Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2015 Sep;14(3):99-105. 10.12779/dnd.2015.14.3.99.
Wandering in Dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Hyoja Geriatric Hospital, Yongin, Korea. kwakdr@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2442984
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2015.14.3.99
Abstract
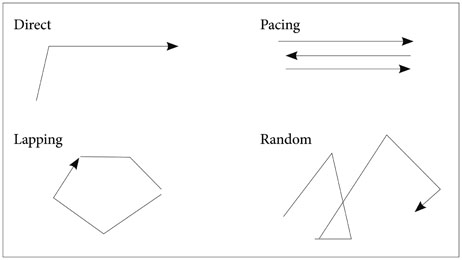
- Wandering is acknowledged as one of the most complex, challenging, and potentially dangerous dementia-related behaviors, and can result in elopement, injury, and even death. For the healthy people, walking is a common and a pleasurable leisure activity. However, wandering in dementia may be an exhausting behavior for caregivers and raise safety concerns. The term 'wandering' covers different types of behavior, including aimless movement without a discernible purpose. Although with respect to the etiology of wandering, biological, psychosocial and person-environment interaction has been suggested, the etiology of wandering is poorly understood. Although it is possible that management of coexistent psychopathology would help to ameliorate this problematic behavior, evidence on the effectiveness of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions is limited.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
Jae Gwon Jeong, Jun Ah Song, Kun Woo Park
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2016;15(1):1-6. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.1.1.A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
Jae Gwon Jeong, Jun Ah Song, Kun Woo Park
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2016;15(1):1-6. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Rolland Y, Gillette-Guyonnet S, Nourhashémi F, Andrieu S, Cantet C, Payoux P, et al. [Wandering and Alzheimer's type disease. Descriptive study. REAL.FR research program on Alzheimer's disease and management]. Rev Med Interne. 2003; 24:Suppl 3. 333s–338s.2. Synder LH, Rupprecht P, Pyrek J, Brekhus S, Moss T. Wandering. Gerontologist. 1978; 18:272–280.
Article3. Dawson P, Reid DW. Behavioral dimensions of patients at risk of wandering. Gerontologist. 1987; 27:104–107.
Article4. Algase DL, Kupferschmid B, Beel-Bates CA, Beattie ER. Estimates of stability of daily wandering behavior among cognitively impaired long-term care residents. Nurs Res. 1997; 46:172–178.
Article5. Carr D, Muschert GW, Kinney J, Robbins E, Petonito G, Manning L, et al. Silver alerts and the problem of missing adults with dementia. Gerontologist. 2010; 50:149–157.
Article6. Martino-Saltzman D, Blasch BB, Morris RD, McNeal LW. Travel behavior of nursing home residents perceived as wanderers and nonwanderers. Gerontologist. 1991; 31:666–672.
Article7. Monsour N, Robb SS. Wandering behavior in old age: a psychosocial study. Soc Work. 1982; 27:411–416.8. Gurwitz JH, Sanchez-Cross MT, Eckler MA, Matulis J. The epidemiology of adverse and unexpected events in the long-term care setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994; 42:33–38.
Article9. Cumming J, Cumming E, Titus J, Schmelzle E, MacDonald J. The episodic nature of behavioural disturbances among residents of facilities for the aged. Can J Public Health. 1982; 73:319–322.10. Hussian RA. Stimulus control in the modification of problematic behavior in elderly institutionalized patients. Int J Behav Geriatr. 1982; 1:33–42.11. Liu L, Gauthier L, Gauthier S. Spatial disorientation in persons with early senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Am J Occup Ther. 1991; 45:67–74.
Article12. Algase DL, Struble L. Wandering: what, why & how?. In : Buckwalter K, editor. Geriatric Mental Health Nursing: Current and Future Challenges. Thorofare, NJ: SLACK Incorporated;1992. p. 61–74.13. Algase DL, Moore DH, Vandeweerd C, Gavin-Dreschnack DJ. Mapping the maze of terms and definitions in dementia-related wandering. Aging Ment Health. 2007; 11:686–698.
Article14. Yang Y, Hwang I, Kwak YT. Neuropsychological characteristics of wandering in patients with drug-naïve Alzheimer's disease. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2014; 13:74–78.
Article15. Klein DA, Steinberg M, Galik E, Steele C, Sheppard JM, Warren A, et al. Wandering behaviour in community-residing persons with dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1999; 14:272–279.
Article16. Hope T, Tilling KM, Gedling K, Keene JM, Cooper SD, Fairburn CG. The structure of wandering in dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1994; 9:149–155.
