Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Mar;25(1):38-43. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.1.38.
Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Efficiency of Swietenia macrophylla Seed Extract on Clinical Wound Pathogens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Universiti Kuala Lumpur, Institute of Medical Science Technology, A1-1, Jalan TKS 1, Taman Kajang Sentral, Selangor, 43000 Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia.
- 2Universiti Kuala Lumpur, Malaysian Institute of Chemical and Bioengineering Technology, Lot 1988 Kawasan Perindustrian Bandar Vendor, Taboh Naning, Alor Gajah, Melaka, Malaysia. wytong@unikl.edu.my
- 3School of Distance Education, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 Minden, Penang, Malaysia.
- KMID: 2443102
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.1.38
Abstract
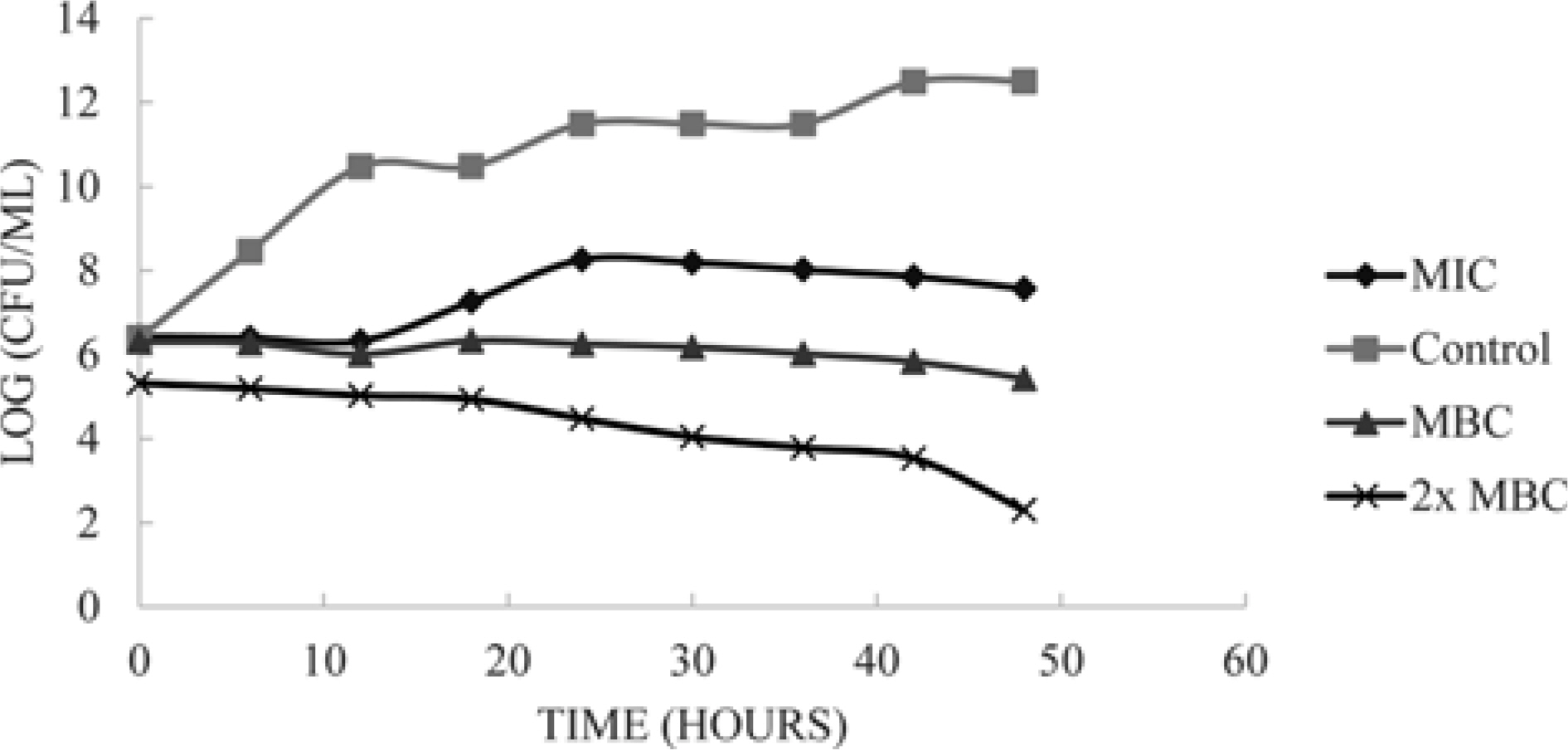
- Microbial wound infection prolonged the hospitalization and increase the cost for wound management. Silver is commonly used as antimicrobial wound dressing. However, it causes several adverse side effects. Hence, this study was aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial efficiency of Swietenia macrophylla seed extract on clinical wound pathogens. Besides, the bioactive constituents of the seed extract were also determined. S. macrophylla seeds were extracted with methanol by maceration method. The seed extract inhibited 5 test bacteria and 1 yeast on disc diffusion assay. The antibacterial activity was broad spectrum, as the extract inhibited both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. On kill curve analysis, the antibacterial activity of the seed extract was concentration-dependent, the increase of extract concentration resulted in more reduction of bacterial growth. The extract also caused 99.9% growth reduction of Bacillus subtilis relative to control. A total of 21 compounds were detected in gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. The predominant compounds present in the extract were oleic acid (18.56%) and linoleic acid (17.72%). In conclusion, the methanolic extract of S. macrophylla seeds exhibited significant antimicrobial activity on clinical wound pathogens. Further investigations should be conducted to purify other bioactive compounds from the seeds of S. macrophylla.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
