Yonsei Med J.
2019 Mar;60(3):267-276. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.3.267.
MicroRNA-370 Regulates Cellepithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration, Invasion, and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting GUCD1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, Taixing People's Hospital, Taizhou, China. rqr555536@163.com
- KMID: 2441304
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.3.267
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive malignant tumor, the prognosis of which remains poor. Recently, microRNAs have been reported to play crucial functions in multiple tumors, including HCC. However, the molecular mechanisms of miR-370 in HCC still remain largely unknown. The present study focused on the effects of miR-370 on HCC migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
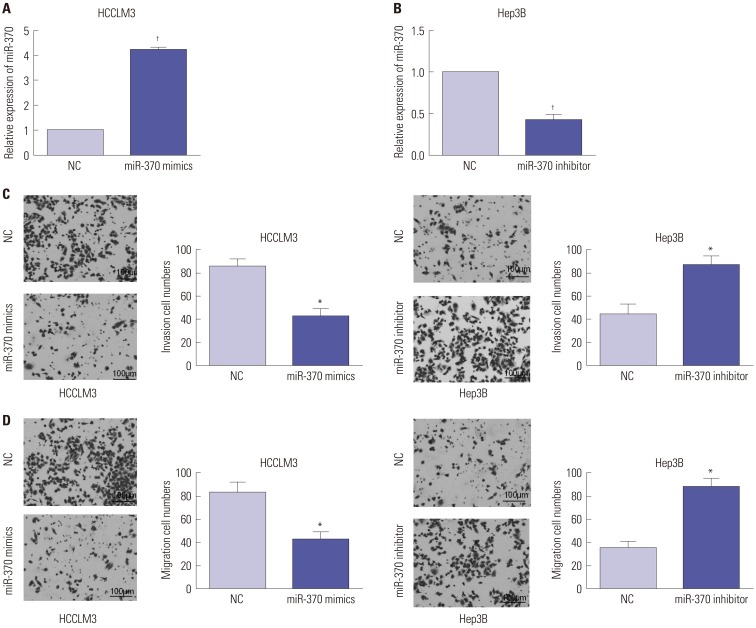
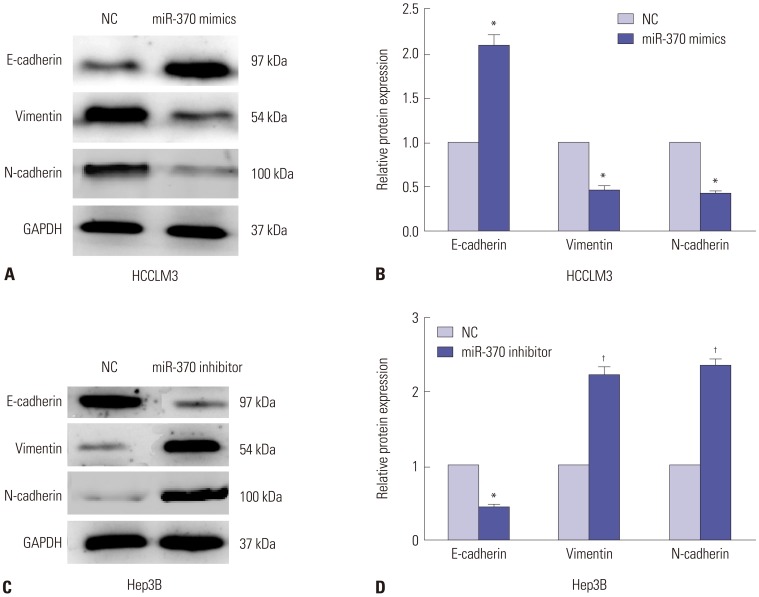
We investigated the key roles and possible regulatory mechanism of miR-370 in regulating HCC metastasis with functional assays, such as transwell assay. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to detect miR-370 and guanylylcyclase domain containing 1 (GUCD1) expression in HCC tissues and cells. Subsequently, we performed transwell assays to determine the functions of miR-370 in HCC cell invasion and migration. Western blot was used to determine protein expressions of relevant genes. Luciferase reporter assays were conducted to confirm the target gene of miR-370.
RESULTS
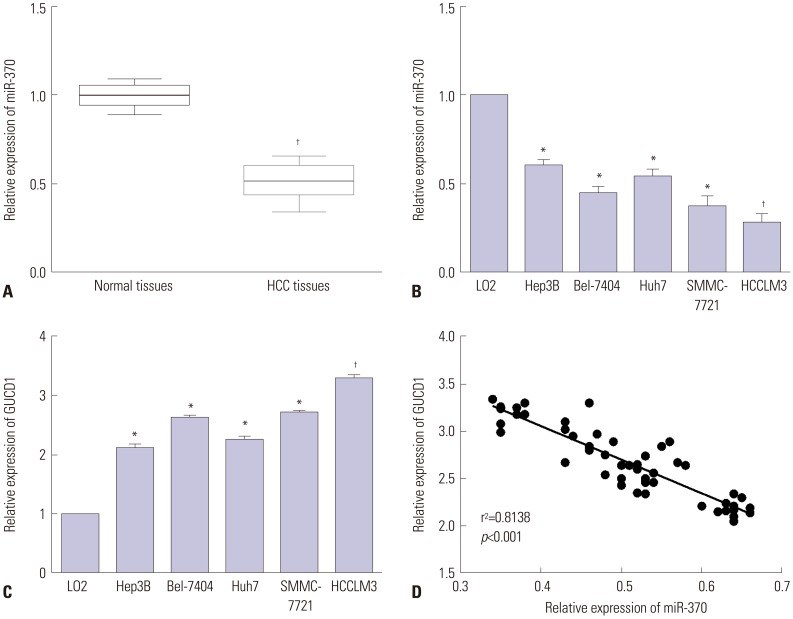
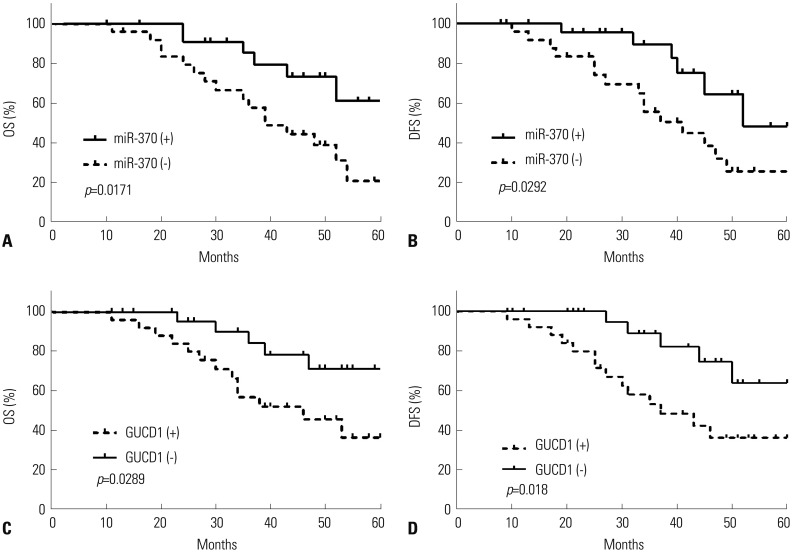
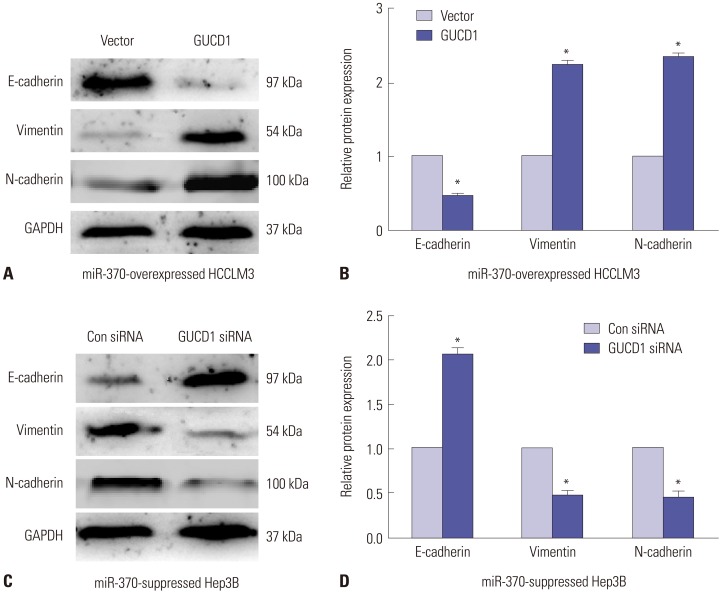
qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that miR-370 was dramatically downregulated in HCC. Moreover, downregulated miR-370 was found to be associated with poor survival and adverse clinicopathologic characteristics of HCC patients. Transwell assays revealed that miR-370 overexpression dramatically suppressed HCC invasion and migration. Meanwhile, miR-370 restoration prominently inhibited EMT progression in HCC cells. Luciferase reporter assays confirmed GUCD1 as a downstream target gene of miR-370. GUCD1 expression in HCC tissues was prominently increased and inversely correlated with miR-370 expression. Furthermore, GUCD1 was verified as mediating the suppressive influence of miR-370 on cell metastasis and EMT in HCC.
CONCLUSION
Taken together, our study confirmed that miR-370 suppressed HCC cell metastasis and EMT via regulating GUCD1. Accordingly, the miR-370/GUCD1 axis may potentially acts as attractive therapeutic targets and novel biomarkers for HCC treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108. PMID: 25651787.
Article2. Kuper H, Ye W, Broomé U, Romelsjö A, Mucci LA, Ekbom A, et al. The risk of liver and bile duct cancer in patients with chronic viral hepatitis, alcoholism, or cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2001; 34(4 Pt 1):714–718. PMID: 11584367.
Article3. Wörns MA, Galle PR. HCC therapies--lessons learned. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 11:447–452. PMID: 24492278.