Article17. Sink KM, Covinsky KE, Newcomer R, Yaffe K. Ethnic differences in the prevalence and pattern of dementia-related behaviors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004; 52:1277–1283.
Article18. Brazil K, Hasler A, McAiney C, Sturdy-Smith C, Tettman M. Perceptions of resident behavior problems and their clinical management in long term care facilities. J Ment Health Aging. 2003; 9:35–42.19. Kiely DK, Morris JN, Algase DL. Resident characteristics associated with wandering in nursing homes. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000; 15:1013–1020.
Article20. Colombo M, Vitali S, Cairati M, Perelli-Cippo R, Bessi O, Gioia P, et al. Wanderers: features, findings, issues. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl. 2001; 7:99–106.
Article21. Algase DL. Wandering in dementia. Annu Rev Nurs Res. 1999; 17:185–217.
Article22. Schonfeld L, King-Kallimanis B, Brown LM, Davis DM, Kearns WD, Molinari VA, et al. Wanderers with cognitive impairment in Department of Veterans Affairs nursing home care units. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007; 55:692–699.
Article23. Utton D. The design of housing for people with dementia. J Care Serv Manag. 2009; 3:380–390.
Article24. Tetewsky SJ, Duffy CJ. Visual loss and getting lost in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1999; 52:958–965.
Article25. McShane R, Gedling K, Keene J, Fairburn C, Jacoby R, Hope T. Getting lost in dementia: a longitudinal study of a behavioral symptom. Int Psychogeriatr. 1998; 10:253–260.
Article26. Rowe MA, Bennett V. A look at deaths occurring in persons with dementia lost in the community. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2003; 18:343–348.
Article27. Kavcic V, Duffy CJ. Attentional dynamics and visual perception: mechanisms of spatial disorientation in Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2003; 126(Pt 5):1173–1181.
Article28. Benton AL. Disorders of spatial orientation. In : Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW, editors. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. New York: Wiley;1969. p. 212–228.29. Chiu YC, Algase D, Whall A, Liang J, Liu HC, Lin KN, et al. Getting lost: directed attention and executive functions in early Alzheimer's disease patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2004; 17:174–180.
Article30. Passini R, Rainville C, Marchand N, Joanette Y. Wayfinding in dementia of the Alzheimer type: planning abilities. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1995; 17:820–832.
Article31. Rolland Y, Payoux P, Lauwers-Cances V, Voisin T, Esquerré JP, Vellas B. A SPECT study of wandering behavior in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2005; 20:816–820.
Article32. Meguro K, Yamaguchi S, Yamazaki H, Itoh M, Yamaguchi T, Matsui H, et al. Cortical glucose metabolism in psychiatric wandering patients with vascular dementia. Psychiatry Res. 1996; 67:71–80.
Article33. Lai CK, Arthur DG. Wandering behaviour in people with dementia. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 44:173–182.
Article34. Phillips VL, Diwan S. The incremental effect of dementia-related problem behaviors on the time to nursing home placement in poor, frail, demented older people. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003; 51:188–193.
Article35. Lee KH, Algase DL, McConnell ES. Relationship between observable emotional expression and wandering behavior of people with dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014; 29:85–92.
Article36. Holtzer R, Tang MX, Devanand DP, Albert SM, Wegesin DJ, Marder K, et al. Psychopathological features in Alzheimer's disease: course and relationship with cognitive status. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003; 51:953–960.
Article37. Lam D, Sewell M, Bell G, Katona C. Who needs psychogeriatric continuing care? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1989; 4:109–114.
Article38. Cooper JK, Mungas D. Risk factor and behavioral differences between vascular and Alzheimer's dementias: the pathway to end-stage disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 1993; 6:29–33.
Article39. Cipriani G, Vedovello M, Ulivi M, Nuti A, Lucetti C. Repetitive and stereotypic phenomena and dementia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2013; 28:223–227.
Article40. Snowden JS, Neary D, Mann DM. Frontotemporal dementia. Br J Psychiatry. 2002; 180:140–143.
Article41. Chiu MJ, Chen TF, Yip PK, Hua MS, Tang LY. Behavioral and psychologic symptoms in different types of dementia. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006; 105:556–562.
Article42. Knuffman J, Mohsin F, Feder J, Grossberg GT. Differentiating between lewy body dementia and Alzheimer's disease: a retrospective brain bank study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2001; 2:146–148.
Article43. Lachs MS, Becker M, Siegal AP, Miller RL, Tinetti ME. Delusions and behavioral disturbances in cognitively impaired elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992; 40:768–773.
Article44. Hope T, Keene J, McShane RH, Fairburn CG, Gedling K, Jacoby R. Wandering in dementia: a longitudinal study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2001; 13:137–147.
