Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2015 Dec;14(4):143-148. 10.12779/dnd.2015.14.4.143.
Reduced Gray Matter Volume in Subjective Cognitive Decline: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. seonghye@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2442931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2015.14.4.143
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Subjective cognitive decline has been proposed as a potential indicator of the preclinical state of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The results of the studies of cortical atrophy on brain MRIs in subjects with subjective cognitive decline are inconsistent across the literatures. We investigated whether subjects with subjective cognitive decline had less gray matter volume compared to controls without subjective cognitive decline as per brain MRI.
METHODS
Thirty-six subjects with subjective cognitive decline and thirty-three controls without subjective cognitive decline were recruited retrospectively from among the patients who had visited the department of neurology at Inha University Hospital between January 2008 and December 2010. All subjects had undergone a brain MRI scan including 3D T1-weighted spoiled gradient recalled echo imaging. We used voxel-based morphometry (VBM) to examine gray matter volumes between the two groups, after controlling for age, sex, education, and total intracranial volumes (TIV).
RESULTS
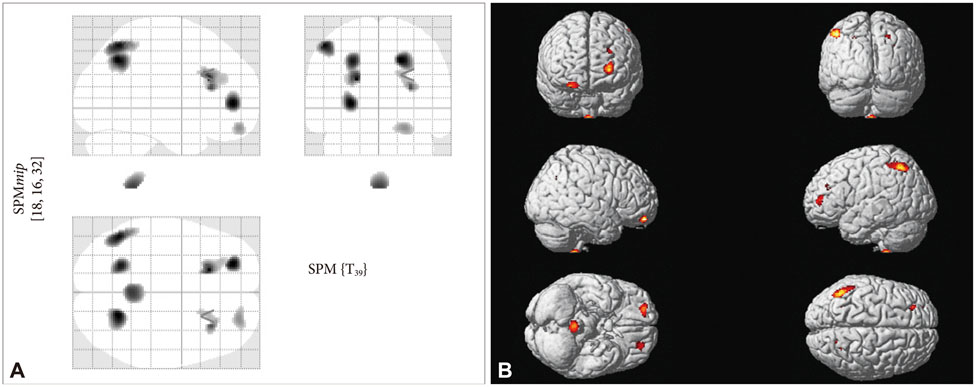
There were no significant differences in age, gender, education, and TIV between the two groups. In comparison to controls without subjective cognitive decline, subjects with subjective cognitive decline showed gray matter atrophy in the left superior and medial frontal gyri, left superior and inferior parietal lobules, and right precuneus and insular in the VBM analysis.
CONCLUSIONS
Individuals with subjective cognitive decline encountered in clinical settings have greater similarity to an AD gray matter atrophy pattern compared with cognitively normal individuals without subjective cognitive decline.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lista S, Molinuevo JL, Cavedo E, Rami L, Amouyel P, Teipel SJ, et al. Evolving Evidence for the Value of Neuroimaging Methods and Biological Markers in Subjects Categorized with Subjective Cognitive Decline. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015; 48:Suppl 1. S171–S191.
Article2. Mitchell AJ. The clinical significance of subjective memory complaints in the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and dementia: a meta-analysis. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2008; 23:1191–1202.
Article3. Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7:280–292.
Article4. Jessen F, Amariglio RE, van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chételat G, et al. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014; 10:844–852.
Article5. Mitchell AJ, Beaumont H, Ferguson D, Yadegarfar M, Stubbs B. Risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in older people with subjective memory complaints: meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2014; 130:439–451.
Article6. Kim JM, Stewart R, Shin IS, Choi SK, Yoon JS. Subjective memory impairment, cognitive function and depression--a community study in older Koreans. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2003; 15:218–225.
Article7. van Harten AC, Visser PJ, Pijnenburg YA, Teunissen CE, Blankenstein MA, Scheltens P, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 is the best predictor of clinical progression in patients with subjective complaints. Alzheimers Dement. 2013; 9:481–487.
Article8. Jessen F, Feyen L, Freymann K, Tepest R, Maier W, Heun R, et al. Volume reduction of the entorhinal cortex in subjective memory impairment. Neurobiol Aging. 2006; 27:1751–1756.
Article9. Hong YJ, Yoon B, Shim YS, Ahn KJ, Yang DW, Lee JH. Gray and White Matter Degenerations in Subjective Memory Impairment: Comparisons with Normal Controls and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:1652–1658.
Article10. Hong JY, Yun HJ, Sunwoo MK, Ham JH, Lee JM, Sohn YH, et al. Cognitive and cortical thinning patterns of subjective cognitive decline in patients with and without Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20:999–1003.
Article11. Mosconi L, De Santi S, Brys M, Tsui WH, Pirraglia E, Glodzik-Sobanska L, et al. Hypometabolism and altered cerebrospinal fluid markers in normal apolipoprotein E E4 carriers with subjective memory complaints. Biol Psychiatry. 2008; 63:609–618.
Article12. Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, et al. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1071–1076.
Article13. Christensen KJ, Multhaup KS, Nordstrom S, Voss K. A cognitive battery for dementia: development and measurement characteristics. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1991; 3:168–174.
Article14. Bae JN, Cho MJ. Development of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale and its short form among elderly psychiatric patients. J Psychosom Res. 2004; 57:297–305.
Article15. Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 149:351–356.
Article16. Peter J, Scheef L, Abdulkadir A, Boecker H, Heneka M, Wagner M, et al. Gray matter atrophy pattern in elderly with subjective memory impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2014; 10:99–108.
Article17. Sperling RA, Laviolette PS, O'Keefe K, O'Brien J, Rentz DM, Pihlajamaki M, et al. Amyloid deposition is associated with impaired default network function in older persons without dementia. Neuron. 2009; 63:178–188.
Article18. Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Jack CR Jr, Scheltens P, Thompson PM. The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010; 6:67–77.
Article19. Chhatwal JP, Schultz AP, Johnson K, Benzinger TL, Jack C Jr, Ances BM, et al. Impaired default network functional connectivity in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2013; 81:736–744.
Article20. Mutschler I, Wieckhorst B, Kowalevski S, Derix J, Wentlandt J, Schulze-Bonhage A, et al. Functional organization of the human anterior insular cortex. Neurosci Lett. 2009; 457:66–70.
Article21. Nagai M, Kishi K, Kato S. Insular cortex and neuropsychiatric disorders: a review of recent literature. Eur Psychiatry. 2007; 22:387–394.
Article22. Royall DR. Insular Alzheimer disease pathology and the psychometric correlates of mortality. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008; 75:Suppl 2. S97–S99.
Article23. Moon Y, Moon WJ, Han SH. Pathomechanisms of atrophy in insular cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2015; 30:497–502.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gray and White Matter Degenerations in Subjective Memory Impairment: Comparisons with Normal Controls and Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Development of a Korean Standard Structural Brain Template in Cognitive Normals and Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease
- A Voxel Based Morphometric Analysis of Longitudinal Cortical Gray Matter Changes in Progranulin Mutation Carriers At-Risk for Frontotemporal Dementia: Preliminary Study
- A Voxel-Based Morphometry of Gray Matter Reduction in Patients with Dementia of the Alzheimer's Type
- Optimized VBM in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease: Gray Matter Loss and Its Correlation with Cognitive Function