Article4. Jin Y, Li Q, Qiu J, Zhao X, Zheng C, Lv S, et al. Downregulation of paraoxonase 3 contributes to aggressive human hepatocellular carcinoma progression and associates with poor prognosis. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:14193–14203. PMID: 27553024.
Article5. Wu X, Chen H, Gao Q, Bai J, Wang X, Zhou J, et al. Downregulation of JWA promotes tumor invasion and predicts poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2014; 53:325–336. PMID: 23169062.
Article6. Reichl P, Mikulits W. Accuracy of novel diagnostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: an update for clinicians (review). Oncol Rep. 2016; 36:613–625. PMID: 27278244.
Article7. Lyons JG, Lobo E, Martorana AM, Myerscough MR. Clonal diversity in carcinomas: its implications for tumour progression and the contribution made to it by epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008; 25:665–677. PMID: 18071912.
Article8. Sung WJ, Kim H, Park KK. The biological role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer (review). Oncol Rep. 2016; 36:1199–1206. PMID: 27460444.
Article9. Xue Y, Xu W, Zhao W, Wang W, Zhang D, Wu P. miR-381 inhibited breast cancer cells proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting CXCR4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; 86:426–433. PMID: 28012397.
Article10. Migita T, Ueda A, Ohishi T, Hatano M, Seimiya H, Horiguchi SI, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes SOX2 and NANOG expression in bladder cancer. Lab Invest. 2017; 97:567–576.
