Ann Dermatol.
2019 Jun;31(3):361-363. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.361.
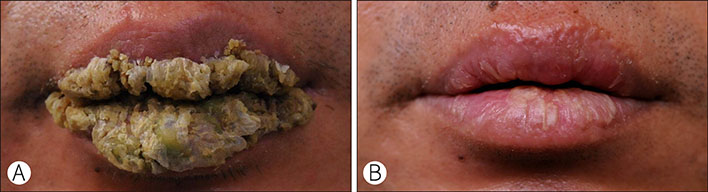
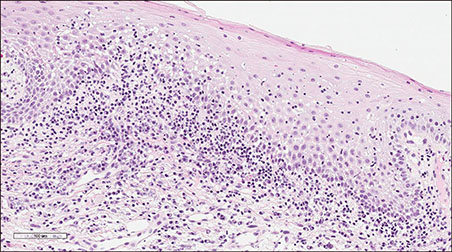
Chronic Exfoliative Cheilitis Successfully Treated by Pinhole Method Using COâ‚‚ Laser
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jh1204.park@samsung.com
- KMID: 2444879
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.361
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Almazrooa SA, Woo SB, Mawardi H, Treister N. Characterization and management of exfoliative cheilitis: a single-center experience. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013; 116:e485–e489.
Article2. Mani SA, Shareef BT. Exfoliative cheilitis: report of a case. J Can Dent Assoc. 2007; 73:629–632.3. Lee SJ, Yeo IK, Kang JM, Chung WS, Kim YK, Kim BJ, et al. Treatment of hypertrophic burn scars by combination laser-cision and pinhole method using a carbon dioxide laser. Lasers Surg Med. 2014; 46:380–384.
Article4. Lee SJ, Goo B, Choi MJ, Oh SH, Chung WS, Cho SB. Treatment of periorbital syringoma by the pinhole method using a carbon dioxide laser in 29 Asian patients. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2015; 17:273–276.
Article5. Chung BY, Han SS, Moon HR, Lee MW, Chang SE. Treatment with the pinhole technique using erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser for a café au lait macule and carbon dioxide laser for facial telangiectasia. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:657–659.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The pinhole method as a novel approach to remove residual hyaluronidase powder: a case report
- A Case of Terra Firma-forme Dermatosis Treated with COâ‚‚ Laser
- Two Cases of Actinic Cheilitis Clinically Mistaken for Candidal Infection
- A Case of Non-functioning Lingual Thyroid Excised with COâ‚‚ Laser Via Transoral Approach
- Cheilitis Glandularis Limited to the Upper Lip