J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Nov;30(11):1652-1658. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.11.1652.
Gray and White Matter Degenerations in Subjective Memory Impairment: Comparisons with Normal Controls and Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. neuroman@catholic.ac.kr
- 4Department of Radiology, Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2351117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.11.1652
Abstract
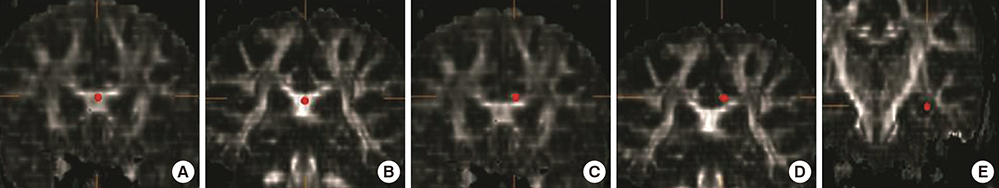
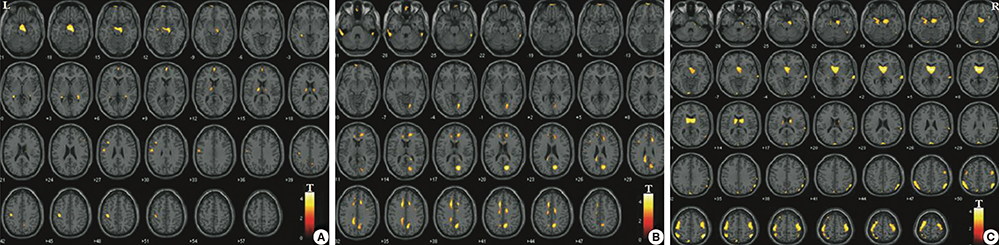
- Subjective memory impairment (SMI) is now increasingly recognized as a risk factor of progression to dementia. This study investigated gray and white matter changes in the brains of SMI patients compared with normal controls and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients. We recruited 28 normal controls, 28 subjects with SMI, and 29 patients with MCI aged 60 or older. We analyzed gray and white matter changes using a voxel-based morphometry (VBM), hippocampal volumetry and regions of interest in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). DTI parameters of corpus callosum and cingulum in SMI showed more white matter changes compared with those in normal controls, they were similar to those in MCI except in the hippocampus, which showed more degenerations in MCI. In VBM, SMI showed atrophy in the frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes compared with normal controls although it was not as extensive as that in MCI. Patients with SMI showed gray and white matter degenerations, the changes were distinct in white matter structures. SMI might be the first presenting symptom within the Alzheimer's disease continuum when combined with additional risk factors and neurodegenerative changes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Brain/*pathology
Diagnosis, Differential
Diffusion Tensor Imaging/methods
Female
Gray Matter/*pathology
Humans
Male
Memory Disorders/*diagnosis/etiology
Mild Cognitive Impairment/complications/*diagnosis
Neurodegenerative Diseases/complications/*pathology
Reference Values
Reproducibility of Results
Sensitivity and Specificity
White Matter/*pathology
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Reduced Gray Matter Volume in Subjective Cognitive Decline: A Voxel-Based Morphometric Study
Yoonjae Choi, Byung-Nam Yoon, Seong Hye Choi, Myung Kwan Lim, Hee-Jin Kim, Dong-Won Yang
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2015;14(4):143-148. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2015.14.4.143.Subjective Cognitive Decline and Alzheimer's Disease Spectrum Disorder
Yun Jeong Hong, Jae-Hong Lee
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2017;16(2):40-47. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2017.16.2.40.Regional Gray Matter Volume Related to High Occupational Stress in Firefighters
Deokjong Lee, Woojin Kim, Jung Eun Lee, Junghan Lee, Seung-Koo Lee, Sei-Jin Chang, Da Yee Jeung, Dae-Sung Hyun, Hye-Yoon Ryu, Changsoo Kim, Young-Chul Jung
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(50):e335. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e335.
Reference
-
1. van Oijen M, de Jong FJ, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM. Subjective memory complaints, education, and risk of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2007; 3:92–97.2. Scheef L, Spottke A, Daerr M, Joe A, Striepens N, Kölsch H, Popp J, Daamen M, Gorris D, Heneka MT, et al. Glucose metabolism, gray matter structure, and memory decline in subjective memory impairment. Neurology. 2012; 79:1332–1339.3. Mosconi L, De Santi S, Brys M, Tsui WH, Pirraglia E, Glodzik-Sobanska L, Rich KE, Switalski R, Mehta PD, Pratico D, et al. Hypometabolism and altered cerebrospinal fluid markers in normal apolipoprotein E E4 carriers with subjective memory complaints. Biol Psychiatry. 2008; 63:609–618.4. Selnes P, Fjell AM, Gjerstad L, Bjørnerud A, Wallin A, Due-Tønnessen P, Grambaite R, Stenset V, Fladby T. White matter imaging changes in subjective and mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2012; 8:S112–S121.5. Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H. Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001; 13:534–546.6. Hong YJ, Yoon B, Lim SC, Shim YS, Kim JY, Ahn KJ, Han IW, Yang DW. Microstructural changes in the hippocampus and posterior cingulate in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neurol Sci. 2013; 34:1215–1221.7. Cho H, Yang DW, Shon YM, Kim BS, Kim YI, Choi YB, Lee KS, Shim YS, Yoon B, Kim W, et al. Abnormal integrity of corticocortical tracts in mild cognitive impairment: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:477–483.8. Wang Y, West JD, Flashman LA, Wishart HA, Santulli RB, Rabin LA, Pare N, Arfanakis K, Saykin AJ. Selective changes in white matter integrity in MCI and older adults with cognitive complaints. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1822:423–430.9. Peter J, Scheef L, Abdulkadir A, Boecker H, Heneka M, Wagner M, Koppara A, Klöppel S, Jessen F. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Gray matter atrophy pattern in elderly with subjective memory impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2014; 10:99–108.10. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, Leirer VO. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res. 1982; 17:37–49.11. Kang Y, Na DL. Seoul neuropsychological screening battery. Incheon: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co;2003.12. Han C, Jo SA, Jo I, Kim E, Park MH, Kang Y. An adaptation of the Korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in elderly Koreans: demographic influence and population-based norms (the AGE study). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008; 47:302–310.13. Christensen KJ, Moye J, Armson RR, Kern TM. Health screening and random recruitment for cognitive aging research. Psychol Aging. 1992; 7:204–208.14. Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Kokmen E, Tangelos EG. Aging, memory, and mild cognitive impairment. Int Psychogeriatr. 1997; 9:65–69.15. Bernasconi N, Bernasconi A, Caramanos Z, Antel SB, Andermann F, Arnold DL. Mesial temporal damage in temporal lobe epilepsy: a volumetric MRI study of the hippocampus, amygdala and parahippocampal region. Brain. 2003; 126:462–469.16. Atmaca M, Ozdemir H, Cetinkaya S, Parmaksiz S, Belli H, Poyraz AK, Tezcan E, Ogur E. Cingulate gyrus volumetry in drug free bipolar patients and patients treated with valproate or valproate and quetiapine. J Psychiatr Res. 2007; 41:821–827.17. Pruessner JC, Li LM, Serles W, Pruessner M, Collins DL, Kabani N, Lupien S, Evans AC. Volumetry of hippocampus and amygdala with high-resolution MRI and three-dimensional analysis software: minimizing the discrepancies between laboratories. Cereb Cortex. 2000; 10:433–442.18. Braak E, Griffing K, Arai K, Bohl J, Bratzke H, Braak H. Neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease: what is new since A. Alzheimer? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999; 249:14–22.19. Papez JW. A proposed mechanism of emotion. 1937. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1995; 7:103–112.20. Yoon B, Shim YS, Hong YJ, Koo BB, Kim YD, Lee KO, Yang DW. Comparison of diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry to detect white matter damage in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2011; 302:89–95.21. Zhuang L, Sachdev PS, Trollor JN, Kochan NA, Reppermund S, Brodaty H, Wen W. Microstructural white matter changes in cognitively normal individuals at risk of amnestic MCI. Neurology. 2012; 79:748–754.22. Stenset V, Bjørnerud A, Fjell AM, Walhovd KB, Hofoss D, Due-Tønnessen P, Gjerstad L, Fladby T. Cingulum fiber diffusivity and CSF T-tau in patients with subjective and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging. 2011; 32:581–589.23. Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Jack CR Jr, Scheltens P, Thompson PM. The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010; 6:67–77.24. Jessen F, Amariglio RE, van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chételat G, Dubois B, Dufouil C, Ellis KA, van der Flier WM, et al. Subjective Cognitive Decline Initiative (SCD-I) Working Group. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014; 10:844–852.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subtypes and Treatment of Mild Cognitive Impairment
- The Neurocognitive Function Between the Patients Who had Subjective Memory Impairment and Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Development of a Korean Standard Structural Brain Template in Cognitive Normals and Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer's Disease
- Prospective Memory Loss and Related White Matter Changes in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Risk Factors for Subjective Memory Impairment in Cognitively Normal Elderly