada S, Shimabuku R, Matsuo M, Matsuo T, Negishi H. Auditory nerve and brainstem responses in newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 1985; Apr. 75(4):703–8.
Article25. Smith CM, Barnes GP, Jacobson CA, Oelberg DG. Auditory brainstem response detects early bilirubin neurotoxicity at low indirect bilirubin values. J Perinatol. 2004; Nov. 24(11):730–2.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Trends of the Hyperbilirubinemia and the Results of Auditory Evoked Potential
- Uasbility of Brainstem Auditory Evoked Responses in Preterm and Postterm Neonates
- Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential and Visual Evoked Potential of High Risk Infants
- Effect of Hyperbilirubinemia on the Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response in Newborn Piglets
- Auditory Brainstem Evoked Potentials in Preterm Infants