Ann Dermatol.
2019 Jun;31(3):347-348. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.347.
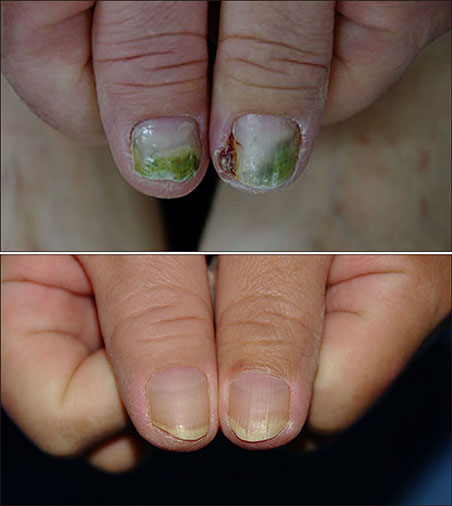
Alitretinoin Treatment for Gefitinib-Induced Paronychia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. lyb80@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2444873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.347
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Agero AL, Dusza SW, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Busam KJ, Myskowski P, Halpern AC. Dermatologic side effects associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006; 55:657–670.
Article2. Alsenaid A, Eder I, Ruzicka T, Braun-Falco M, Wolf R. Successful treatment of nail lichen planus with alitretinoin: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Dermatology. 2014; 229:293–296.
Article3. Iorizzo M. Nail lichen planus-a possible new indication for oral alitretinoin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016; 30:509–510.
Article4. Milanesi N, D'Erme AM, Gola M. Nail improvement during alitretinoin treatment: three case reports and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015; 40:533–536.
Article5. Figueiras Dde A, Ramos TB, Marinho AK, Bezerra MS, Cauas RC. Paronychia and granulation tissue formation during treatment with isotretinoin. An Bras Dermatol. 2016; 91:223–225.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gefitinib-induced Paronychia Teated by Cyosurgery
- Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Induced by Gefitinib (Iressa) in Lung Cancer Patients
- Alitretinoin-induced Pseudotumor Cerebri: A Case Report
- The Effectiveness of Gefitinib on Spinal Metastases of Lung Cancer: Report of Two Cases
- Alitretinoin Compliance in Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema