Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2018 Sep;17(3):100-109. 10.12779/dnd.2018.17.3.100.
Usefulness of the Clock Drawing Test as a Cognitive Screening Instrument for Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia: an Evaluation Using Three Scoring Systems
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Psychology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea. ykang@hallym.ac.kr
- 4Department of Psychology, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2442799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2018.17.3.100
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Although the clock drawing test (CDT) is a widely used cognitive screening instrument, there have been inconsistent findings regarding its utility with various scoring systems in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia. The present study aimed to identify whether patients with MCI or dementia exhibited impairment on the CDT using three different scoring systems, and to determine which scoring system is more useful for detecting MCI and mild dementia.
METHODS
Patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), vascular mild cognitive impairment (VaMCI), mild Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild vascular dementia (VaD), and cognitively normal older adults (CN) were included. All participants were administered the CDT, the Korean-Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), and the Clinical Dementia Rating scale. The CDT was scored using the 3-, 5-, and 15-point scoring systems.
RESULTS
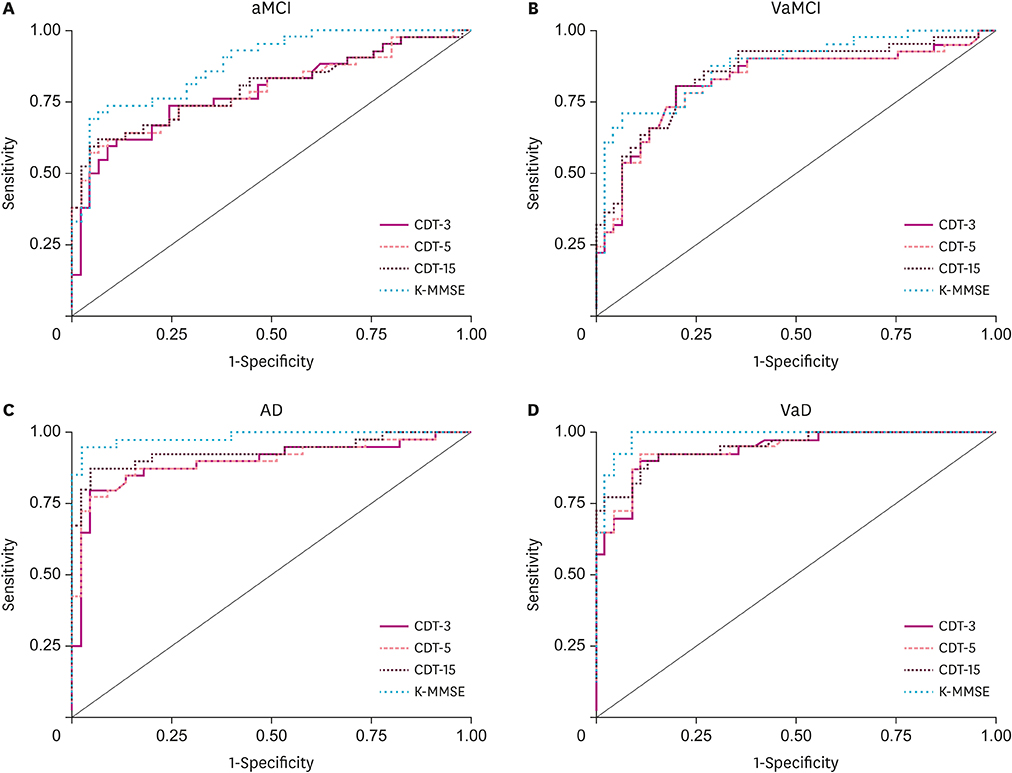
On all three scoring systems, all patient groups demonstrated significantly lower scores than the CN. However, while there were no significant differences among patients with aMCI, VaMCI, and AD, those with VaD exhibited the lowest scores. Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curves revealed that the three CDT scoring systems were comparable with the K-MMSE in differentiating aMCI, VaMCI, and VaD from CN. In differentiating AD from CN, however, the CDT using the 15-point scoring system demonstrated the most comparable discriminability with K-MMSE.
CONCLUSIONS
The results demonstrated that the CDT is a useful cognitive screening tool that is comparable with the Mini-Mental State Examination, and that simple CDT scoring systems are sufficient for differentiating patients with MCI and mild dementia from CN.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ismail Z, Rajji TK, Shulman KI. Brief cognitive screening instruments: an update. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2010; 25:111–120.
