Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2016 Mar;15(1):1-6. 10.12779/dnd.2016.15.1.1.
A Relationship between Depression and Wandering in Community-Dwelling Elders with Dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kunu@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2442864
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2016.15.1.1
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Wandering is one of the most common behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia, and associated with some of the adverse outcomes in dementia, such as getting lost or even death. The etiology of wandering is not yet clearly known. As depression and wandering are both very common among the patients with dementia, this study examined the relationship between the depression and wandering among the community dwelling patients with dementia.
METHODS
Fifty community dwelling patients diagnosed with dementia were included in this study if they had primary family caregiver, older than age 18 in Seoul, South Korea. The Geriatric Depression Scale, Korean Version (GDS-K), Korean Version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) and Korean Version of Revised Algase Wandering Scale-Community Version (K-RAWS-CV) were used to measure the severity of depression, cognitive function and wandering.
RESULTS
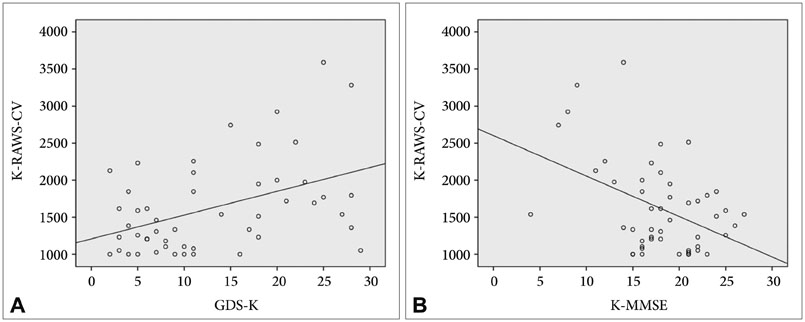
Thirty percents of the patients showed wandering. Mean score of GDS-K was significantly higher in wanderers than non-wanderers. Severity of depression was significantly correlated with the total score of K-RAWS-CV and subscales of persistent walking, repetitive walking, eloping behavior, and mealtime impulsivity in whole sample. K-MMSE score also was related to wandering behavior. The prevalence odds ratio for wandering in depressed patients compared with undepressed group was 8.386 (95% confidence interval: 1.978-35.561).
CONCLUSIONS
This study implicates that not only cognitive impairment but also psychosocial aspects should be considered in wandering patients with dementia and suggests assessing the depression in patients would be helpful in identifying the causes of wandering.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rolland Y, Gillette-Guyonnet S, Nourhashémi F, Andrieu S, Cantet C, Payoux P, et al. [Wandering and Alzheimer’s type disease. Descriptive study. REAL.FR research program on Alzheimer’s disease and management]. Rev Med Interne. 2003; 24:Suppl 3. 333s–338s.
Article2. Gurwitz JH, Sanchez-Cross MT, Eckler MA, Matulis J. The epidemiology of adverse and unexpected events in the long-term care setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1994; 42:33–38.3. Morley JE. Nutrition assessment is a key component of geriatric assessment. In : Vellas B, Guigoz Y, Garry P, Albarede J, editors. Facts and Research in Gerontology. 3rd ed. Paris: Serdi Publishing Company;1997. p. 5–10.4. Yang CH, Hwang JP, Tsai SJ, Liu CM. Wandering and associated factors in psychiatric inpatients with dementia of Alzheimer’s type in Taiwan: clinical implications for management. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1999; 187:695–697.
Article5. Beattie ER, Song J, LaGore S. A comparison of wandering behavior in nursing homes and assisted living facilities. Res Theory Nurs Pract. 2005; 19:181–196.
Article6. Phillips VL, Diwan S. The incremental effect of dementia-related problem behaviors on the time to nursing home placement in poor, frail, demented older people. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003; 51:188–193.7. Aud MA. Dangerous wandering: elopements of older adults with dementia from long-term care facilities. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2004; 19:361–368.8. Dawson P, Reid DW. Behavioral dimensions of patients at risk of wandering. Gerontologist. 1987; 27:104–107.
Article9. Algase DL, Moore DH, Vandeweerd C, Gavin-Dreschnack DJ. Mapping the maze of terms and definitions in dementia-related wandering. Aging Ment Health. 2007; 11:686–698.
Article10. Klein DA, Steinberg M, Galik E, Steele C, Sheppard JM, Warren A, et al. Wandering behaviour in community-residing persons with dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1999; 14:272–279.11. Yang Y, Hwang I, Kwak YT. Neuropsychological characteristics of wandering in patients with drug-naive Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2014; 13:74–78.12. Schonfeld L, King-Kallimanis B, Brown LM, Davis DM, Kearns WD, Molinari VA, et al. Wanderers with cognitive impairment in Department of Veterans Affairs nursing home care units. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007; 55:692–699.
Article13. Algase DL. Wandering: clues to effective management. Geriatr Aging. 2005; 8:55–59.
Article14. Song JA, Lim YM, Hong GR. Wandering behavior in Korean elders with dementia residing in nursing homes. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2008; 38:29–38.
Article15. Jost BC, Grossberg GT. The evolution of psychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: a natural history study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996; 44:1078–1081.
