J Vet Sci.
2019 Jan;20(1):34-42. 10.4142/jvs.2019.20.1.34.
High-content analysis of in vitro hepatocyte injury induced by various hepatotoxicants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Toxicological Evaluation Laboratory, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, Gimcheon 39660, Korea. kuho@korea.kr
- KMID: 2434775
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2019.20.1.34
Abstract
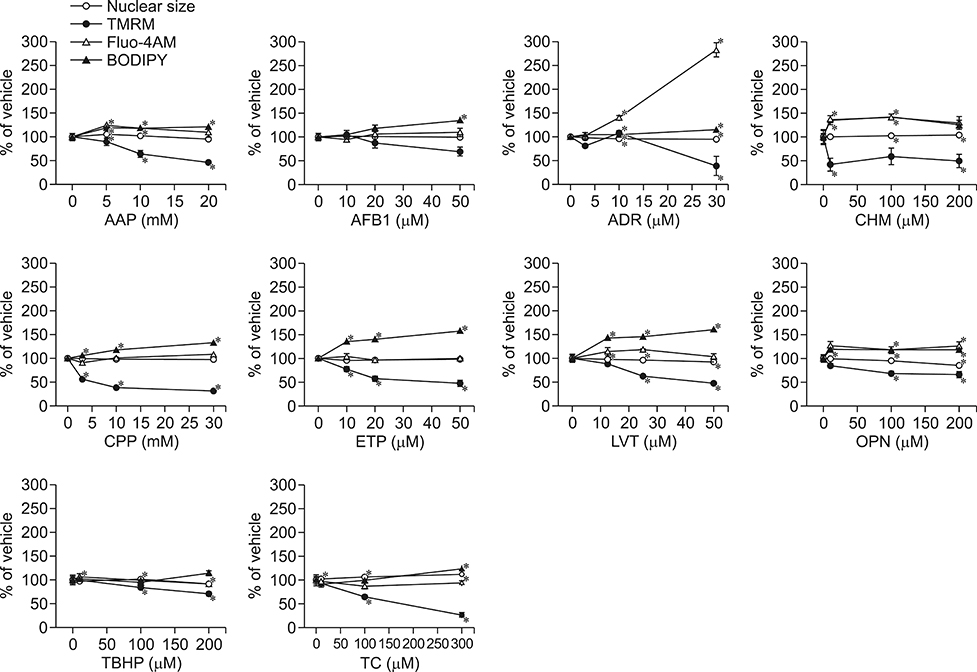
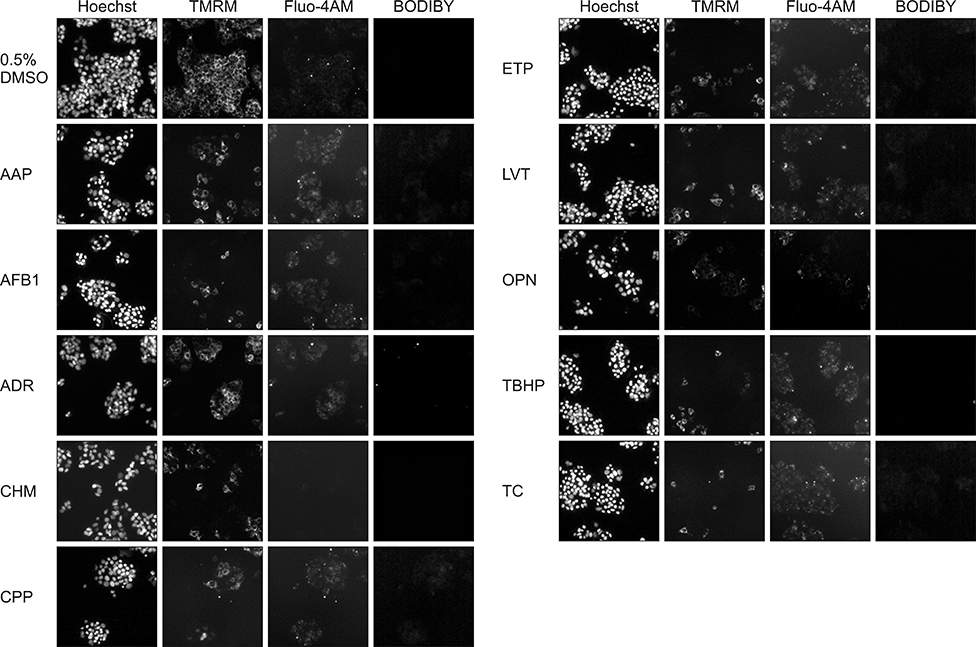
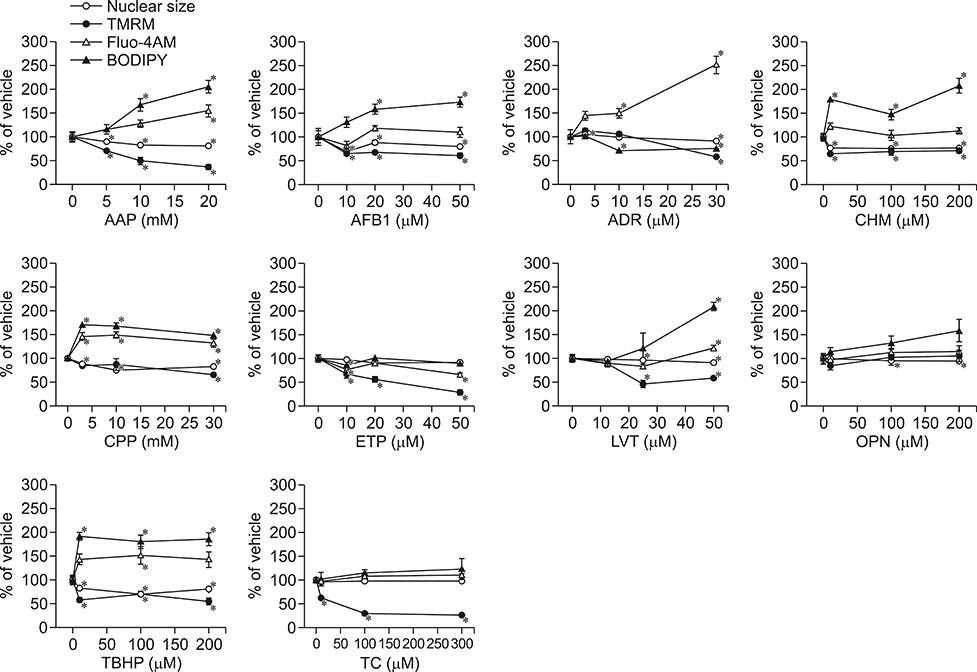
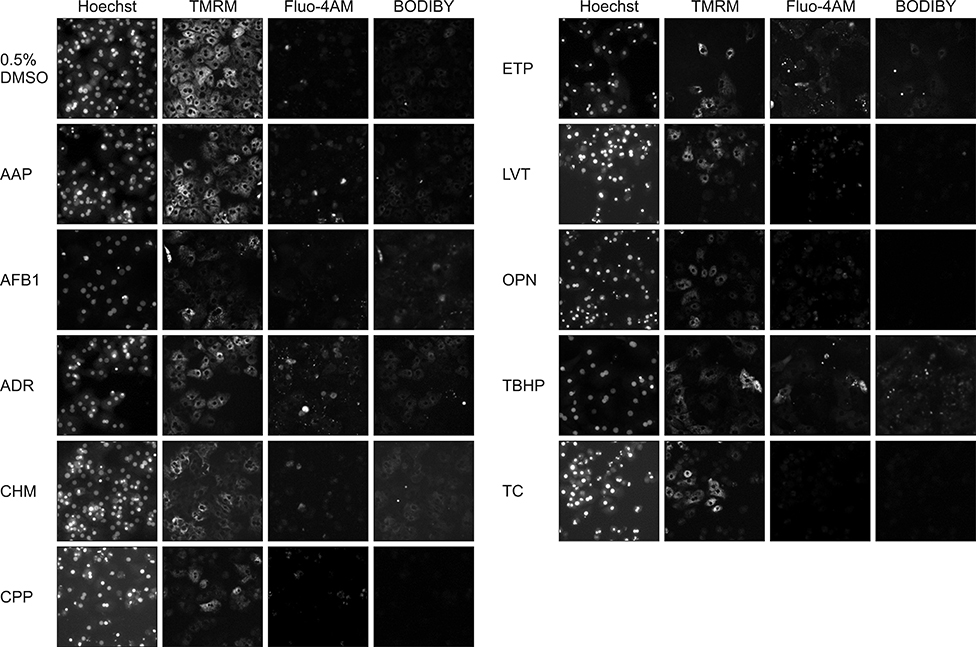
- In vitro prediction of hepatotoxicity can enhance the performance of non-clinical animal testing for identifying chemical hazards. In this study, we assessed high-content analysis (HCA) using multi-parameter cell-based assays as an in vitro hepatotoxicity testing model using various hepatotoxicants and human hepatocytes such as HepG2 cells and human primary hepatocytes (hPHs). Both hepatocyte types were exposed separately to multiple doses of ten hepatotoxicants associated with liver injury whose mechanisms of action have been described. HCA data were obtained using fluorescence probes for nuclear size (Hoechst), mitochondrial membrane potential (TMRM), cytosolic free calcium (Fluo-4AM), and lipid peroxidation (BODIPY). Cellular alterations were observed in response to all hepatotoxicants tested. The most sensitive parameter was TMRM, with high sensitivity at a low dose, next was BODIPY, followed by Fluo-4AM. HCA data from HepG2 cells and hPHs were generally concordant, although some inconsistencies were noted. Both hepatocyte types showed mild or severe mitochondrial impairment and lipid peroxidation in response to several hepatotoxicants. The results demonstrate that the application of HCA to in vitro hepatotoxicity testing enables more efficient hazard identification, and further, they suggest that certain parameters could serve as sensitive endpoints for predicting the hepatotoxic potential of chemical compounds.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abraham VC, Towne DL, Waring JF, Warrior U, Burns DJ. Application of a high-content multiparameter cytotoxicity assay to prioritize compounds based on toxicity potential in humans. J Biomol Screen. 2008; 13:527–537.
Article2. Begriche K, Massart J, Robin MA, Borgne-Sanchez A, Fromenty B. Drug-induced toxicity on mitochondria and lipid metabolism: mechanistic diversity and deleterious consequences for the liver. J Hepatol. 2011; 54:773–794.
Article3. Davidson MD, Ware BR, Khetani SR. Stem cell-derived liver cells for drug testing and disease modeling. Discov Med. 2015; 19:349–358.4. Donato MT, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Tolosa L. Using high-content screening technology for studying drug-induced hepatotoxicity in preclinical studies. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017; 12:201–211.
Article5. Garside H, Marcoe KF, Chesnut-Speelman J, Foster AJ, Muthas D, Kenna JG, Warrior U, Bowes J, Baumgartner J. Evaluation of the use of imaging parameters for the detection of compound-induced hepatotoxicity in 384-well cultures of HepG2 cells and cryopreserved primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014; 28:171–181.
Article6. Gómez-Lechón MJ, Lahoz A, Gombau L, Castell JV, Donato MT. In vitro evaluation of potential hepatotoxicity induced by drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 2010; 16:1963–1977.
Article7. Gómez-Lechón MJ, Tolosa L, Castell JV, Donato MT. Mechanism-based selection of compounds for the development of innovative in vitro approaches to hepatotoxicity studies in the LIINTOP project. Toxicol In Vitro. 2010; 24:1879–1889.
Article8. Grattagliano I, Bonfrate L, Diogo CV, Wang HH, Wang DQ, Portincasa P. Biochemical mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: certainties and doubts. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:4865–4876.
Article9. Grimm FA, Iwata Y, Sirenko O, Bittner M, Rusyn I. High-content assay multiplexing for toxicity screening in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2015; 13:529–546.
Article10. Guguen-Guillouzo C, Guillouzo A. General review on in vitro hepatocyte models and their applications. Methods Mol Biol. 2010; 640:1–40.
Article11. Kang SJ, Lee HM, Park YI, Yi H, Lee H, So B, Song JY, Kang HG. Chemically induced hepatotoxicity in human stem cell-induced hepatocytes compared with primary hepatocytes and HepG2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016; 32:403–417.
Article12. Lee JI, Lee KS, Paik YH, Park YN, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM. Apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury of the rat: analysis of isolated hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol. 2003; 39:960–966.