Article2. Shulman KI. Clock-drawing: is it the ideal cognitive screening test? Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2000; 15:548–561.
Article3. Mainland BJ, Amodeo S, Shulman KI. Multiple clock drawing scoring systems: simpler is better. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014; 29:127–136.
Article4. Pinto E, Peters R. Literature review of the clock drawing test as a tool for cognitive screening. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2009; 27:201–213.
Article5. Tuokko H, Hadjistavropoulos T, Rae S, O'Rourke N. A comparison of alternative approaches to the scoring of clock drawing. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2000; 15:137–148.
Article6. Manos PJ, Wu R. The ten point clock test: a quick screen and grading method for cognitive impairment in medical and surgical patients. Int J Psychiatry Med. 1994; 24:229–244.
Article7. Lam LC, Chiu HF, Ng KO, Chan C, Chan WF, Li SW, et al. Clock-face drawing, reading and setting tests in the screening of dementia in Chinese elderly adults. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 1998; 53:353–357.
Article8. Cacho J, García-García R, Arcaya J, Vicente JL, Lantada N. A proposal for application and scoring of the clock drawing test in Alzheimer's disease. Rev Neurol. 1999; 28:648–655.9. Tariq SH, Tumosa N, Chibnall JT, Perry MH 3rd, Morley JE. Comparison of the Saint Louis University mental status examination and the mini-mental state examination for detecting dementia and mild neurocognitive disorder--a pilot study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2006; 14:900–910.
Article10. Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bédirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005; 53:695–699.
Article11. Darvesh S, Leach L, Black SE, Kaplan E, Freedman M. The behavioural neurology assessment. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005; 32:167–177.
Article12. Mendez MF, Ala T, Underwood KL. Development of scoring criteria for the clock drawing task in Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992; 40:1095–1099.
Article13. Esteban-Santillan C, Praditsuwan R, Ueda H, Geldmacher DS. Clock drawing test in very mild Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998; 46:1266–1269.
Article14. Lee H, Swanwick GR, Coen RF, Lawlor BA. Use of the clock drawing task in the diagnosis of mild and very mild Alzheimer's disease. Int Psychogeriatr. 1996; 8:469–476.
Article15. Seigerschmidt E, Mösch E, Siemen M, Förstl H, Bickel H. The clock drawing test and questionable dementia: reliability and validity. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002; 17:1048–1054.
Article16. Ricci M, Pigliautile M, D'Ambrosio V, Ercolani S, Bianchini C, Ruggiero C, et al. The clock drawing test as a screening tool in mild cognitive impairment and very mild dementia: a new brief method of scoring and normative data in the elderly. Neurol Sci. 2016; 37:867–873.
Article17. Chen L, Xu S, Jin X, Lu X, Liu L, Lou Y, et al. A comparison of six clock-drawing test scoring methods in a nursing home. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2018; 30:775–781.
Article18. Lee KS, Kim EA, Hong CH, Lee DW, Oh BH, Cheong HK. Clock drawing test in mild cognitive impairment: quantitative analysis of four scoring methods and qualitative analysis. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2008; 26:483–489.
Article19. Ehreke L, Luppa M, König HH, Riedel-Heller SG. Is the clock drawing test a screening tool for the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment? A systematic review. Int Psychogeriatr. 2010; 22:56–63.
Article20. Ehreke L, Luck T, Luppa M, König HH, Villringer A, Riedel-Heller SG. Clock drawing test - screening utility for mild cognitive impairment according to different scoring systems: results of the Leipzig Longitudinal Study of the Aged (LEILA 75+). Int Psychogeriatr. 2011; 23:1592–1601.
Article21. Tan LP, Herrmann N, Mainland BJ, Shulman K. Can clock drawing differentiate Alzheimer's disease from other dementias? Int Psychogeriatr. 2015; 27:1649–1660.
Article22. Moretti R, Torre P, Antonello RM, Cazzato G, Bava A. Ten-point clock test: a correlation analysis with other neuropsychological tests in dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002; 17:347–353.
Article23. Heinik J, Solomesh I, Raikher B, Lin R. Can clock drawing test help to differentiate between dementia of the Alzheimer's type and vascular dementia? A preliminary study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002; 17:699–703.
