Lab Med Online.
2019 Apr;9(2):84-87. 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.84.
A Clue to Discovering Unstable Hemoglobin Variants via Abnormal WBC Differential Scattergrams Using the Sysmex Automated Hematology Analyzer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. JungWonH@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2441828
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2019.9.2.84
Abstract
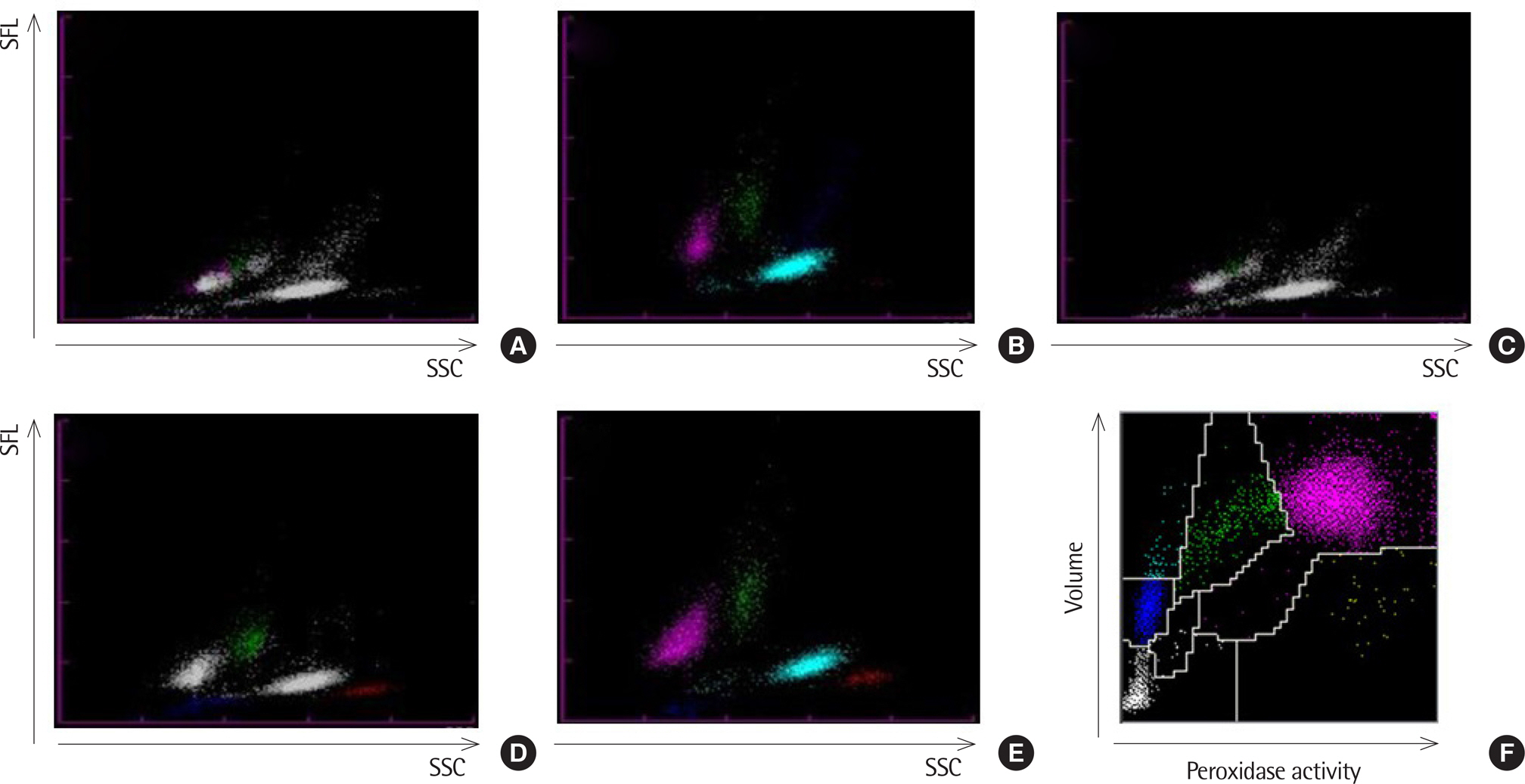
- Incidentally, hemoglobin (Hb) variants can be detected using HbA1c tests in clinical laboratories. We found 38 patients with Hb variants after reviewing a total of 29,398 HbA1c test results from January 2017 to December 2017. While reviewing the complete blood count results of the patients (N=36) using the Sysmex XN-9000 analyzer (Sysmex, Japan), 35 patients were flagged as unremarkable with respect to differential white blood cell (WBC) counts. However, 1 patient with a normal WBC count did not obtain a differential WBC count while being flagged for an abnormal WBC scattergram in the white blood cell differential (WDF) channel. The WBC histogram showed an abnormally low fluorescent signal in the WDF channel; however, the differential WBC count was normal upon microscopic examination. After testing the patient's buffy coat suspended in normal saline and removing red blood cells (RBCs), the WBC scattergram and differential WBC count returned to normal. This finding suggests that the presence of a patient's RBCs may affect WBC scattergrams and Hb variants may interfere with the fluorescent dye in the differential WBC count. Therefore, when an abnormal WBC scattergram with an abnormally low fluorescent signal is encountered on the Sysmex XN-9000 analyzer, the presence of an Hb variant can be suspected.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Thom CS, Dickson CF, Gell DA, Weiss MJ. Hemoglobin variants: biochemical properties and clinical correlates. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013; 3:a011858.
Article2. Park S, Lee W, Chung HS, Hong KS. Diagnostic utility of serum glycated albumin for diabetes mellitus and its correlation with hyperlipidemia. Ann Lab Med. 2016; 36:306–12.
Article3. Rosetti M, Poletti G, Sensi A, Ravani A, Rondoni M, Baldrati L, et al. A rare case of hemoglobin Leiden interfering with the DIFF channel of Sysmex XE-2100. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015; 75:436–7.
Article4. Rosetti M, Poletti G, Ivaldi G, Rondoni M, Baldrati L, Dorizzi RM. Serendipitous detection of hemoglobin G-Ferrara variant with Sysmex DIFF channel. Clin Biochem. 2016; 49:192–3.
Article5. Mongelli F, Barberio G, Ivaldi G. A rare and unstable hemoglobin variant, Hb M Dothan β 25/26 (−GTG), detected by the anomalous cyto-gram on Sysmex XE-2100. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2016; 54:e31–3.
Article6. Teixeira C, Pina D, Freitas MI. Automated detection of unstable hemoglobin variants by Sysmex XE-Series analyzers. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017; 55:e243–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Spuriously Decreased White Blood Cell Count on an Automated Sysmex XN Hematology Analyzer: The Difference Between the WNR and WDF Channels
- Evaluation of the Automated Hematology Analyzer Sysmex XN-2000 and the Accuracy of Differential Leukocyte Counts Using the Low WBC Mode
- Evaluating the Performance of the Sysmex DI-60 Automated Cell Image Analyzer for the Differential Analysis of Leukocytes
- Performance Analysis of the Beckman Coulter GEN-S Automated Hematology Analyzer
- Performance Evaluation of the Mindray BC-6200 Hematology Analyzer; Comparison with Sysmex XE-2100 and Manual Microscopy