Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2019 May;62(3):166-172. 10.5468/ogs.2019.62.3.166.
Experiences of localization and removal of non-palpable subdermal contraceptive implants with ultrasound
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sihyuncho@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Institute of Women's Life Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. AGN70@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2445074
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2019.62.3.166
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study was to present experiences in localization and removal of non-palpable subdermal contraceptive implants with ultrasonography.
METHODS
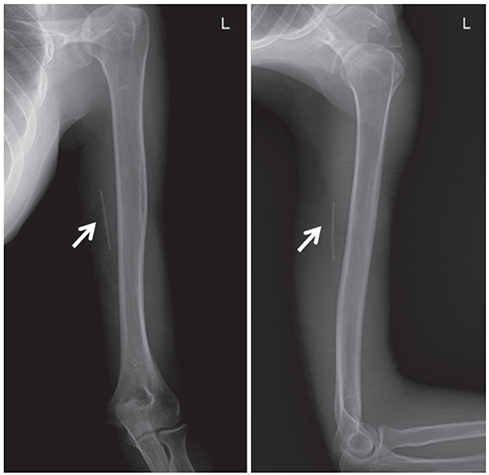
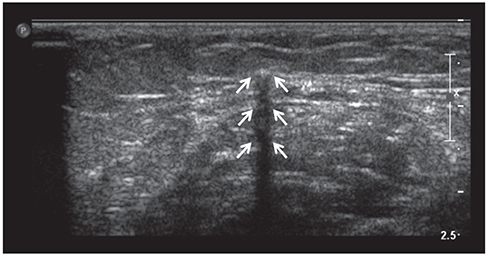
Medical records from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, were retrospectively reviewed for 21 patients who were referred to a single institution and had an impalpable implant despite following the removal instruction. In all the cases, more than one attempt was made to remove the implant before referral. The rod was detected using radiography and ultrasonography. In all the cases, localization of the single implant was achieved with ultrasonography. The distal depth of the rod was measured, and skin marking was made following the echogenicity. The implants were subsequently removed under anesthesia.
RESULTS
In 18 cases, the rods were localized using ultrasonography and successfully removed under local anesthesia. In the other three cases, removal with local anesthesia failed. Although the rod was detected successful with ultrasonography, the implants were removed under general anesthesia in the operating room. The depth from skin to rod, measured with ultrasonography, was >12.0 mm in all the cases and located deep in the muscular layer in the failure cases. The depth of the implants positively correlated with the time spent for removal (r=0.525; P=0.015).
CONCLUSION
High frequency ultrasonography is a highly accurate tool for localization and measurement of the skin-to-rod depth. It is also useful for removing non-palpable implants. If the depth of the implant is >12.0 mm, removal of the implant in the operating room under general anesthesia is recommended.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Darney PD. Implantable contraception. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2000; 5:Suppl 2. 2–11.2. Mansour D, Mommers E, Teede H, Sollie-Eriksen B, Graesslin O, Ahrendt HJ, et al. Clinician satisfaction and insertion characteristics of a new applicator to insert radiopaque Implanon: an open-label, noncontrolled, multicenter trial. Contraception. 2010; 82:243–249.
Article3. Mansour D, Fraser IS, Walling M, Glenn D, Graesslin O, Egarter C, et al. Methods of accurate localisation of non-palpable subdermal contraceptive implants. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2008; 34:9–12.
Article4. James P, Trenery J. Ultrasound localisation and removal of non-palpable Implanon implants. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006; 46:225–228.
Article5. Schnabel P, Merki-Feld GS, Malvy A, Duijkers I, Mommers E, van den Heuvel MW. Bioequivalence and x-ray visibility of a radiopaque etonogestrel implant versus a non-radiopaque implant: a 3-year, randomized, double-blind study. Clin Drug Investig. 2012; 32:413–422.6. Singh M, Mansour D, Richardson D. Location and removal of non-palpable Implanon® implants with the aid of ultrasound guidance. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2006; 32:153–156.7. Shulman LP, Gabriel H. Management and localization strategies for the nonpalpable Implanon rod. Contraception. 2006; 73:325–330.
Article8. Kim S, Seo K, Song HT, Suh JS, Yoon CS, Ryu JA, et al. Determination of optimal imaging mode for ultrasonographic detection of subdermal contraceptive rods: comparison of spatial compound, conventional, and tissue harmonic imaging methods. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13:602–609.
Article9. Pearson S, Stewart M, Bateson D. Implanon NXT: expert tips for best-practice insertion and removal. Aust Fam Physician. 2017; 46:104–108.10. Choi JH, Kim HY, Lee SS, Cho S. Migration of a contraceptive subdermal device into the lung. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017; 60:314–317.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Migration of a contraceptive subdermal device into the lung
- Removal of migrated subdermal contraceptive implant (Implanon) to axillar: A case report
- Acute Median Neuropathy after Subdermal Contraceptive Implant Removal
- Perceptions and Knowledge of Women Regarding Contraception and Current Trends in Contraceptive Use in Korea
- Removal of non-palpable Implanon(TM) by ultrasound guidance