Article24. Sallam K, Amr M. The use of the mini-mental state examination and the clock-drawing test for dementia in a tertiary hospital. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:484–488.
Article25. de Jager CA. Changes over time in memory, processing speed and clock drawing tests help to discriminate between vascular cognitive impairment, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurol Res. 2004; 26:481–487.
Article26. Allone C, Lo Buono V, Corallo F, Bonanno L, Palmeri R, Di Lorenzo G, et al. Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's dementia, and vascular dementia: the role of the clock-drawing test. Psychogeriatrics. 2018; 18:123–131.
Article27. Petersen RC. Clinical practice. Mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:2227–2234.28. McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011; 7:263–269.
Article29. Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, Decarli C, Greenberg SM, Iadecola C, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011; 42:2672–2713.
Article30. Christensen KJ, Multhaup KS, Nordstrom S, Voss K. A cognitive battery for dementia: Development and measurement characteristics. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2004; 19:759–767.
Article31. Kang Y. A normative study of the Korean-Mini Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in the elderly. Korean J Psychol. 2006; 25:1–12.32. Goodglass H, Kaplan E. The Assessment of Aphasia and Related Disorders. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger;1983.33. Freedman M, Leach L, Kaplan E, Winocur G, Shulman KI, Delis D. Clock Drawing: a Neuropsychological Analysis. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Inc.;1994.34. Blake H, McKinney M, Treece K, Lee E, Lincoln NB. An evaluation of screening measures for cognitive impairment after stroke. Age Ageing. 2002; 31:451–456.
Article35. Nys GM, van Zandvoort MJ, de Kort PL, Jansen BP, Kappelle LJ, de Haan EH. Restrictions of the Mini-Mental State Examination in acute stroke. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2005; 20:623–629.
Article36. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993; 43:2412–2414.37. Beinhoff U, Hilbert V, Bittner D, Gron G, Riepe MW. Screening for cognitive impairment: a triage for outpatient care. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2005; 20:278–285.
Article38. Sager MA, Hermann BP, La Rue A, Woodard JL. Screening for dementia in community-based memory clinics. WMJ. 2006; 105:25–29.39. Ehreke L, Luppa M, Luck T, Wiese B, Weyerer S, Eifflaender-Gorfer S, et al. Is the clock drawing test appropriate for screening for mild cognitive impairment?--Results of the German study on Ageing, Cognition and Dementia in Primary Care Patients (AgeCoDe). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2009; 28:365–372.
Article40. Royall DR, Cordes JA, Polk M. CLOX: an executive clock drawing task. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 64:588–594.
Article41. Baudic S, Barba GD, Thibaudet MC, Smagghe A, Remy P, Traykov L. Executive function deficits in early Alzheimer's disease and their relations with episodic memory. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2006; 21:15–21.
Article42. Graham NL, Emery T, Hodges JR. Distinctive cognitive profiles in Alzheimer's disease and subcortical vascular dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:61–71.43. Lee AY, Kim JS, Choi BH, Sohn EH. Characteristics of clock drawing test (CDT) errors by the dementia type: quantitative and qualitative analysis. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009; 48:58–60.
Article44. Salimi S, Irish M, Foxe D, Hodges JR, Piguet O, Burrell JR. Can visuospatial measures improve the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease? Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2017; 10:66–74.
Article45. Iachini I, Iavarone A, Senese VP, Ruotolo F, Ruggiero G. Visuospatial memory in healthy elderly, AD and MCI: a review. Curr Aging Sci. 2009; 2:43–59.
Article46. Tiraboschi P, Salmon DP, Hansen LA, Hofstetter RC, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J. What best differentiates Lewy body from Alzheimer's disease in early-stage dementia? Brain. 2006; 129:729–735.
Article47. Kato Y, Narumoto J, Matsuoka T, Okamura A, Koumi H, Kishikawa Y, et al. Diagnostic performance of a combination of Mini-Mental State Examination and Clock Drawing Test in detecting Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013; 9:581–586.48. Cacho J, Benito-León J, García-García R, Fernández-Calvo B, Vicente-Villardón JL, Mitchell AJ. Does the combination of the MMSE and clock drawing test (mini-clock) improve the detection of mild Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment? J Alzheimers Dis. 2010; 22:889–896.
Article