Anesth Pain Med.
2018 Jan;13(1):65-71. 10.17085/apm.2018.13.1.65.
Beneficial aspect of dexmedetomidine as a postoperative sedative for cardiac surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. twowind@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2436058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2018.13.1.65
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to compare the clinical outcomes of the sedative, analgesic, and hemodynamic effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
METHODS
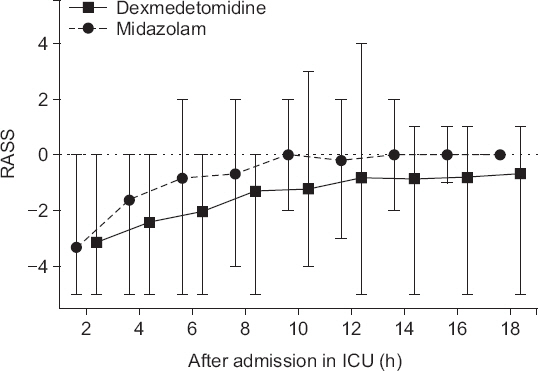
The adult patients undergoing elective CABG surgery under general anesthesia were randomly assigned to the dexmedetomidine (DEX) and midazolam (MDZ) groups. From the time of the sternal closure, dexmedetomidine (0.5-0.7 μg/kg/h) was continuously administered (DEX group), and midazolam (0.03-0.1 mg/kg) was administered by bolus (MDZ group). To maintain the target sedation level (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale [RASS] range, −2 to −1) until extubation in the intensive care unit (ICU), continuous doses of dexmedetomidine were regulated and midazolam was administered intermittently. Sedation (RASS) and pain scores (visual analogue scale) and hemodynamic changes were recorded every two hours, until the end of the mechanical ventilation assistance after entering the ICU.
RESULTS
The mean of the fraction within the target sedation level in each patient's total sedation time was 41.0% in the DEX group and 20.7% in the MDZ group (P = 0.026). In the DEX group, the RASS (P < 0.001) and cardiac index were lower (P = 0.047) than those in the MDZ group, but the other hemodynamic parameters and pain scores were not different.
CONCLUSIONS
This study showed that post-operative infusion of dexmedetomidine maintained a stable sedation without side effects in patients who underwent CABG surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dawood MM, Gutpa DK, Southern J, Walia A, Atkinson JB, Eagle KA. Pathology of fatal perioperative myocardial infarction: implications regarding pathophysiology and prevention. Int J Cardiol. 1996; 57:37–44. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-5273(96)02769-6.2. Warltier DC, Pagel PS, Kersten JR. Approaches to the prevention of perioperative myocardial ischemia. Anesthesiology. 2000; 92:253–9. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200001000-00038. PMID: 10638923.3. Payen JF, Bosson JL, Chanques G, Mantz J, Labarere J. DOLOREA Investigators. Pain assessment is associated with decreased duration of mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit: a post Hoc analysis of the DOLOREA study. Anesthesiology. 2009; 111:1308–16. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181c0d4f0. PMID: 19934877.4. Afonso J, Reis F. Dexmedetomidine: current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2012; 62:118–33. DOI: 10.1016/S0034-7094(12)70110-1.5. Talke P, Richardson CA, Scheinin M, Fisher DM. Postoperative pharmacokinetics and sympatholytic effects of dexmedetomidine. Anesth Analg. 1997; 85:1136–42. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-199711000-00033. PMID: 9356115.6. Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2009; 301:489–99. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2009.56. PMID: 19188334.7. Sessler CN, Gosnell MS, Grap MJ, Brophy GM, O’Neal PV, Keane KA, et al. The Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale: validity and reliability in adult intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:1338–44. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.2107138. PMID: 12421743.8. Adams R, Brown GT, Davidson M, Fisher E, Mathisen J, Thomson G, et al. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for sedation in adult intensive care patients: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth. 2013; 111:703–10. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aet194. PMID: 23748199.9. Dutta S, Lal R, Karol MD, Cohen T, Ebert T. Influence of cardiac output on dexmedetomidine pharmacokinetics. J Pharm Sci. 2000; 89:519–27. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6017(200004)89:4<519::AID-JPS9>3.0.CO;2-U.10. Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000; 93:382–94. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-200008000-00016. PMID: 10910487.11. Shafer A. Complications of sedation with midazolam in the intensive care unit and a comparison with other sedative regimens. Crit Care Med. 1998; 26:947–56. DOI: 10.1097/00003246-199805000-00034. PMID: 9590327.12. Forster A, Gardaz JP, Suter PM, Gemperle M. Respiratory depression by midazolam and diazepam. Anesthesiology. 1980; 53:494–7. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-198012000-00010. PMID: 7457966.13. Barletta JF, Miedema SL, Wiseman D, Heiser JC, McAllen KJ. Impact of dexmedetomidine on analgesic requirements in patients after cardiac surgery in a fast-track recovery room setting. Pharmacotherapy. 2009; 29:1427–32. DOI: 10.1592/phco.29.12.1427. PMID: 19947802.14. Friesen RH, Nichols CS, Twite MD, Cardwell KA, Pan Z, Pietra B, et al. The hemodynamic response to dexmedetomidine loading dose in children with and without pulmonary hypertension. Anesth Analg. 2013; 117:953–9. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a15aa6. PMID: 23960035. PMCID: PMC3830564.15. Yeom JH, Oh MK, Ahn D, Park SI. A loading dose of 1 μg/kg and maintenance dose of 0.5 μg/kg/h of dexmedetomidine for sedation under spinal anesthesia may induce excessive sedation and airway obstruction. Anesth Pain Med. 2016; 11:255–9. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2016.11.3.255.16. Tan JA, Ho KM. Use of dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic agent in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:926–39. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-010-1877-6. PMID: 20376429.17. Lee SH, Choi YS, Hong GR, Oh YJ. Echocardiographic evaluation of the effects of dexmedetomidine on cardiac function during total intravenous anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2015; 70:1052–9. DOI: 10.1111/anae.13084. PMID: 25919658.18. Hammer GB, Drover DR, Cao H, Jackson E, Williams GD, Ramamoorthy C, et al. The effects of dexmedetomidine on cardiac electrophysiology in children. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:79–83. DOI: 10.1213/01.ane.0000297421.92857.4e. PMID: 18165557.19. Bharati S, Pal A, Biswas C, Biswas R. Incidence of cardiac arrest increases with the indiscriminate use of dexmedetomidine: a case series and review of published case reports. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2011; 49:165–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.aat.2011.11.010. PMID: 22221692.20. Sichrovsky TC, Mittal S, Steinberg JS. Dexmedetomidine sedation leading to refractory cardiogenic shock. Anesth Analg. 2008; 106:1784–6. DOI: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318172fafc. PMID: 18499610.21. Herr DL, Sum-Ping ST, England M. ICU sedation after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: dexmedetomidine-based versus propofol-based sedation regimens. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2003; 17:576–84. DOI: 10.1016/S1053-0770(03)00200-3.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine for Postoperative Delirium in Adult Cardiac Surgery on Cardiopulmonary Bypass
- Dexmedetomidine: present and future directions
- Sedation with Dexmedetomidine during Tracheostomy in Severe Tracheal Stenotic Patients
- The alternative of oral sedation for pediatric dental care
- Postoperative infusion of a low dose of dexmedetomidine reduces intravenous consumption of sufentanil in patient-controlled analgesia