(1). Bowler P. G., Duerden B. I., Armstrong D. G.Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001; 14:244–269.(2). Abeysinghe P. D., Weeraddana C. S. J.Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2011; 11:1–4.(3). Rai M. K., Deshmukh S. D., Ingle A. P., Gade A. K. J.Appl. Microbiol. 2012; 112:841–852.(4). Panyala N. R., Pena-Mendez E. M., Havel J. J.Appl. Biomed. 2008; 6:117–129.(5). Gillies A. C. M., Navarro C., Lowe A. J., Newton A. C., Hernández M., Wilson J., Cornelius J. P.Heredity. 1999; 83:722–732.(6). Eid A. M. M., Elmarzugi N. A., El-Enshasy H. A.Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013; 5:47–53.(7). Paritala V., Chiruvella K. K., Thammineni C., Ghanta, R. G.;Mohammed A. Braz. J.Pharm. 2015; 25:61–83.(8). Pamplona S., Sá P., Lopes D., Costa E., Yamada E., e Silva C., Arruda M., Souza J., da Silva M.Molecules. 2015; 20:18777–18788.(9). Tong W. Y., Ang S. N., Darah I., Latiffah Z.World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014; 3:121–132.(10). Chen Q., Fung K. Y., Lau Y. T., Ng K. M, Lau D. T. W.Food Bioprod. Process. 2016; 98:236–243.(11). Onivogui G., Letsididi R., Diaby M., Wang L, Song Y.Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016; 6:20–25.(12). Siripatrawan U., Kaewklin P.Food Hydrocolloid. 2018; 84:125–134.(13). Panghal M., Singh K., Kadyan S., Chaudary U., Yadav J. P.Burns. 2015; 41:812–819.(14). Habermann E., Pereira V. D. C., Imatomi M., Pontes F. C., Gualtieri S. C. J. Braz. J.Bot. 2017; 40:33–40.(15). Ertas A., Boga M., Gazioglu I., Yesil Y., Hasimi N., Ozaslan C., Yilmaz H., Kaplan M.Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016; 43:89–99.(16). Pushparaj S. P., Nellore J., Balaraman R. M., Sekar U., Tippabathani J.Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018; 46:268–273.(17). Adesanwo J. K., Ogundele S. B., Akinpelu D. A., McDonald A. G. J.Explor. Res. Pharmacol. 2017; 2:67–77.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Artemisia Capillaris Extract on the Growth of Food-Borne Pathogens
- Effect of Agrimonia Pilosa Ledeb. Extract on the Growth of Food-Borne Pathogens
- Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Helminthostachys zeylanica against Foodborne Bacillus cereus
- Antimicrobial Efficacy of Penicillium amestolkiae elv609 Extract Treated Cotton Fabric for Diabetic Wound Care
- Essential Oil of Marrubium vulgare: Chemical Composition and Biological Activities. A Review