Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2017 Dec;16(4):114-120. 10.12779/dnd.2017.16.4.114.
Cerebrospinal Biomarker Cut-off Methods Defined Only by Alzheimer's Disease Predict More Precisely Conversions of Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dementia Center, Stroke Center, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. jhlee@nhimc.or.kr
- 2Clinical Research Management Team, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. seonghye@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2442728
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2017.16.4.114
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers play an important supportive role as diagnostic and predictive indicators of Alzheimer's disease (AD). About 30% of controls in old age show abnormal values of CSF biomarkers and display a higher risk for AD compared with those showing normal values. The cut-off values are determined by their diagnostic accuracy. However, the current cut-off values may be less accurate, because controls include high-risk groups of AD. We sought to develop models of patients with AD, who are homogenous for CSF biomarkers.
METHODS
We included participants who had CSF biomarker data in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative database. We investigated the factors related to CSF biomarkers in patients with AD using linear mixed models. Using the factors, we developed models corresponding to CSF biomarkers to classify patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) into high risk and low risk and analyzed the conversion from MCI to AD using the Cox proportional hazards model.
RESULTS
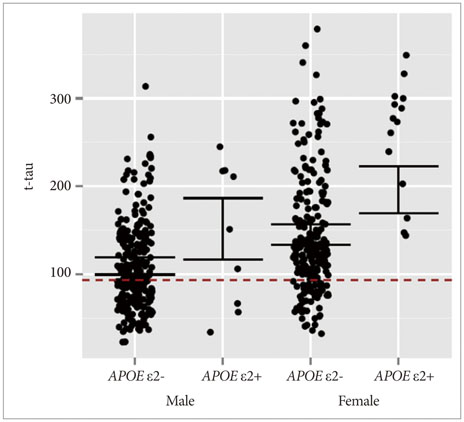
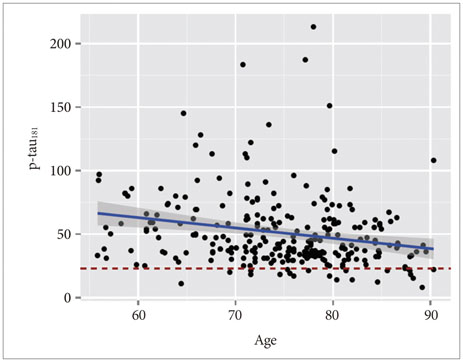
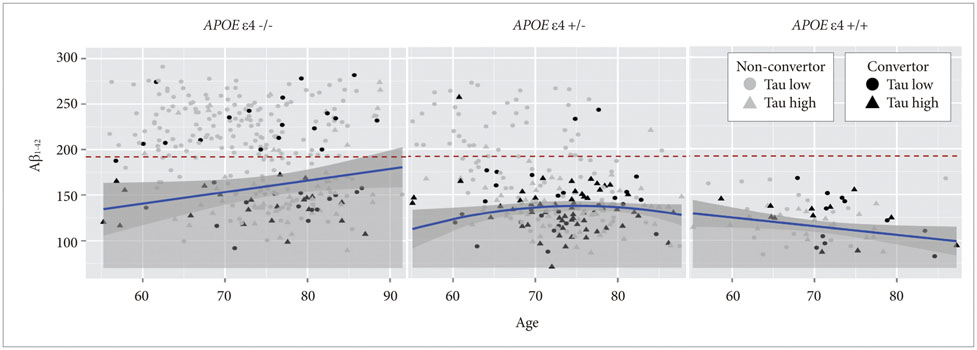
APOE ε4 status and age were significantly related to CSF Aβ1-42. CSF t-tau, APOE ε2 status and sex were significant factors. The CSF p-tau181 was associated with age and frequency of diagnosis. Accordingly, we modeled the three CSF biomarkers of AD. In MCI without APOE ε4, our models were better predictors of conversion.
CONCLUSIONS
We can interpret CSF biomarkers based on the models derived from the data obtained from patients with AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984; 34:939–944.
Article2. Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Clark CM, Aisen PS, Petersen RC, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann Neurol. 2009; 65:403–413.
Article3. Walhovd KB, Fjell AM, Brewer J, McEvoy LK, Fennema-Notestine C, Hagler DJ Jr, et al. Combining MR imaging, positron-emission tomography, and CSF biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 31:347–354.
Article4. Olsson A, Vanderstichele H, Andreasen N, De Meyer G, Wallin A, Holmberg B, et al. Simultaneous measurement of beta-amyloid (1-42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau (Thr181) in cerebrospinal fluid by the xMAP technology. Clin Chem. 2005; 51:336–345.
Article5. Shin S, Kim JH, Cho JH, Kim GS, Choi SA, Lee JH. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer disease is less likely under the age of 65. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2015; 29:26–31.
Article6. Nettiksimmons J, Harvey D, Brewer J, Carmichael O, DeCarli C, Jack CR Jr, et al. Subtypes based on cerebrospinal fluid and magnetic resonance imaging markers in normal elderly predict cognitive decline. Neurobiol Aging. 2010; 31:1419–1428.
Article7. Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, et al. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975; 32:632–637.
Article8. Sheikh JI, Yesavage JA. Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS): recent evidence and development of a shorter version. In : Brink TL, editor. Clinical Gerontology: A Guide to Assessment and Intervention. New York: The Haworth Press;1986. p. 165–174.9. Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E. Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol. 1999; 56:303–308.10. Bertens D, Knol DL, Scheltens P, Visser PJ. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Temporal evolution of biomarkers and cognitive markers in the asymptomatic, MCI, and dementia stage of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015; 11:511–522.
Article11. Shaw LM, Vanderstichele H, Knapik-Czajka M, Figurski M, Coart E, Blennow K, et al. Qualification of the analytical and clinical performance of CSF biomarker analyses in ADNI. Acta Neuropathol. 2011; 121:597–609.
Article12. Savva GM, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C. Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study. Age, neuropathology, and dementia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2302–2309.
Article13. Jack CR Jr. PART and SNAP. Acta Neuropathol. 2014; 128:773–776.
Article14. Caroli A, Prestia A, Galluzzi S, Ferrari C, van der Flier WM, Ossenkoppele R, et al. Mild cognitive impairment with suspected nonamyloid pathology (SNAP): Prediction of progression. Neurology. 2015; 84:508–515.
Article15. Li G, Shofer JB, Petrie EC, Yu CE, Wilkinson CW, Figlewicz DP, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer's and vascular disease vary by age, gender, and APOE genotype in cognitively normal adults. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017; 9:48.
Article16. Lautner R, Insel PS, Skillbäck T, Olsson B, Landén M, Frisoni GB, et al. Preclinical effects of APOE ε4 on cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 concentrations. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017; 9:87.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuroimaging Markers for Alzheimer's Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI)
- Neuropsychological Assessment of Dementia and Cognitive Disorders
- Biochemical Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Peripheral Blood
- Mild Cognitive Impairment - Aging to Alzheimer's Disease -
- Prediction of Cognitive Progression in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Radiomics as an Improvement of the ATN System: A Five-Year Follow-Up Study