Korean J Leg Med.
2019 Feb;43(1):28-32. 10.7580/kjlm.2019.43.1.28.
Accidental Sharp Force Fatality Caused by a Broken Glass Cup
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Forensic Investigation, National Forensic Service Seoul Institute, Seoul, Korea. sanchee@korea.kr
- KMID: 2440396
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2019.43.1.28
Abstract
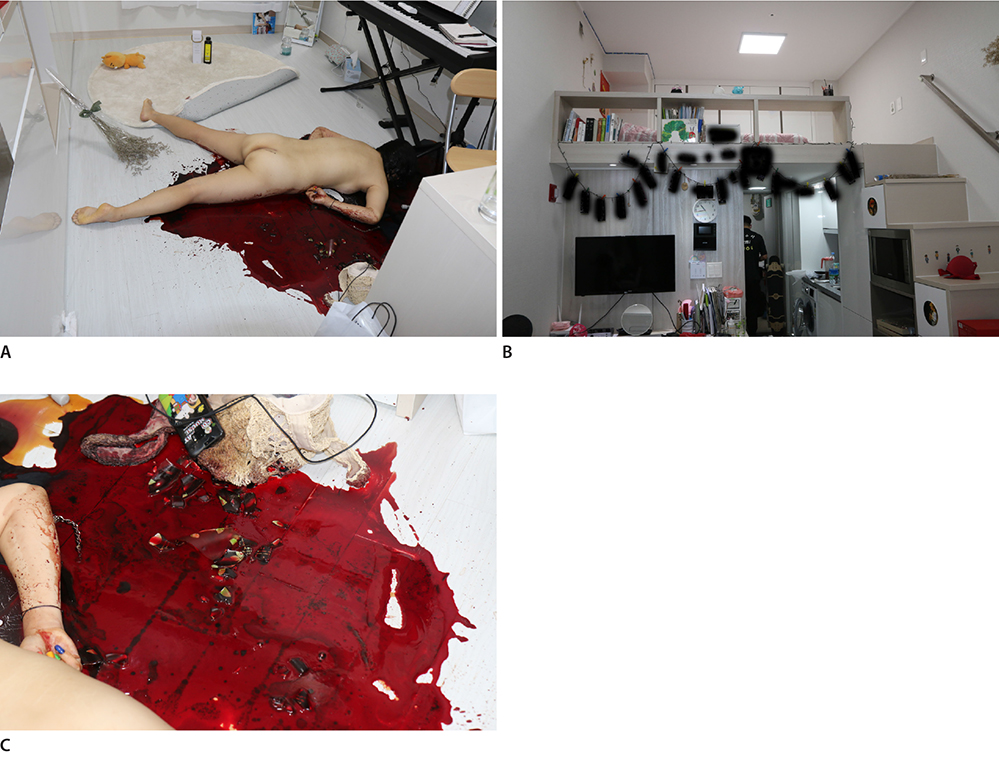
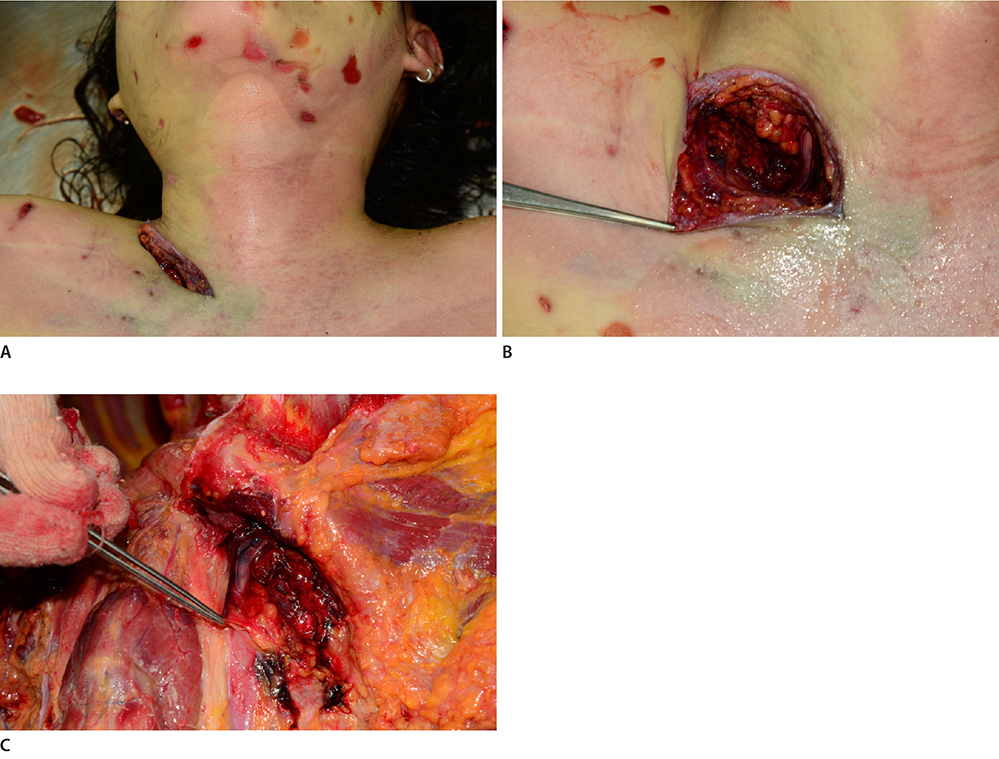
- Most sharp force fatalities are attributed to homicide or suicide, with only a few accidental cases reported to date. Broken glass accounts for most of these accidental fatalities. We herein report an unusual accidental death caused by a broken glass cup. A 21-year-old woman was found dead on the floor of her studio apartment. The studio was a duplex consisting of one room and a bathroom, with a stepped drawer leading to the second floor. She was lying face down with her legs spread apart in a large pool of blood, surrounded by many pieces of broken glass. There was an oblique cut measuring 9 cm in length in the right sternocleidomastoid region just above the right clavicle. The surface of the cut wound showed irregular edges and the internal jugular vein was severed in the depth of the wound. She appeared to have fallen down the steps onto the ground floor and been fatally injured in the neck by a piece of broken glass.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karger B, Rothschild MA, Pfeiffer H. Accidental sharp force fatalities: beware of architectural glass, not knives. Forensic Sci Int. 2001; 123:135–139.2. Vassalini M, Verzeletti A, De Ferrari F. Sharp force injury fatalities: a retrospective study (1982-2012) in Brescia (Italy). J Forensic Sci. 2014; 59:1568–1574.
Article3. Prahlow JA, Ross KF, Lene WJ, et al. Accidental sharp force injury fatalities. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2001; 22:358–366.
Article4. Murphy GK. A single fatal penetrating chest wound from shattered wind-blown glass. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1985; 6:332–335.
Article5. Ormstad K, Karlsson T, Enkler L, et al. Patterns in sharp force fatalities: a comprehensive forensic medical study. J Forensic Sci. 1986; 31:529–542.6. Shiono H, Fujiwara M, Tabata N, et al. A single fatal penetrating chest wound caused by a dagger-shaped fragment of broken door glass. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1987; 8:346–349.
Article7. Roh JH, Park HJ, Kim HJ, et al. Fatal injury due to shattered fragments of brittle materials. Korean J Leg Med. 2010; 34:63–66.8. Byard RW, Cains GE, Gilbert JD. Use of a pig model to demonstrate vulnerability of major neck vessels to inflicted trauma from common household items. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2007; 28:31–34.
Article9. Lee SH, Lee SD, Heo KY, et al. textbook of legal medicine. Seoul: Jungmunkag;2018. p. 118–122.10. Dettmeyer R, Verhoff MA, Schutz HF. Forensic medicine: fundamentals and perspectives. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;2014. p. 141–142.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The shear bond strength of two adhesives bonded to composite resin and glass ionomer cement restorations
- Effects of a Finger Guard while Opening the Glass Ampoule by Nursing Students
- Rectal Foreign Body (Glass Cup) Extracted by Laparotomy
- Radiological , Biomechanical and Histological Analysis on the Surgical Treatment of Bone Defect in Rabbit Tibia using Glass Ceramics
- Significance of Knife Tip Injuries as Hesitation Marks