Korean J Radiol.
2019 Mar;20(3):469-478. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0517.
Cervical Spine CT Using Spectral Shaping: Can It Be a Solution to Overcome Artifacts in the Lower Cervical Spinal Region?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea. hyejungchoo@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2438277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0517
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the image quality, radiation dose, and intermodality agreement of cervical spine CT using spectral shaping at 140 kVp by a tin filter (Sn140-kVp) in comparison with those of conventional CT at 120 kVp.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
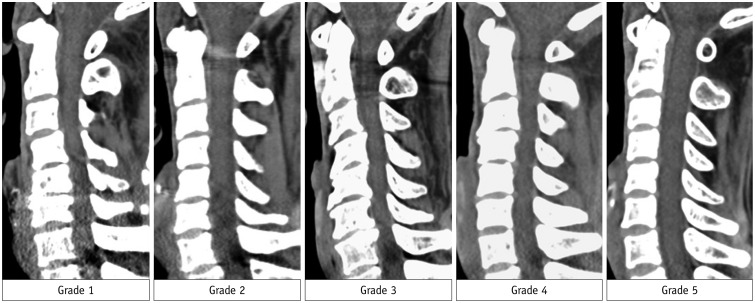
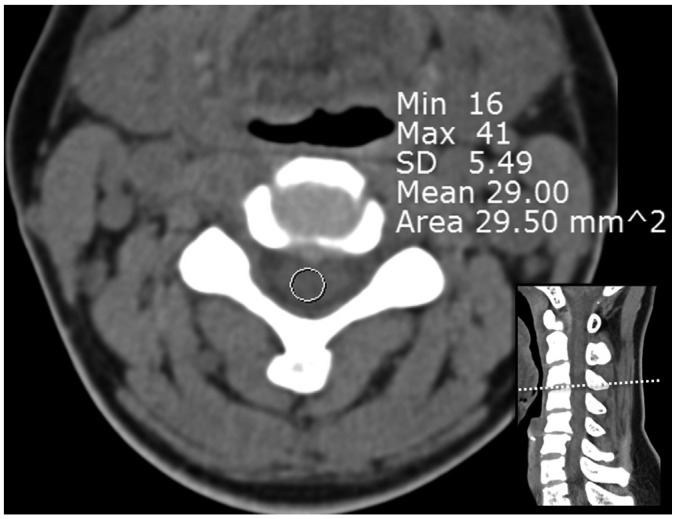
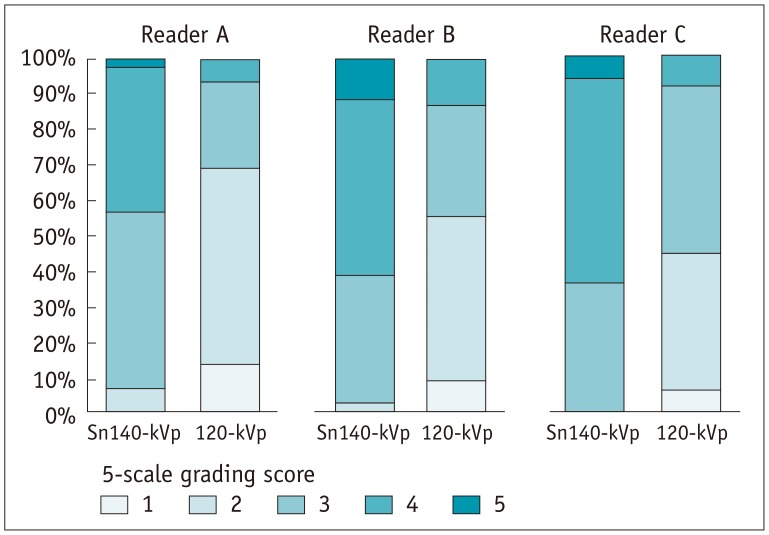
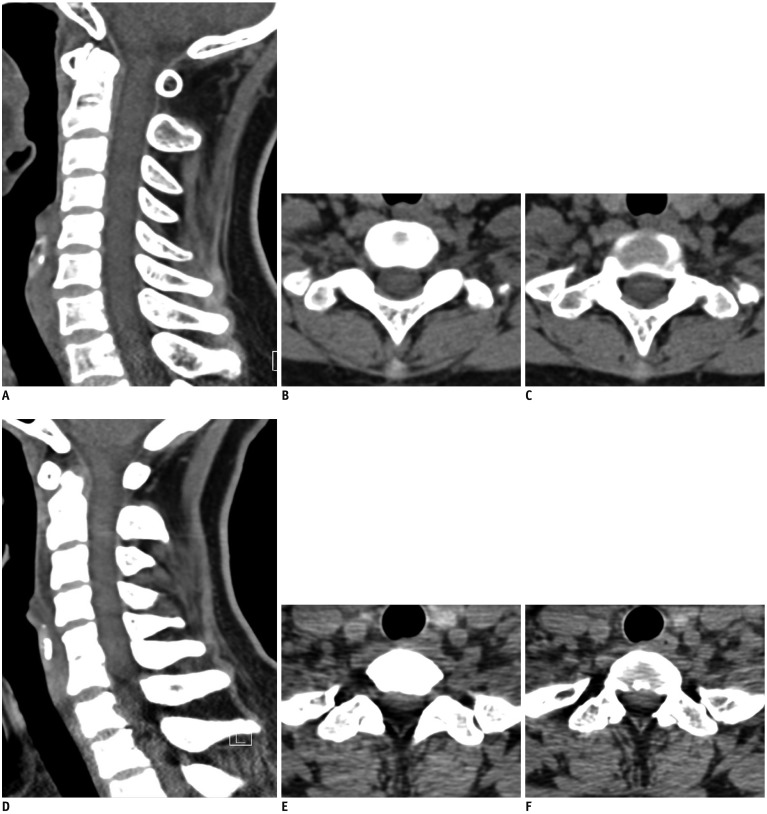
Patients who had undergone cervical spine CT with Sn140-kVp (n = 58) and conventional 120 kVp (n = 49) were included. Qualitative image quality was analyzed using a 5-point Likert scale. Quantitative image quality was assessed by measuring the noise and attenuation within the central spinal canals at C3/4, C6/7, and C7/T1 levels. Radiation doses received by patients were estimated. The intermodality agreement for disc morphology between CT and MRI was assessed at C3/4, C5/6, C6/7, and C7/T1 levels in 75 patients who had undergone cervical spine MRI as well as CT.
RESULTS
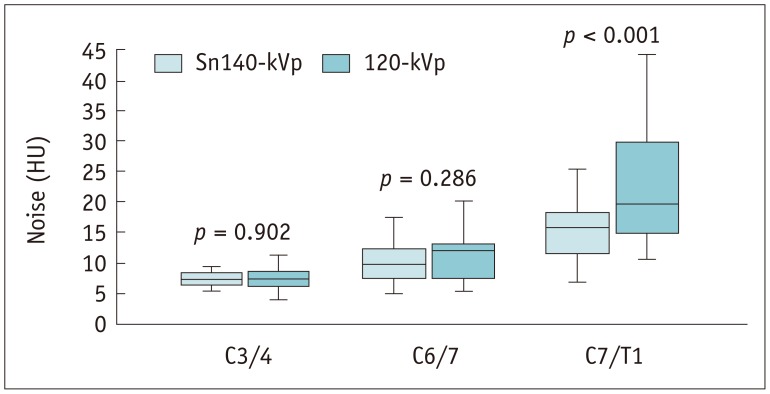
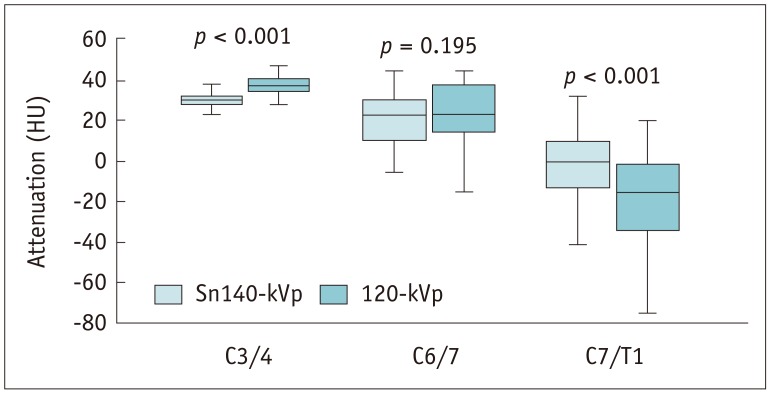
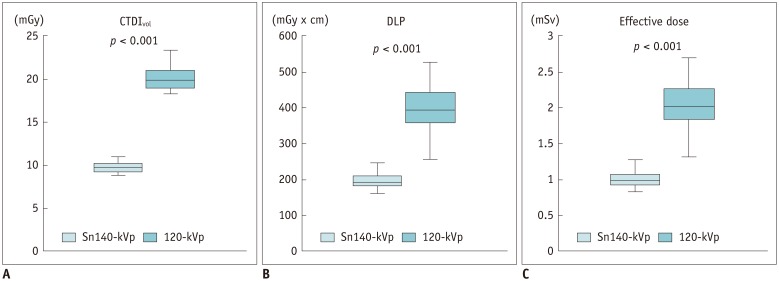
Qualitative image quality was significantly superior in Sn140-kVp scans than in the conventional scans (p < 0.001). At C7/T1 level, the noise was significantly lower and the decrease in attenuation was significantly less in Sn140-kVp scans, than in the conventional scans (p < 0.001). Radiation doses were significantly reduced in Sn140-kVp scans by 50% (effective dose: 1.0 ± 0.1 mSv vs. 2.0 ± 0.4 mSv; p < 0.001). Intermodality agreement in the lower cervical spine region tended to be better in Sn140-kVp acquisitions than in the conventional acquisitions.
CONCLUSION
Cervical spine CT using Sn140-kVp improves image quality of the lower cervical region without increasing the radiation dose. Thus, this protocol can be helpful to overcome the artifacts in the lower cervical spine CT images.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Daffner RH, Hackney DB. ACR Appropriateness Criteria on suspected spine trauma. J Am Coll Radiol. 2007; 4:762–775. PMID: 17964500.
Article2. Douglas-Akinwande AC, Rydberg J, Shah MV, Phillips MD, Caldemeyer KS, Lurito JT, et al. Accuracy of contrast-enhanced MDCT and MRI for identifying the severity and cause of neural foraminal stenosis in cervical radiculopathy: a prospective study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:55–61. PMID: 20028905.
Article3. Barrett JF, Keat N. Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics. 2004; 24:1679–1691. PMID: 15537976.
Article4. Mori I, Machida Y, Osanai M, Iinuma K. Photon starvation artifacts of X-ray CT: their true cause and a solution. Radiol Phys Technol. 2013; 6:130–141. PMID: 23054905.
Article5. Mayo-Smith WW, Hara AK, Mahesh M, Sahani DV, Pavlicek W. How I do it: managing radiation dose in CT. Radiology. 2014; 273:657–672. PMID: 25420167.
Article6. Mueck FG, Roesch S, Geyer L, Scherr M, Seidenbusch M, Stahl R, et al. Emergency CT head and neck imaging: effects of swimmer's position on dose and image quality. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24:969–979. PMID: 24531843.
Article7. Primak AN, Ramirez Giraldo JC, Liu X, Yu L, McCollough CH. Improved dual-energy material discrimination for dual-source CT by means of additional spectral filtration. Med Phys. 2009; 36:1359–1369. PMID: 19472643.
Article8. Braun FM, Johnson TR, Sommer WH, Thierfelder KM, Meinel FG. Chest CT using spectral filtration: radiation dose, image quality, and spectrum of clinical utility. Eur Radiol. 2015; 25:1598–1606. PMID: 25515204.
Article9. Gordic S, Morsbach F, Schmidt B, Allmendinger T, Flohr T, Husarik D, et al. Ultralow-dose chest computed tomography for pulmonary nodule detection: first performance evaluation of single energy scanning with spectral shaping. Invest Radiol. 2014; 49:465–473. PMID: 24598443.10. Haubenreisser H, Meyer M, Sudarski S, Allmendinger T, Schoenberg SO, Henzler T. Unenhanced third-generation dual-source chest CT using a tin filter for spectral shaping at 100kVp. Eur J Radiol. 2015; 84:1608–1613. PMID: 26001437.11. May MS, Brand M, Lell MM, Sedlmair M, Allmendinger T, Uder M, et al. Radiation dose reduction in parasinus CT by spectral shaping. Neuroradiology. 2017; 59:169–176. PMID: 28091696.
