Ann Clin Microbiol.
2019 Mar;22(1):9-13. 10.5145/ACM.2019.22.1.9.
Development and Evaluation of Multiplex PCR for the Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Semyung University, Jecheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Dental Hygiene, Silla University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. jhsmile@inje.ac.kr
- 4Paik Institute for Clinical Research, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2441651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2019.22.1.9
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The isolation of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) has become increasingly common. Continuous surveillance for these organisms is essential because their infections are closely related to outbreaks of illness and are associated with high mortality rates. The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate multiplex PCR as a means of detecting several important CPE genes simultaneously.
METHODS
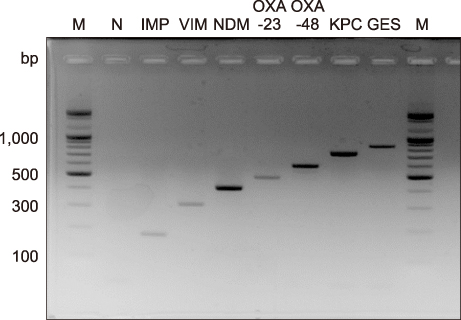
We aimed to develop a multiplex PCR that could detect seven CPE genes simultaneously. The multiplex PCR was composed of seven primer sets for the detection of KPC, IMP, VIM, NDM-1, GES, OXA-23, and OXA-48. We designed different PCR product sizes of at least 100 bp. We evaluated the performance of this new test using 69 CPE-positive clinical isolates. Also, we confirmed the specificity to rule out false-positive reactions by using 71 carbapenem-susceptible clinical strains.
RESULTS
A total of 69 CPE clinical isolates showed positive results and were correctly identified as KPC (N=14), IMP (N=13), OXA-23 (N=12), OXA-48 (N=11), VIM (N=9), GES (N=5), and NDM (N=5) by the multiplex PCR. All 71 carbapenem-susceptible clinical isolates, including Enterococcus faecalis , Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, showed negative results.
CONCLUSION
This multiplex PCR can detect seven CPE genes at a time and will be useful in clinical laboratories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pitout JD. Infections with extended-spectrum beta-lactamaseproducing Enterobacteriaceae: changing epidemiology and drug treatment choices. Drugs. 2010; 70:313–333.2. Nordmann P, Naas T, Poirel L. Global spread of carbapenemaseproducing Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011; 17:1791–1798.3. Gupta N, Limbago BM, Patel JB, Kallen AJ. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: epidemiology and prevention. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 53:60–67.4. Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T. The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009; 9:228–236.
Article5. Tzouvelekis LS, Markogiannakis A, Psichogiou M, Tassios PT, Daikos GL. Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae: an evolving crisis of global dimensions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25:682–707.6. Jeong SH, Song W, Bae IK, Kim HS, Kim JS, Park MJ, et al. Broth microdilution methods using B-lactamase inhibitors for the identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases and metallo-β-lactamases in Gram-negative bacilli. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2014; 44:49–55.7. Anderson KF, Lonsway DR, Rasheed JK, Biddle J, Jensen B, McDougal LK, et al. Evaluation of methods to identify the Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase in Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2723–2725.8. Pasteran F, Mendez T, Rapoport M, Guerriero L, Corso A. Controlling false-positive results obtained with the Hodge and Masuda assays for detection of class a carbapenemase in species of enterobacteriaceae by incorporating boronic acid. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:1323–1332.
Article9. Yoon EJ, Yang JW, Kim JO, Lee H, Lee KJ, Jeong SH. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in South Korea: a report from the National Laboratory Surveillance System. Future Microbiol. 2018; 13:771–783.10. Yoon EJ, Kim JO, Yang JW, Kim HS, Lee KJ, Jeong SH, et al. The blaOXA-23-associated transposons in the genome of Acinetobacter spp. represent an epidemiological situation of the species encountering carbapenems. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017; 72:2708–2714.
Article11. Bush K. Alarming β-lactamase-mediated resistance in multidrugresistant Enterobacteriaceae. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010; 13:558–564.12. Gasink LB, Edelstein PH, Lautenbach E, Synnestvedt M, Fishman NO. Risk factors and clinical impact of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2009; 30:1180–1185.
Article13. Park JW, Lee EJ, Lee DH. Status of carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae in Korea, 2014. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2016; 9:9–13.14. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. CLSI document M100-S23. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2013.15. Doumith M, Ellington MJ, Livermore DM, Woodford N. Molecular mechanisms disrupting porin expression in ertapenemresistant Klebsiella and Enterobacter spp. clinical isolates from the UK. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 63:659–667.
Article16. Poirel L, Walsh TR, Cuvillier V, Nordmann P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 70:119–123.
Article17. You JS. Emergence and characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) in Korea, 2012. Public Health Wkly Rep. 2013; 6:425–428.18. Huang TD, Bogaerts P, Ghilani E, Heinrichs A, Gavage P, Roisin S, et al. Multicentre evaluation of the Check-Direct CPE® assay for direct screening of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from rectal swabs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015; 70:1669–1673.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapid Identification of OXA-48-like, KPC, NDM, and VIM Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae From Culture: Evaluation of the RESIST-4 O.K.N.V. Multiplex Lateral Flow Assay
- Development of a Two Triplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid Detection of Six Carbapenemase Genes in Enterobacteriaceae
- Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Rapid Laboratory Diagnosis and Surveillance Culture for Infection Control
- Carbapenem Inactivation Method: Accurate Detection and Easy Interpretation of Carbapenemase Production in Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas spp.
- Evaluation of Diagnostic Performance of RAPIDEC CARBA NP Test for Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae