Nutr Res Pract.
2019 Apr;13(2):150-158. 10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.150.
Development of a food-based index of dietary inflammatory potential for Koreans and its relationship with metabolic syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Wonkwang University, 460, Iksan-daero, Iksan-si, Jeonbuk, 54538, Republic of Korea. ccha@wku.ac.kr
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Jeonbuk, Iksan, Republic of Korea. yutaeyang@gmail.com
- KMID: 2442372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2019.13.2.150
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Inflammation is known to be a risk factor for metabolic diseases. This study aimed to develop a Food-based Index of Dietary Inflammatory Potential (FBDI) and examine its association with metabolic biomarkers.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
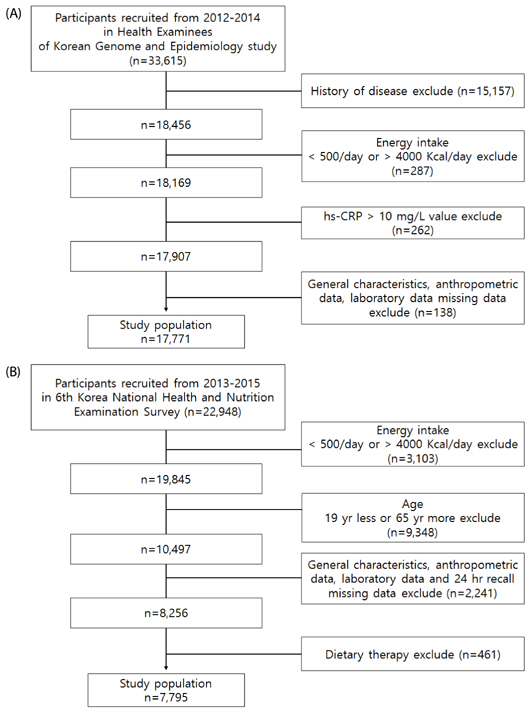
This study analyzed the raw data from the 2012-2014 Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study data of 17,771 people. To analyze the relationship between foods consumed by Koreans and inflammation, we conducted a correlation analysis between 51 food groups and hs-CRP levels. The FBDI was developed from 17 food groups selected by multiple regression method. We examined whether FBDI was associated with metabolic markers (waist circumference, blood pressure, fasting glucose, triglyceride, and HDL-cholesterol) in the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). We used binary logistic regression analysis to examine the association.
RESULTS
The FBDI model included seven of the anti-inflammatory food groups and three of the pro-inflammatory food groups. The FBDI formula was calculated by multiplying the intake of food group by β-coefficients derived from the multiple regression model based on the correlation analysis. The FBDI was significantly associated with waist circumference (P < 0.001), blood pressure (P < 0.001), triglyceride level (P < 0.001), and HDL-cholesterol (P < 0.001) level among adults aged 20-64 years in the KNHANES. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 2.618 times higher in the group with the highest FBDI than in the group with the lowest one (95% confidence interval: 1.778-3.856, P for trend < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
This study established an FBDI reflecting food intake patterns of Koreans, which showed a significant relationship with the prevalence of metabolic syndrome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhu S, St-Onge MP, Heshka S, Heymsfield SB. Lifestyle behaviors associated with lower risk of having the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism. 2004; 53:1503–1511.
Article2. Hoffmann IS, Cubeddu LX. Salt and the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009; 19:123–128.
Article3. Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010; 87:4–14.
Article4. Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Won Yoon J, Choi SH, Cho SI, Park KS, Lee HK, Jang HC, Koh KK. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998-2007. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1323–1328.
Article5. Tran BT, Jeong BY, Oh JK. The prevalence trend of metabolic syndrome and its components and risk factors in Korean adults: results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2013. BMC Public Health. 2017; 17:71.
Article6. Korea Insurance Research Institute. KIRI Research Report. Strengthening the protection of national health insurance through efficient expenditure of medical expenses [Internet]. Seoul:: Korea Insurance Research Institute;2017. cited 2018 April 10. Available from: http://www.kiri.or.kr/html/reportList.asp?part=report.7. Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Pepys MB, Gudnason V. C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1387–1397.
Article8. Pearson TA, Mensah GA, Alexander RW, Anderson JL, Cannon RO 3rd, Criqui M, Fadl YY, Fortmann SP, Hong Y, Myers GL, Rifai N, Smith SC Jr, Taubert K, Tracy RP, Vinicor F. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. American Heart Association. Markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease: application to clinical and public health practice: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2003; 107:499–511.9. Kitabchi AE, McDaniel KA, Wan JY, Tylavsky FA, Jacovino CA, Sands CW, Nyenwe EA, Stentz FB. Effects of high-protein versus highcarbohydrate diets on markers of β-cell function, oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, proinflammatory cytokines, and adipokines in obese, premenopausal women without diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:1919–1925.
