J Korean Med Assoc.
2019 Apr;62(4):224-230. 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.4.224.
Upper airway myofunctional exercise: a systematic review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division for New Health Technology Assessment, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea. shkim@neca.re.kr
- KMID: 2442739
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2019.62.4.224
Abstract
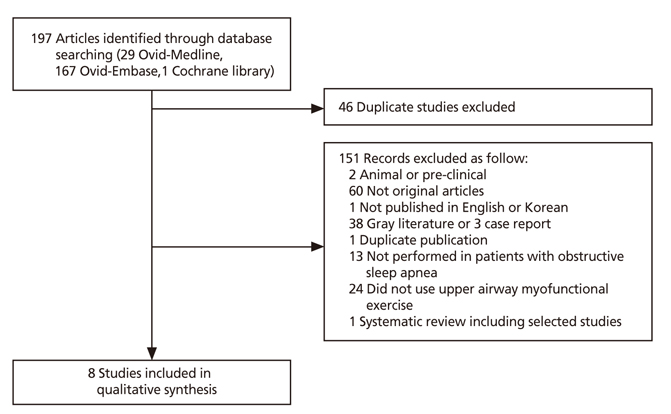
- Upper airway myofunctional exercise is a training technique for patients with obstructive sleep apnea involving isotonic and isometric exercises of the upper airway muscles involved in obstructive sleep apnea designed to strengthen upper airway myofunction and improve patients' symptoms. The objective of this review was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of upper airway myofunctional exercise. A literature search was conducted using 8 Korean databases, Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library. Of the 197 articles that were initially identified, 8 studies were included in this review. The results show that upper airway myofunctional exercise improved the apnea-hypopnea index in adult patients, and that it led to improvements in symptoms and upper airway myofunction when administered alone or after adenoidectomy in pediatric patients. On the basis of the current data, upper airway myofunctional exercise can be considered a safe and effective technique for patients with obstructive sleep apnea.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung YS. Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Hanyang Med Rev. 2013; 33:227–232.
Article2. Isidoro SI, Salvaggio A, Lo Bue A, Romano S, Marrone O, Insalaco G. Effect of obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis on health related quality of life. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015; 13:68.
Article3. Min J, Kim SJ. Medical management of obstructive sleep apnea. Korean J Med. 2015; 89:21–26.
Article4. Eckert DJ, Malhotra A. Pathophysiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008; 5:144–153.
Article5. Mohamed AS, Sharshar RS, Elkolaly RM, Serageldin SM. Upper airway muscle exercises outcome in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2017; 66:121–125.
Article6. Camacho M, Certal V, Abdullatif J, Zaghi S, Ruoff CM, Capa-sso R, Kushida CA. Myofunctional therapy to treat obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. 2015; 38:669–675.
Article7. Diaferia G, Santos-Silva R, Truksinas E, Haddad FLM, Santos R, Bommarito S, Gregorio LC, Tufik S, Bittencourt L. Myo-functional therapy improves adherence to continuous positive airway pressure treatment. Sleep Breath. 2017; 21:387–395.
Article8. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009; 62:1006–1012.
Article9. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Critical appraisal notes and checklists [Internet]. Edinburgh: Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network;2011. cited 2019 Mar 30. Available from: http://www.sign.ac.uk/checklists-and-notes.html.10. Ieto V, Kayamori F, Montes MI, Hirata RP, Gregorio MG, Alencar AM, Drager LF, Genta PR, Lorenzi-Filho G. Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on snoring: a randomized trial. Chest. 2015; 148:683–691.11. Villa MP, Brasili L, Ferretti A, Vitelli O, Rabasco J, Mazzotta AR, Pietropaoli N, Martella S. Oropharyngeal exercises to reduce symptoms of OSA after AT. Sleep Breath. 2015; 19:281–289.
Article12. Guimaraes KC, Drager LF, Genta PR, Marcondes BF, Lorenzi-Filho G. Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 179:962–966.
Article13. Villa MP, Evangelisti M, Martella S, Barreto M, Del Pozzo M. Can myofunctional therapy increase tongue tone and reduce symptoms in children with sleep-disordered breathing? Sleep Breath. 2017; 21:1025–1032.
Article14. Guilleminault C, Huang YS, Monteyrol PJ, Sato R, Quo S, Lin CH. Critical role of myofascial reeducation in pediatric sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2013; 14:518–525.
Article15. Verma RK, Johnson J JR, Goyal M, Banumathy N, Goswami U, Panda NK. Oropharyngeal exercises in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea: our experience. Sleep Breath. 2016; 20:1193–1201.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Pressure of the Tongue, Lips, and Cheeks in Patients with Myofunctional Therapy and Appliance
- The Effects of Orofacial Myofunctional Training on the Changes of Lip and Tongue Strength in Elderly People
- Upper airway studies in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- Effects of Myofunctional Appliance in Children with Sleep-Disordered Breathing: Two Case Reports
- Developmental Characteristics of Upper Airway Anatomy in Pediatric Obstructive Sleep Apnea