J Korean Soc Radiol.
2019 Mar;80(2):259-273. 10.3348/jksr.2019.80.2.259.
Exploiting the Vulnerability of Deep Learning-Based Artificial Intelligence Models in Medical Imaging: Adversarial Attacks
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Center for Clinical Imaging Data Science, Research Institute of Radiological Sciences, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bchoi@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2442517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2019.80.2.259
Abstract
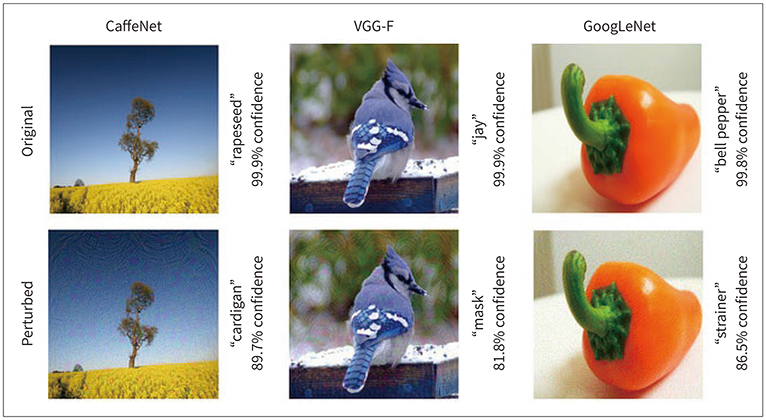
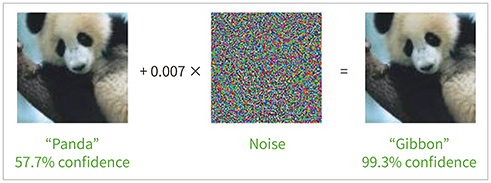
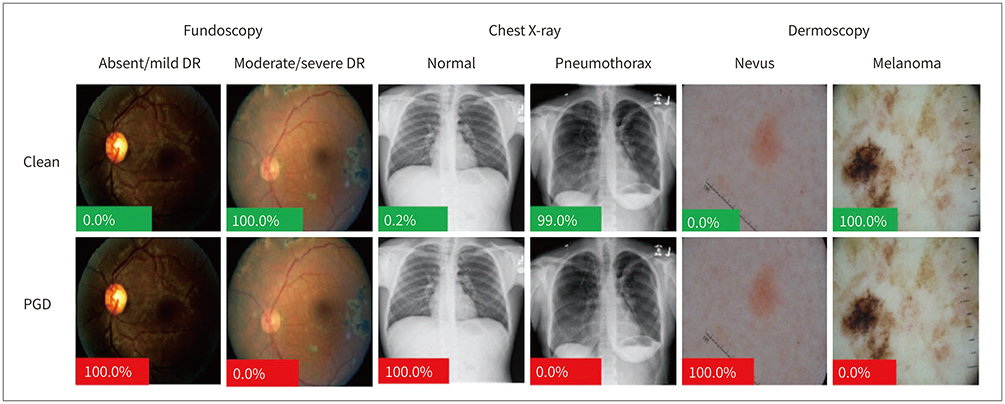
- Due to rapid developments in the deep learning model, artificial intelligence (AI) models are expected to enhance clinical diagnostic ability and work efficiency by assisting physicians. Therefore, many hospitals and private companies are competing to develop AI-based automatic diagnostic systems using medical images. In the near future, many deep learning-based automatic diagnostic systems would be used clinically. However, the possibility of adversarial attacks exploiting certain vulnerabilities of the deep learning algorithm is a major obstacle to deploying deep learning-based systems in clinical practice. In this paper, we will examine in detail the kinds of principles and methods of adversarial attacks that can be made to deep learning models dealing with medical images, the problems that can arise, and the preventive measures that can be taken against them.