Article10. Ferrucci L, Cherubini A, Bandinelli S, Bartali B, Corsi A, Lauretani F, Martin A, Andres-Lacueva C, Senin U, Guralnik JM. Relationship of plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids to circulating inflammatory markers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:439–446.
Article11. Ma Y, Griffith JA, Chasan-Taber L, Olendzki BC, Jackson E, Stanek EJ 3rd, Li W, Pagoto SL, Hafner AR, Ockene IS. Association between dietary fiber and serum C-reactive protein. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006; 83:760–766.
Article12. Bertran N, Camps J, Fernandez-Ballart J, Arija V, Ferre N, Tous M, Simo D, Murphy MM, Vilella E, Joven J. Diet and lifestyle are associated with serum C-reactive protein concentrations in a population-based study. J Lab Clin Med. 2005; 145:41–46.
Article13. Wannamethee SG, Lowe GD, Rumley A, Bruckdorfer KR, Whincup PH. Associations of vitamin C status, fruit and vegetable intakes, and markers of inflammation and hemostasis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006; 83:567–574.
Article14. Esmaillzadeh A, Kimiagar M, Mehrabi Y, Azadbakht L, Hu FB, Willett WC. Fruit and vegetable intakes, C-reactive protein, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006; 84:1489–1497.
Article15. Lutsey PL, Jacobs DR Jr, Kori S, Mayer-Davis E, Shea S, Steffen LM, Szklo M, Tracy R. Whole grain intake and its cross-sectional association with obesity, insulin resistance, inflammation, diabetes and subclinical CVD: the MESA study. Br J Nutr. 2007; 98:397–405.
Article16. Esposito K, Marfella R, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, D'Armiento M, D'Andrea F, Giugliano D. Effect of a mediterranean-style diet on endothelial dysfunction and markers of vascular inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2004; 292:1440–1446.
Article17. Johansson-Persson A, Ulmius M, Cloetens L, Karhu T, Herzig KH, Onning G. A high intake of dietary fiber influences C-reactive protein and fibrinogen, but not glucose and lipid metabolism, in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Nutr. 2014; 53:39–48.
Article18. Shivappa N, Steck SE, Hurley TG, Hussey JR, Hébert JR. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014; 17:1689–1696.
Article19. Shivappa N, Steck SE, Hussey JR, Ma Y, Hebert JR. Inflammatory potential of diet and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Study. Eur J Nutr. 2017; 56:683–692.
Article20. Kim M, Sohn C. Analysis of dietary inflammatory index of metabolic syndrome in Korean: data from the health examinee cohort (2012-2014). Korean J Hum Ecol. 2016; 25:823–834.
Article21. Garcia-Arellano A, Ramallal R, Ruiz-Canela M, Salas-Salvadó J, Corella D, Shivappa N, Schröder H, Hébert JR, Ros E, Gómez-Garcia E, Estruch R, Lapetra J, Arós F, Fiol M, Serra-Majem L, Pintó X, Babio N, González JI, Fitó M, Martínez JA, Martínez-González MA. Predimed Investigators. Dietary inflammatory index and incidence of cardiovascular disease in the PREDIMED study. Nutrients. 2015; 7:4124–4138.
Article22. Ramallal R, Toledo E, Martínez-González MA, Hernández-Hernández A, García-Arellano A, Shivappa N, Hébert JR, Ruiz-Canela M. Dietary inflammatory index and incidence of cardiovascular disease in the SUN Cohort. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0135221.
Article23. Neufcourt L, Assmann KE, Fezeu LK, Touvier M, Graffouillère L, Shivappa N, Hébert JR, Wirth MD, Hercberg S, Galan P, Julia C, Kesse-Guyot E. Prospective association between the dietary inflammatory index and cardiovascular diseases in the SUpplémentation en VItamines et Minéraux AntioXydants (SU.VI.MAX) cohort. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016; 5:e002735.
Article24. Tabung FK, Smith-Warner SA, Chavarro JE, Wu K, Fuchs CS, Hu FB, Chan AT, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. Development and validation of an empirical dietary inflammatory index. J Nutr. 2016; 146:1560–1570.
Article25. Na W, Kim M, Park S, Lee M, Sohn C. Development and validation of Korean Inflammtory Index (K-DII) for metabolic disease patients: by using the Health Examinee Cohort (2012-2014). Korean J Hum Ecol. 2017; 26:369–381.
Article26. Kim Y, Han BG. KoGES group. Cohort Profile: the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:1350.