Article13. López-Riera M, Conde I, Tolosa L, Zaragoza Á, Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Jover R. New microRNA biomarkers for drug-induced steatosis and their potential to predict the contribution of drugs to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Pharmacol. 2017; 8:3.
Article14. Mattiazzi Usaj M, Styles EB, Verster AJ, Friesen H, Boone C, Andrews BJ. High-content screening for quantitative cell biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2016; 26:598–611.
Article15. O'Brien PJ. High-content analysis in toxicology: screening substances for human toxicity potential, elucidating subcellular mechanisms and in vivo use as translational safety biomarkers. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014; 115:4–17.16. O'Brien PJ, Edvardsson A. Validation of a multiparametric, high-content-screening assay for predictive/investigative cytotoxicity: evidence from technology transfer studies and literature review. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017; 30:804–829.17. O'Brien PJ, Irwin W, Diaz D, Howard-Cofield E, Krejsa CM, Slaughter MR, Gao B, Kaludercic N, Angeline A, Bernardi P, Brain P, Hougham C. High concordance of drug-induced human hepatotoxicity with in vitro cytotoxicity measured in a novel cell-based model using high content screening. Arch Toxicol. 2006; 80:580–604.18. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 423: acute oral toxicity - acute toxic class method. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Section 4. Paris: OECD Publishing;2002.19. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Test No. 425: acute oral toxicity: up-and-down procedure. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Section 4. Paris: OECD Publishing;2008.20. Pernelle K, Le Guevel R, Glaise D, Stasio CG, Le Charpentier T, Bouaita B, Corlu A, Guguen-Guillouzo C. Automated detection of hepatotoxic compounds in human hepatocytes using HepaRG cells and image-based analysis of mitochondrial dysfunction with JC-1 dye. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011; 254:256–266.
Article21. Persson M, Hornberg JJ. Advances in predictive toxicology for discovery safety through high content screening. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016; 29:1998–2007.
Article22. Persson M, Løye AF, Mow T, Hornberg JJ. A high content screening assay to predict human drug-induced liver injury during drug discovery. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2013; 68:302–313.
Article23. Rodríguez-Antona C, Donato MT, Boobis A, Edwards RJ, Watts PS, Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ. Cytochrome P450 expression in human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell lines: molecular mechanisms that determine lower expression in cultured cells. Xenobiotica. 2002; 32:505–520.
Article24. Russmann S, Kullak-Ublick GA, Grattagliano I. Current concepts of mechanisms in drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16:3041–3053.
Article25. Sirenko O, Hesley J, Rusyn I, Cromwell EF. High-content assays for hepatotoxicity using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cells. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2014; 12:43–54.
Article26. Szewczyk A, Wojtczak L. Mitochondria as a pharmacological target. Pharmacol Rev. 2002; 54:101–127.
Article27. Taylor DL, Haskins JR, Giuliano KA. High Content Screening: A Powerful Approach to Systems Cell Biology and Drug Discovery. Totowa: Humana Press;2006.28. Tolosa L, Pinto S, Donato MT, Lahoz A, Castell JV, O'Connor JE, Gómez-Lechón MJ. Development of a multiparametric cell-based protocol to screen and classify the hepatotoxicity potential of drugs. Toxicol Sci. 2012; 127:187–198.
Article29. Tomida T, Okamura H, Satsukawa M, Yokoi T, Konno Y. Multiparametric assay using HepaRG cells for predicting drug-induced liver injury. Toxicol Lett. 2015; 236:16–24.
Article30. Wilkening S, Bader A. Influence of culture time on the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes in primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line HepG2. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2003; 17:207–213.
Article31. Xu JJ, Henstock PV, Dunn MC, Smith AR, Chabot JR, de Graaf D. Cellular imaging predictions of clinical druginduced liver injury. Toxicol Sci. 2008; 105:97–105.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Short-term Effect of Iron on the Hyperplastic Lesions of Chemical Hepatocarcinogenesis
- Ito Cell Activity and Hepatocyte Proliferation Activity According to Collagen Content in Liver Cirrhosis
- Concise Review: Differentiation of Human Adult Stem Cells Into Hepatocyte-like Cells In vitro
- Transferrin receptor expression of the hyperplastic lesions of hepatocyte in experimental hepatocarcinogenesis
- Significance of Bioelectrical Impedance Change after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Liver and What it Causes?