Figure
Reference
-
1. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015; 521:436–444.2. Schroff F, Kalenichenko D, Philbin J. FaceNet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Piscataway: IEEE;2015. p. 815–823.3. Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, Antonoglou I, Huang A, Guez A, et al. Mastering the game of Go without human knowledge. Nature. 2017; 550:354–359.4. Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, Stumpe MC, Wu D, Narayanaswamy A, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016; 316:2402–2410.5. Liu F, Zhou Z, Samsonov A, Blankenbaker D, Larison W, Kanarek A, et al. Deep learning approach for evaluating knee MR images: achieving high diagnostic performance for cartilage lesion detection. Radiology. 2018; 289:160–169.6. McBee MP, Awan OA, Colucci AT, Ghobadi CW, Kadom N, Kansagra AP, et al. Deep learning in radiology. Acad Radiol. 2018; 25:1472–1480.7. Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, et al. CheXNet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest x-rays with deep learning. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1711.05225.8. Ehteshami Bejnordi B, Veta M, Johannes van, Van Ginneken B, Karssemeijer N, Litjens G, et al. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases in women with breast cancer. JAMA. 2017; 318:2199–2210.9. Golden JA. Deep learning algorithms for detection of lymph node metastases from breast cancer. JAMA. 2017; 318:2184–2186.10. Giger ML, Suzuki K. Computer-aided diagnosis. Biomedical Information Technology. New York: Academic Press;2008.11. Böröczky L, Zhao L, Lee KP. Feature subset selection for improving the performance of false positive reduction in lung nodule CAD. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2006; 10:504–511.12. Tan M, Deklerck R, Jansen B, Bister M, Cornelis J. A novel computer-aided lung nodule detection system for CT images. Med Phys. 2011; 38:5630–5645.13. Cao P, Liu X, Yang J, Zhao D, Li W, Huang M, et al. A multi-kernel based framework for heterogeneous feature selection and over-sampling for computer-aided detection of pulmonary nodules. Pattern Recognit. 2017; 64:327–346.14. Baker JA, Rosen EL, Lo JY, Gimenez EI, Walsh R, Soo MS. Computer-aided detection (CAD) in screening mammography: sensitivity of commercial CAD systems for detecting architectural distortion. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:1083–1088.15. Dromain C, Boyer B, Ferré R, Canale S, Delaloge S, Balleyguier C. Computed-aided diagnosis (CAD) in the detection of breast cancer. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:417–423.16. Gal Y. Uncertainty in deep learning. In : IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing; Los Altos. 2017.17. Holzinger A. From machine learning to explainable AI. In : 2018 World Symposium on Digital Intelligence for Systems and Machines (DISA); Piscataway: IEEE;2018. p. 55–66.18. Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, Bruna J, Erhan D, Goodfellow I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv preprint. 2013; arXiv:1312.6199.19. Moosavi-Dezfooli SM, Fawzi A, Fawzi O, Frossard P. Universal adversarial perturbations. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Piscataway: IEEE;2017. p. 1765–1773.20. Papernot N, McDaniel P, Wu X, Jha S, Swami A. Distillation as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks. In : In 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP); Piscataway: IEEE;2016. p. 582–597.21. Melis M, Demontis A, Biggio B, Brown G, Fumera G, Roli F. Is deep learning safe for robot vision? adversarial examples against the icub humanoid. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; Piscataway: IEEE;2017. p. 751–759.22. Kurakin A, Goodfellow I, Bengio S. Adversarial examples in the physical world. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv: 1607.02533.23. Athalye A, Engstrom L, Ilyas A, Kwok K. Synthesizing robust adversarial examples. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv: 1707.07397.24. Paschali M, Conjeti S, Navarro F, Navab N. Generalizability vs. robustness: adversarial examples for medical imaging. arXiv preprint. 2018; arXiv:1804.00504.25. Akhtar N, Mian A. Threat of adversarial attacks on deep learning in computer vision: a survey. IEEE Access. 2018; 6:14410–14430.26. Papernot N, McDaniel P, Sinha A, Wellman M. Towards the science of security and privacy in machine learning. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1611.03814.27. Bun M, Steinke T. Concentrated differential privacy: simplifications, extensions, and lower bounds. In : Theory of Cryptography Conference; Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer;2016. p. 635–658.28. Goodfellow IJ, Shlens J, Szegedy C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. arXiv preprint. 2014; arXiv:1412.6572.29. Moosavi-Dezfooli SM, Fawzi A, Frossard P. Deepfool: a simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Piscataway: IEEE;2016. p. 2574–2582.30. Papernot N, Mcdaniel P, Jha S, Fredrikson M, Celik ZB, Swami A. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings. In : In 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P); Piscataway: IEEE;2016. p. 372–387.31. Jang U, Wu X, Jha S. Objective metrics and gradient descent algorithms for adversarial examples in machine learning. In : In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Computer Security Applications Conference; Piscataway: IEEE;2017. p. 262–277.32. Evtimov I, Eykholt K, Fernandes E, Kohno T, Li B, Prakash A, et al. Robust physical-world attacks on deep learning models. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1707.08945.33. Carlini N, Wagner D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks. In : In 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP); Piscataway: IEEE;2017.34. Lu J, Sibai H, Fabry E, Forsyth D. No need to worry about adversarial examples in object detection in autonomous vehicles. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1707.03501.35. Taghanaki SA, Das A, Hamarneh G. Vulnerability analysis of chest x-ray image classification against adversarial attacks. Understanding and Interpreting Machine Learning in Medical Image Computing Applications. Cham: Springer;2018.36. Finlayson SG, Chung HW, Kohane IS, Beam AL. Adversarial attacks against medical deep learning systems. arXiv preprint. 2018; arXiv:1804.05296.37. Papangelou K, Sechidis K, Weatherall J, Brown G. Toward an understanding of adversarial examples in clinical trials. Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Cham: Springer;2018. p. 35–51.38. Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Piscataway: IEEE;2015.39. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Cham: Springer;2015. p. 234–241.40. Sun M, Tang F, Yi J, Wang F, Zhou J. Identify susceptible locations in medical records via adversarial attacks on deep predictive models. In : In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining; New York: ACM;2018. p. 793–801.41. Graves A, Liwicki M, Fernández S, Bertolami R, Bunke H, Schmidhuber J. A novel connectionist system for unconstrained handwriting recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2009; 31:855–868.42. Gers FA, Schmidhuber J, Cummins F. Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000; 12:2451–2471.43. Miyato T, Dai AM, Goodfellow I. Adversarial training methods for semi-supervised text classification. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1605.07725.44. Zheng S, Song Y, Leung T, Goodfellow I. Improving the robustness of deep neural networks via stability training. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1604.04326.45. Lyu C, Huang K, Liang HN. A unified gradient regularization family for adversarial examples. In : In 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining; Piscataway: IEEE;2015. p. 301–309.46. Nguyen L, Wang S, Sinha A. A learning and masking approach to secure learning. In : In International Conference on Decision and Game Theory for Security; Cham: Springer;2018. p. 453–464.47. Xu W, Evans D, Qi Y. Feature squeezing: detecting adversarial examples in deep neural networks. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1704.01155.48. Feinman R, Curtin RR, Shintre S, Gardner AB. Detecting adversarial samples from artifacts. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1703.00410.49. Lu J, Issaranon T, Forsyth D. SafetyNet: detecting and rejecting adversarial examples robustly. In : In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; Piscataway: IEEE;2017. p. 446–454.50. Strauss T, Hanselmann M, Junginger A, Ulmer H. Ensemble methods as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1709.03423.51. Buckman J, Roy A, Raffel C, Goodfellow I. Thermometer encoding: one hot way to resist adversarial examples. In : In ICLR 2018 Conference; La Jolla: ICLR;2018.52. Zantedeschi V, Nicolae MI, Rawat A. Efficient defenses against adversarial attacks. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1707.06728.53. Sun S, Yeh CF, Ostendorf M, Hwang MY, Xie L. Training augmentation with adversarial examples for robust speech recognition. arXiv preprint. 2018; arXiv:1806.02782.54. Su J, Vargas DV, Kouichi S. One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks. arXiv preprint. 2012; arXiv: 1710.08864.55. Sarkar S, Bansal A, Mahbub U, Chellappa R. UPSET and ANGRI : breaking high performance image classifiers. arXiv preprint. 2017; arXiv:1707.01159.56. Papernot N, McDaniel P, Goodfellow I, Jha S, Berkay Celik Z, Swami A. Practical black-box attacks against machine learning. arXiv preprint. 2016; arXiv:1602.02697.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Artificial Intelligence in Neuro-Oncologic Imaging: A Brief Review for Clinical Use Cases and Future Perspectives
- Basics of Deep Learning: A Radiologist's Guide to Understanding Published Radiology Articles on Deep Learning
- The Latest Trends in the Use of Deep Learning in Radiology Illustrated Through the Stages of Deep Learning Algorithm Development
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- Current status of deep learning applications in abdominal ultrasonography