Article12. Kim CR, Jeon JY. Radiation dose and image conspicuity comparison between conventional 120 kVp and 150 kVp with spectral beam shaping for temporal bone CT. Eur J Radiol. 2018; 102:68–73. PMID: 29685547.13. Suntharalingam S, Mikat C, Wetter A, Guberina N, Salem A, Heil P, et al. Whole-body ultra-low dose CT using spectral shaping for detection of osteolytic lesion in multiple myeloma. Eur Radiol. 2018; 28:2273–2280. PMID: 29322333.
Article14. Becce F, Ben Salah Y, Verdun FR, Vande Berg BC, Lecouvet FE, Meuli R, et al. Computed tomography of the cervical spine: comparison of image quality between a standard-dose and a low-dose protocol using filtered back-projection and iterative reconstruction. Skeletal Radiol. 2013; 42:937–945. PMID: 23359034.
Article15. Lee SH, Lee YH, Suh JS. Accelerating knee MR imaging: compressed sensing in isotropic three-dimensional fast spin-echo sequence. Magn Reson Imaging. 2018; 46:90–97. PMID: 29103976.
Article16. Fardon DF, Williams AL, Dohring EJ, Murtagh FR, Gabriel Rothman SL, Sze GK. Lumbar disc nomenclature: version 2.0: recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology. Spine J. 2014; 14:2525–2545. PMID: 24768732.17. Deak PD, Smal Y, Kalender WA. Multisection CT protocols: sex- and age-specific conversion factors used to determine effective dose from dose-length product. Radiology. 2010; 257:158–166. PMID: 20851940.
Article18. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–174. PMID: 843571.
Article19. Krauss B, Grant KL, Schmidt BT, Flohr TG. The importance of spectral separation: an assessment of dual-energy spectral separation for quantitative ability and dose efficiency. Invest Radiol. 2015; 50:114–118. PMID: 25373305.20. Stolzmann P, Leschka S, Scheffel H, Rentsch K, Baumüller S, Desbiolles L, et al. Characterization of urinary stones with dual-energy CT: improved differentiation using a tin filter. Invest Radiol. 2010; 45:1–6. PMID: 19996763.21. Wang CK, Tsai JM, Chuang MT, Wang MT, Huang KY, Lin RM. Bone marrow edema in vertebral compression fractures: detection with dual-energy CT. Radiology. 2013; 269:525–533. PMID: 23801776.
Article22. Jeon JY, Lee SW, Jeong YM, Baek HJ. The effect of tube voltage combination on image artefact and radiation dose in dual-source dual-energy CT: comparison between conventional 80/140 kV and 80/150 kV plus tin filter for gout protocol. Eur Radiol. 2018; 7. 09. [Epub ahead of print]. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-018-5622-9.
Article23. Wichmann JL, Hardie AD, Schoepf UJ, Felmly LM, Perry JD, Varga-Szemes A, et al. Single- and dual-energy CT of the abdomen: comparison of radiation dose and image quality of 2nd and 3rd generation dual-source CT. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:642–650. PMID: 27165140.
Article24. Yi JS, Cha JG, Han JK, Kim HJ. Imaging of herniated discs of the cervical spine: inter-modality differences between 64-slice multidetector CT and 1.5-T MRI. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:881–888. PMID: 26175589.
Article25. Iyama Y, Nakaura T, Iyama A, Kidoh M, Katahira K, Oda S, et al. Feasibility of iterative model reconstruction for unenhanced lumbar CT. Radiology. 2017; 284:153–160. PMID: 28156203.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Motion Induced Artifact Mimicking Cervical Dens Fracture on the CT Scan: A Case Report
- Maximal Benefit Zone of Endoscopic Spine Surgery in the Cervical and Thoracic Spine: Rationale of Endoscopic Spine Surgery in the Cervical-thoracic Region
- Radiographic Measurement of Normal Adult Cervical Spinal Region in the Korean Population
- Clinical Analysis of Lower Cervical Spine-Injuried Patients
- Pattern of Cervical Spine Injury in Patients with a Facial Fracture