Article16. Hope T, Keene J, McShane RH, Fairburn CG, Gedling K, Jacoby R. Wandering in dementia: a longitudinal study. Int Psychogeriatr. 2001; 13:137–147.
Article17. Sink KM, Covinsky KE, Newcomer R, Yaffe K. Ethnic differences in the prevalence and pattern of dementia-related behaviors. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004; 52:1277–1283.
Article18. Kwak YT, Yang Y, Koo MS. Wandering in dementia. Dement Neurocognitive Disord. 2015; 14:99–105.
Article19. Lai CK, Arthur DG. Wandering behaviour in people with dementia. J Adv Nurs. 2003; 44:173–182.
Article20. McShane R, Gedling K, Keene J, Fairburn C, Jacoby R, Hope T. Getting lost in dementia: a longitudinal study of a behavioral symptom. Int Psychogeriatr. 1998; 10:253–260.21. Kavcic V, Duffy CJ. Attentional dynamics and visual perception: mechanisms of spatial disorientation in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2003; 126(Pt 5):1173–1181.22. Tetewsky SJ, Duffy CJ. Visual loss and getting lost in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1999; 52:958–965.
Article23. Benton AL. Disorders of spatial Orientation. In : Wincken PJ, Bruyn GW, editors. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Amsterdam: North Holland;1969.
Article24. Passini R, Rainville C, Marchand N, Joanette Y. Wayfinding in dementia of the Alzheimer type: planning abilities. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1995; 17:820–832.25. Lim YM, Hong GR, Song JA. Correlation of way-finding and wandering in Korean elders with dementia at home. J Korean Gerontol Soc. 2008; 28:69–86.26. Algase DL, Beck C, Kolanowski A, Whall A, Berent S, Richards K, et al. Need-driven dementia-compromised behavior: An alternative view of disruptive behavior. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 1996; 11:10–19.
Article27. Nelson AL, Algase DL. Evidence-based protocols for managing wandering behaviors. New York: Springer Publishing;2007.
Article28. Kiely DK, Morris JN, Algase DL. Resident characteristics associated with wandering in nursing homes. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000; 15:1013–1020.
Article29. Bartol MA. Dialogue with dementia: nonverbal communication in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol Nurs. 1979; 5:21–31.
Article30. Mayhew M. The growing challenge of Alzheimer disease part 2. J Nurse Pract. 2005; 1:149–156.31. Lyketsos CG, Steele C, Baker L, Galik E, Kopunek S, Steinberg M, et al. Major and minor depression in Alzheimer’s disease: prevalence and impact. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1997; 9:556–561.32. Teri L, Ferretti LE, Gibbons LE, Logsdon RG, McCurry SM, Kukull WA, et al. Anxiety of Alzheimer’s disease: prevalence, and comorbidity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999; 54:M348–M352.33. Eldridge LL, Masterman D, Knowlton BJ. Intact implicit habit learning in Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Neurosci. 2002; 116:722–726.34. Parks RW, Haxby JV, Grady CL. Positron emission tomography in Alzheimer's disease. In : Parks RW, Zec RF, Wilson RS, editors. Neuropsychology of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. New York: Oxford University Press;1993. p. 459–488.
Article35. Mielke R, Heiss WD. Positron emission tomography for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1998; 53:237–250.
Article36. Yao L, Algase D. Environmental ambiance as a new window on wandering. West J Nurs Res. 2006; 28:89–104.
Article37. Morris R. The cognitive neuropsychology of Alzheimer-type dementia. Oxford: Oxford University Press;1996.
Article38. Yao L, Algase D. Emotional intervention strategies for dementia-related behavior: a theory synthesis. J Neurosci Nurs. 2008; 40:106–115.39. Son GR, Song J, Lim Y. Translation and validation of the Revised-Algase Wandering Scale (community version) among Korean elders with dementia. Aging Ment Health. 2006; 10:143–150.40. Algase DL, Son GR, Beattie E, Song JA, Leitsch S, Yao L. The interrelatedness of wandering and wayfinding in a community sample of persons with dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2004; 17:231–239.
Article41. Cho MJ, Bae JN, Suh GH, Hahm BJ, Kim JK, Lee DW, et al. Validation of Geriatric Depression Scale, Korean version (GDS) in the assessment of DSM-III-R major depression. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1999; 38:48–63.
Article42. Rowe MA, Glover JC. Antecedents, descriptions and consequences of wandering in cognitively-impaired adults and the Safe Return (SR) program. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Deme. 2001; 16:344–352.
Article43. Holtzer R, Tang MX, Devanand DP, Albert SM, Wegesin DJ, Marder K, et al. Psychopathological features in Alzheimer’s disease: course and relationship with cognitive status. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003; 51:953–960.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Influencing Ego-Integrity in Community Dwelling Elders
- Attitudes Toward General Elders and Elders with Dementia Among Baccalaureate Junior Nursing Students
- Wandering Behavior in Korean Elders with Dementia Residing in Nursing Homes
- Wandering in Dementia
- Effects of a Dementia Family Education Program for Dementia Recognition, Burden, and Depression in Caregivers of Elders with Dementia