Article27. Vainio H, Bianchini F. IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention, Volume 8. Fruit and Vegetables. Lyon: IARC Press;2003.28. Linseisen J, Kesse E, Slimani N, Bueno-De-Mesquita HB, Ocké MC, Skeie G, Kumle M, Dorronsoro Iraeta M, Morote Gómez P, Janzon L, Stattin P, Welch AA, Spencer EA, Overvad K, Tjønneland A, Clavel-Chapelon F, Miller AB, Klipstein-Grobusch K, Lagiou P, Kalapothaki V, Masala G, Giurdanella MC, Norat T, Riboli E. Meat consumption in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohorts: results from 24-hour dietary recalls. Public Health Nutr. 2002; 5:1243–1258.
Article29. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F. American Heart Association. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005; 112:2735–2752.30. Oliveira A, Rodríguez-Artalejo F, Lopes C. The association of fruits, vegetables, antioxidant vitamins and fibre intake with highsensitivity C-reactive protein: sex and body mass index interactions. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009; 63:1345–1352.
Article31. Chun OK, Chung SJ, Claycombe KJ, Song WO. Serum C-reactive protein concentrations are inversely associated with dietary flavonoid intake in U.S. adults. J Nutr. 2008; 138:753–760.
Article32. Esmaillzadeh A, Azadbakht L. Legume consumption is inversely associated with serum concentrations of adhesion molecules and inflammatory biomarkers among Iranian women. J Nutr. 2012; 142:334–339.
Article33. Bonaccio M, Di Castelnuovo A, De Curtis A, Costanzo S, Bracone F, Persichillo M, Donati MB, de Gaetano G, Iacoviello L. Moli-sani Project investigators. Nut consumption is inversely associated with both cancer and total mortality in a Mediterranean population: prospective results from the Moli-sani study. Br J Nutr. 2015; 114:804–811.
Article34. Yu Z, Malik VS, Keum N, Hu FB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Fuchs CS, Bao Y. Associations between nut consumption and inflammatory biomarkers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016; 104:722–728.
Article35. Zuñiga YL, Rebello SA, Oi PL, Zheng H, Lee J, Tai ES, Van Dam RM. Rice and noodle consumption is associated with insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia in an Asian population. Br J Nutr. 2014; 111:1118–1128.
Article36. Yamashita K, Yatsuya H, Muramatsu T, Toyoshima H, Murohara T, Tamakoshi K. Association of coffee consumption with serum adiponectin, leptin, inflammation and metabolic markers in Japanese workers: a cross-sectional study. Nutr Diabetes. 2012; 2:e33.
Article37. Je Y, Jeong S, Park T. Coffee consumption patterns in Korean adults: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2001-2011). Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2014; 23:691–702.38. Shon JK. The effect of cognition at regional area on image, attitude & intention of behavior - focus on Korea food consumer behavior. J Foodserv Manag. 2011; 14:321–336.39. Kim WY, Kim JE, Choi YJ, Huh KB. Nutritional risk and metabolic syndrome in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2008; 17:Suppl 1. 47–51.40. Song SJ, Lee JE, Paik HY, Park MS, Song YJ. Dietary patterns based on carbohydrate nutrition are associated with the risk for diabetes and dyslipidemia. Nutr Res Pract. 2012; 6:349–356.
Article41. Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Yaghootkar H, Lanham-New SA, Lamb DJ, Ferns GA. Association between serum CRP concentrations with dietary intake in healthy and dyslipidaemic patients. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007; 16:262–268.42. Kim M, Kim J, Bae W, Kim S, Lee Y, Na W, Sohn C. Relationship between nutrients intakes, dietary quality, and serum concentrations of inflammatory markers in metabolic syndrome patients. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16:51–61.
Article43. Ridker PM, Buring JE, Cook NR, Rifai N. C-reactive protein, the metabolic syndrome, and risk of incident cardiovascular events: an 8-year follow-up of 14 719 initially healthy American women. Circulation. 2003; 107:391–397.
Article44. Santos AC, Lopes C, Guimarães JT, Barros H. Central obesity as a major determinant of increased high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in metabolic syndrome. Int J Obes. 2005; 29:1452–1456.
Article45. Indulekha K, Surendar J, Mohan V. High sensitivity C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 levels in Asian Indians with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance (CURES-105). J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011; 5:982–988.
Article46. Vu JD, Vu JB, Pio JR, Malik S, Franklin SS, Chen RS, Wong ND. Impact of C-reactive protein on the likelihood of peripheral arterial disease in United States adults with the metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, and preexisting cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005; 96:655–658.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between Nutrients Intakes, Dietary Quality, and Serum Concentrations of Inflammatory Markers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients
- The Relationship Between the Korean Adults Diet Evaluated Using Dietary Quality Indices and Metabolic Risk Factors: Based on the 2016 ~ 2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- The Quality of a Traditional Dietary Pattern in Relation to Metabolic Syndrome in Elderly South Koreans
- 2020 Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans: vitamin C
- High fiber and high carbohydrate intake and its association with the metabolic disease using the data of KNHANES 2013 ~ 2017