Article45. Lyketsos CG, Steele C, Baker L, Galik E, Kopunek S, Steinberg M, et al. Major and minor depression in Alzheimer's disease: prevalence and impact. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997; 9:556–561.
Article46. Ott BR, Lapane KL, Gambassi G. Gender differences in the treatment of behavior problems in Alzheimer's disease. SAGE Study Group. Systemic Assessment of Geriatric drug use via Epidemiology. Neurology. 2000; 54:427–432.
Article47. Algase DL, Beattie ER, Bogue EL, Yao L. The Algase Wandering Scale: initial psychometrics of a new caregiver reporting tool. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2001; 16:141–152.
Article48. Morley JE. Nutrition assessment is a key component of geriatric assessment. In : Vellas B, Guigoz Y, Garry P, editors. Facts, Research and Intervention in Geriatrics. 3rd ed. Paris, France: Serdi Publishing Company;1997. p. 5–10.49. Yang CH, Hwang JP, Tsai SJ, Liu CM. Wandering and associated factors in psychiatric inpatients with dementia of Alzheimer's type in Taiwan: clinical implications for management. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1999; 187:695–697.
Article50. Beattie ER, Song J, LaGore S. A comparison of wandering behavior in nursing homes and assisted living facilities. Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2005; 19:181–196.
Article51. Aud MA. Dangerous wandering: elopements of older adults with dementia from long-term care facilities. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2004; 19:361–368.
Article52. Wick JY, Zanni GR. Aimless excursions: wandering in the elderly. Consult Pharm. 2006; 21:608–612. 615–618.
Article53. Volicer L, van der Steen JT, Frijters DH. Involvement in activities and wandering in nursing home residents with cognitive impairment. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2013; 27:272–277.
Article54. Shinoda-Tagawa T, Leonard R, Pontikas J, McDonough JE, Allen D, Dreyer PI. Resident-to-resident violent incidents in nursing homes. JAMA. 2004; 291:591–598.
Article55. Fopma-Loy J. Wandering: causes, consequences, and care. J Psychosoc Nurs Ment Health Serv. 1988; 26:8–11. 15–18.
Article56. Ballard C, O'Brien J, James I, Swann A. Dementia. Management of Behavioural and Psychological Symptoms. Oxford: Oxford University Press;2001.57. Meguro K, Meguro M, Tanaka Y, Akanuma K, Yamaguchi K, Itoh M. Risperidone is effective for wandering and disturbed sleep/wake patterns in Alzheimer's disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2004; 17:61–67.
Article58. Kwak YT, Yang Y, Kwak SG. Clinical characteristics of behavioral and psychological symptoms in patients with drug-naïve Alzheimer's disease. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2012; 11:87–94.
Article59. Robinson L, Hutchings D, Dickinson HO, Corner L, Beyer F, Finch T, et al. Effectiveness and acceptability of non-pharmacological interventions to reduce wandering in dementia: a systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007; 22:9–22.
Article60. Futrell M, Melillo KD, Remington R, Schoenfelder DP. Evidence-based guideline. Wandering. J Gerontol Nurs. 2010; 36:6–16.61. Allen-Burge R, Stevens AB, Burgio LD. Effective behavioral interventions for decreasing dementia-related challenging behavior in nursing homes. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1999; 14:213–228. discussion 228-232
Article62. Coltharp W Jr, Richie MF, Kaas MJ. Wandering. J Gerontol Nurs. 1996; 22:5–10.
Article63. Miskelly F. A novel system of electronic tagging in patients with dementia and wandering. Age Ageing. 2004; 33:304–306.
Article64. McShane R, Hope T, Wilkinson J. Tracking patients who wander: ethics and technology. Lancet. 1994; 343:1274.
Article65. Hughes JC, Louw SJ. Electronic tagging of people with dementia who wander. BMJ. 2002; 325:847–848.
Article66. Holmberg SK. Evaluation of a clinical intervention for wanderers on a geriatric nursing unit. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 1997; 11:21–28.
Article67. Heard K, Watson TS. Reducing wandering by persons with dementia using differential reinforcement. J Appl Behav Anal. 1999; 32:381–384.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
- Effects of Aromatherapy and Foot Reflex Massage on Emotion, Sleep Disturbance, and Wandering Behavior in Older Adults with Dementia
- Neuropsychological Characteristics of Wandering in Patients with Drug-naive Alzheimer's Disease
- Wandering Behavior in Korean Elders with Dementia Residing in Nursing Homes
- Non-pharmacological Intervention for Wandering Behavior in Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis