Ann Dermatol.
2019 Apr;31(2):127-132. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.127.
Analysis of Clinical Features and Treatment Outcomes Using 1,064-nm Nd-YAG Laser with Topical Hydroquinone in Patients with Riehl's Melanosis: A Retrospective Study in 10 Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jehomun@gmail.com
- 2Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Institute of Human-Environment Interface Biology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2439057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.2.127
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Hyperpigmentation on the face and neck can be a devastating psychological burden in patients with Riehl's melanosis. However, successful treatment of the disease is challenging for clinicians.
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of low-fluence neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser in the treatment of Riehl's melanosis and to identify prognostic factors determining the response to laser treatment.
METHODS
We enrolled 10 Korean patients with Riehl's melanosis. The patients received 10~28 treatment sessions at 3-week intervals with low-fluence Nd:YAG laser.
RESULTS
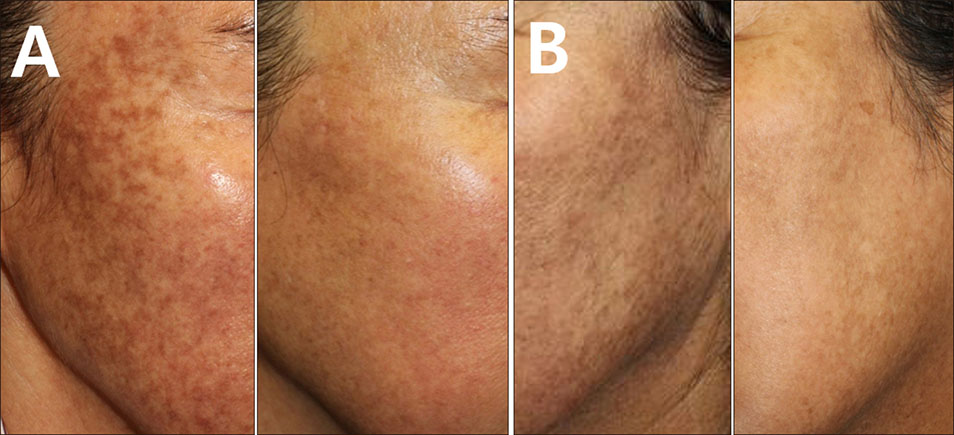
Among all the patients, seven reached near total improvement, and two and one patient reached marked improvement and minimal improvement, respectively, after low-fluence Nd:YAG laser treatment. The mean number of needed laser treatment sessions to reach marked improvement and near total improvement was 12.1±4.0 (ranged from 6 to 17) and 14.6±4.4 (ranged from 9 to 20), respectively. A further analysis revealed the proportion of patients who reached near total improvement was higher, and the mean number of necessary laser treatment sessions to reach minimal improvement was less in patients with dark brown pigmentation compared to those with light brown pigmentation. Among all patients, three complained of guttate hypopigmentation. However, the hypopigmented lesions spontaneously improved after the interruption of the treatment.
CONCLUSION
We found that low-fluence Nd:YAG laser is an effective and safe treatment modality for Riehl's melanosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Serrano G, Pujol C, Cuadra J, Gallo S, Aliaga A. Riehl's melanosis: pigmented contact dermatitis caused by fragrances. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989; 21:1057–1060.
Article2. Chung BY, Kim JE, Ko JY, Chang SE. A pilot study of a novel dual--pulsed 1064 nm Q-switched Nd: YAG laser to treat Riehl's melanosis. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2014; 16:290–292.
Article3. Choi CW, Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Kim YH, Kim WS. Treatment of nevus of Ota using low fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. Int J Dermatol. 2014; 53:861–865.
Article4. Jeong SY, Shin JB, Yeo UC, Kim WS, Kim IH. Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser for melasma with pre- or post-treatment triple combination cream. Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:909–918.
Article5. Kim S, Cho KH. Treatment of procedure-related postinflammatory hyperpigmentation using 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with low fluence in Asian patients: report of five cases. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2010; 9:302–306.
Article6. Nam JH, Kim HS, Lee GY, Kim WS. Beneficial effect of low fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet laser in the treatment of senile lentigo. Ann Dermatol. 2017; 29:427–432.
Article7. Nam JH, Kim HS, Choi YJ, Jung HJ, Kim WS. Treatment and classification of nevus of ota: a seven-year review of a single institution's experience. Ann Dermatol. 2017; 29:446–453.
Article8. Mun JY, Jeong SY, Kim JH, Han SS, Kim IH. A low fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser modifies the 3D structure of melanocyte and ultrastructure of melanosome by subcellular-selective photothermolysis. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2011; 60:11–18.
Article9. Kwon HH, Ohn J, Suh DH, Park HY, Choi SC, Jung JY, et al. A pilot study for triple combination therapy with a low-fluence 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser, hydroquinone cream and oral tranexamic acid for recalcitrant Riehl's Melanosis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017; 28:155–159.
Article10. Sugai T, Takahashi Y, Takagi T. Pigmented cosmetic dermatitis and coal tar dyes. Contact Dermatitis. 1977; 3:249–256.11. Kim S, Cho KH. Treatment of facial postinflammatory hyperpigmentation with facial acne in Asian patients using a Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser. Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:1374–1380.
Article12. Wong Y, Lee SS, Goh CL. Hypopigmentation induced by frequent low-fluence, large-spot-size QS Nd:YAG laser treatments. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:751–755.
Article13. Grimes PE, Bhawan J, Kim J, Chiu M, Lask G. Laser resurfacing-induced hypopigmentation: histologic alterations and repigmentation with topical photochemotherapy. Dermatol Surg. 2001; 27:515–520.
Article14. Weismann K, Lorentzen HF. Dermoscopic color perspective. Arch Dermatol. 2006; 142:1250.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effective Treatment of Suspicious Riehl's Melanosis Using Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser and 595 nm Pulsed Dye Laser
- Two Cases of Toenail Onychomycosis Treated by 1,064 nm Nd:YAG Laser
- Beneficial Effect of Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Neodymium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser in the Treatment of Senile Lentigo
- Treatment Outcomes of Combination Therapy with 1,064-nm Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Laser and Efinaconazole 10% Solution for Big Toenail Onychomycosis: a Retrospective Study
- 1,064 nm Long-Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser for the Treatment of Onychomycosis