Article11. Gandellini P, Giovannetti E, Nicassio F. MicroRNAs in cancer management: big challenges for small molecules. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:982156. PMID: 25879042.
Article12. Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ, Bushell M. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:e249–e258. PMID: 22652233.
Article13. Garzon R, Marcucci G. Potential of microRNAs for cancer diagnostics, prognostication and therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012; 24:655–659. PMID: 23079782.
Article14. Hu C, Lv L, Peng J, Liu D, Wang X, Zhou Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 suppresses esophageal cancer cell growth and invasion by repressing metadherin expression. Oncol Lett. 2017; 13:4769–4775. PMID: 28599478.
Article15. Guan H, Li W, Li Y, Wang J, Li Y, Tang Y, et al. MicroRNA-93 promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via targeting TIMP2. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0189490. PMID: 29220395.
Article16. Gao H, Cong X, Zhou J, Guan M. MicroRNA-222 influences migration and invasion through MIA3 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2017; 17:78. PMID: 28855850.
Article17. Pan XP, Huang LH, Wang X. MiR-370 functions as prognostic marker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017; 21:3581–3585. PMID: 28925487.18. Pan XP, Wang HX, Tong DM, Li Y, Huang LH, Wang C. miRNA-370 acts as a tumor suppressor via the downregulation of PIM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017; 21:1254–1263. PMID: 28387905.19. Bellet MM, Piobbico D, Bartoli D, Castelli M, Pieroni S, Brunacci C, et al. NEDD4 controls the expression of GUCD1, a protein upregulated in proliferating liver cells. Cell Cycle. 2014; 13:1902–1911. PMID: 24743017.
Article20. Della Fazia MA, Servillo G, Sassone-Corsi P. Cyclic AMP signalling and cellular proliferation: regulation of CREB and CREM. FEBS Lett. 1997; 410:22–24. PMID: 9247115.
Article21. Sands WA, Palmer TM. Regulating gene transcription in response to cyclic AMP elevation. Cell Signal. 2008; 20:460–466. PMID: 17993258.
Article22. Wang TH, Lin YS, Chen Y, Yeh CT, Huang YL, Hsieh TH, et al. Long non-coding RNA AOC4P suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by enhancing vimentin degradation and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:23342–23357. PMID: 26160837.
Article23. Chang RM, Xiao S, Lei X, Yang H, Fang F, Yang LY. miRNA-487a promotes proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 23:2593–2604. PMID: 27827315.
Article24. Li Q, Li S, Wu Y, Gao F. miRNA-708 functions as a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SMAD3. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14:2552–2558. PMID: 28789462.
Article25. Zeng YB, Liang XH, Zhang GX, Jiang N, Zhang T, Huang JY, et al. miRNA-135a promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting forkhead box O1. Cancer Cell Int. 2016; 16:63. PMID: 27486383.
Article26. Ning T, Zhang H, Wang X, Li S, Zhang L, Deng T, et al. miR-370 regulates cell proliferation and migration by targeting EGFR in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2017; 38:384–392. PMID: 28534999.
Article27. Han Y, Yang X, Zhao N, Peng J, Gao H, Qiu X. Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling. Am J Cancer Res. 2016; 6:2755–2771. PMID: 28042498.28. Li W, Cheng P, Nie S, Cui W. miR-370 mimic inhibits replication of Japanese encephalitis virus in glioblastoma cells. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016; 12:2411–2417. PMID: 27703358.29. Giannelli G, Villa E, Lahn M. Transforming growth factor-β as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014; 74:1890–1894. PMID: 24638984.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to “MicroRNA-370 Regulates Cellepithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration, Invasion, and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting GUCD1†by He Y and He X (Yonsei Med J 2019;60:267–276.)
- Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
- CDH3/P-Cadherin regulates migration of HuCCT1 cholangiocarcinoma cells
- MicroRNA-373 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Targeting BRF2 in Human Non-small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cell Line
- MicroRNA-98-5p Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase