J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2012 Dec;42(6):243-247.
A comparison of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric ultrasonic scaling devices: an in vitro study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Periodontology, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry, Ahwaz, Iran. Hojjatyoosefi@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Oral Medicine, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry, Ahwaz, Iran.
- 3Department of Periodontology, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran, Iran.
- 4Department of Periodontology, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry, Mashhad, Iran.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The effects of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric devices on tooth surfaces seem to differ with regard to the root surface roughness they produce. This study aimed to compare the results of scaling using magnetostrictive and piezoelectric devices on extracted teeth.
METHODS
Forty-four human extracted teeth were assigned to four study groups (n=11). In two groups (C100 and C200), the teeth were scaled using a magnetostrictive device and two different lateral forces: 100 g and 200 g, respectively. In the other two groups (P100 and P200), the teeth were scaled with a piezoelectric device with 100 g and 200 g of lateral force, respectively. he teeth were scaled and the data on the duration of scaling and the amount of surface were collected and analyzed using the t-test.
RESULTS
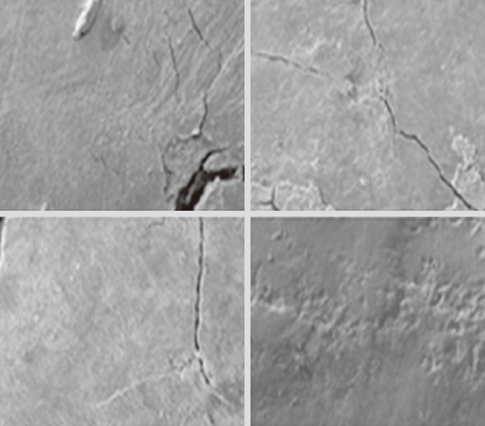
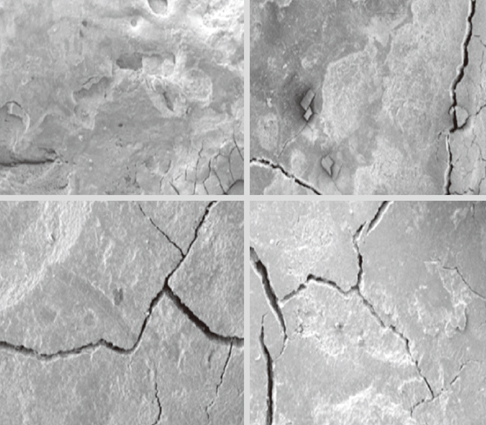
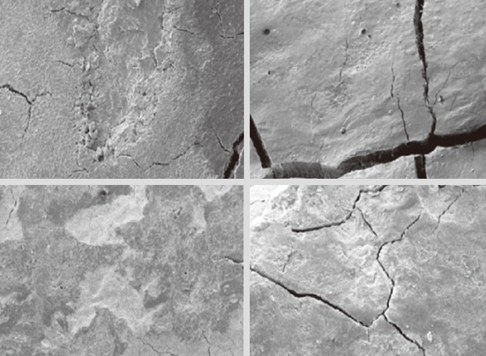
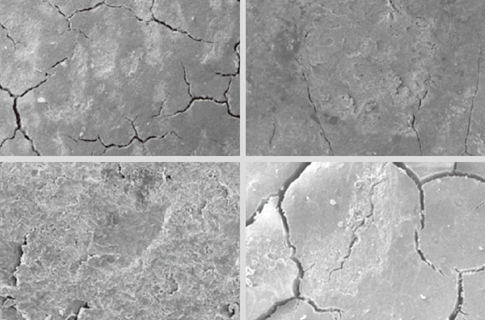
The mean time needed for instrumentation for the piezoelectric and magnetostrictive devices was 50:54 and 41:10, respectively, but their difference was not statistically significant (P=0.171). For root surface roughness, we only found a statistically significantly poorer result for the C200 group in comparison to the P200 group (P=0.033).
CONCLUSIONS
This study revealed that applying a piezoelectric scaler with 200 g of lateral force leaves smoother surfaces than a magnetostrictive device with the same lateral force.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rosling B, Hellstrom MK, Ramberg P, Socransky SS, Lindhe J. The use of PVP-iodine as an adjunct to non-surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 2001. 28:1023–1031.
Article2. Obeid PR, D'Hoore W, Bercy P. Comparative clinical responses related to the use of various periodontal instrumentation. J Clin Periodontol. 2004. 31:193–199.
Article3. Petersilka GJ, Draenert M, Mehl A, Hickel R, Flemmig TF. Safety and efficiency of novel sonic scaler tips in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 2003. 30:551–555.
Article4. Jotikasthira NE, Lie T, Leknes KN. Comparative in vitro studies of sonic, ultrasonic and reciprocating scaling instruments. J Clin Periodontol. 1992. 19:560–569.
Article5. Copulos TA, Low SB, Walker CB, Trebilcock YY, Hefti AF. Comparative analysis between a modified ultrasonic tip and hand instruments on clinical parameters of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1993. 64:694–700.
Article6. Schenk G, Flemmig TF, Lob S, Ruckdeschel G, Hickel R. Lack of antimicrobial effect on periodontopathic bacteria by ultrasonic and sonic scalers in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 2000. 27:116–119.
Article7. Arabaci T, Cicek Y, Canakci CF. Sonic and ultrasonic scalers in periodontal treatment: a review. Int J Dent Hyg. 2007. 5:2–12.
Article8. Flemmig TF, Petersilka GJ, Mehl A, Hickel R, Klaiber B. Working parameters of a magnetostrictive ultrasonic scaler influencing root substance removal in vitro. J Periodontol. 1998. 69:547–553.
Article9. Busslinger A, Lampe K, Beuchat M, Lehmann B. A comparative in vitro study of a magnetostrictive and a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaling instrument. J Clin Periodontol. 2001. 28:642–649.
Article10. Kocher T, Langenbeck N, Rosin M, Bernhardt O. Methodology of three-dimensional determination of root surface roughness. J Periodontal Res. 2002. 37:125–131.
Article11. Leknes KN, Lie T, Wikesjo UM, Bogle GC, Selvig KA. Influence of tooth instrumentation roughness on subgingival microbial colonization. J Periodontol. 1994. 65:303–308.
Article12. Flemmig TF, Petersilka GJ, Mehl A, Hickel R, Klaiber B. The effect of working parameters on root substance removal using a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaler in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 1998. 25:158–163.
Article13. Santos FA, Pochapski MT, Leal PC, Gimenes-Sakima PP, Marcantonio E Jr. Comparative study on the effect of ultrasonic instruments on the root surface in vivo. Clin Oral Investig. 2008. 12:143–150.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Pain Reduction and Clinical Efficacy of Feedback-Controlled Ultrasonic Scaler
- The Effect of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Scaler with Curette Tip on Root Substitute Removal in Vitro
- The Effect of a Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Scaler with Curette Tip on Casting Gold Removal in Vitro
- Comparative evaluation of roughness of titanium surfaces treated by different hygiene instruments
- Effect of a metallic ultrasonic scaler tip on titanium surfaces: a preliminary study