J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jan;62(1):71-82. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0012.
Parkinson's Disease as Risk Factor in Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture : Prevalence Study Using National Inpatient Sample Database in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Public Health Medical Service, Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Institute of Health Policy and Management, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical Administration and Information, Daejeon Health Institute of Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Seoul National University College of Natural Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Nursing Science, Shinsung University, Dangjin, Korea.
- 9Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ddolbae01@naver.com
- KMID: 2434348
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0012
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the prevalence of osteoporosis (OP) and osteoporotic vertebral fracture (OVF) in people with Parkinson's disease (PD) in Korea and its association with socioeconomic status.
METHODS
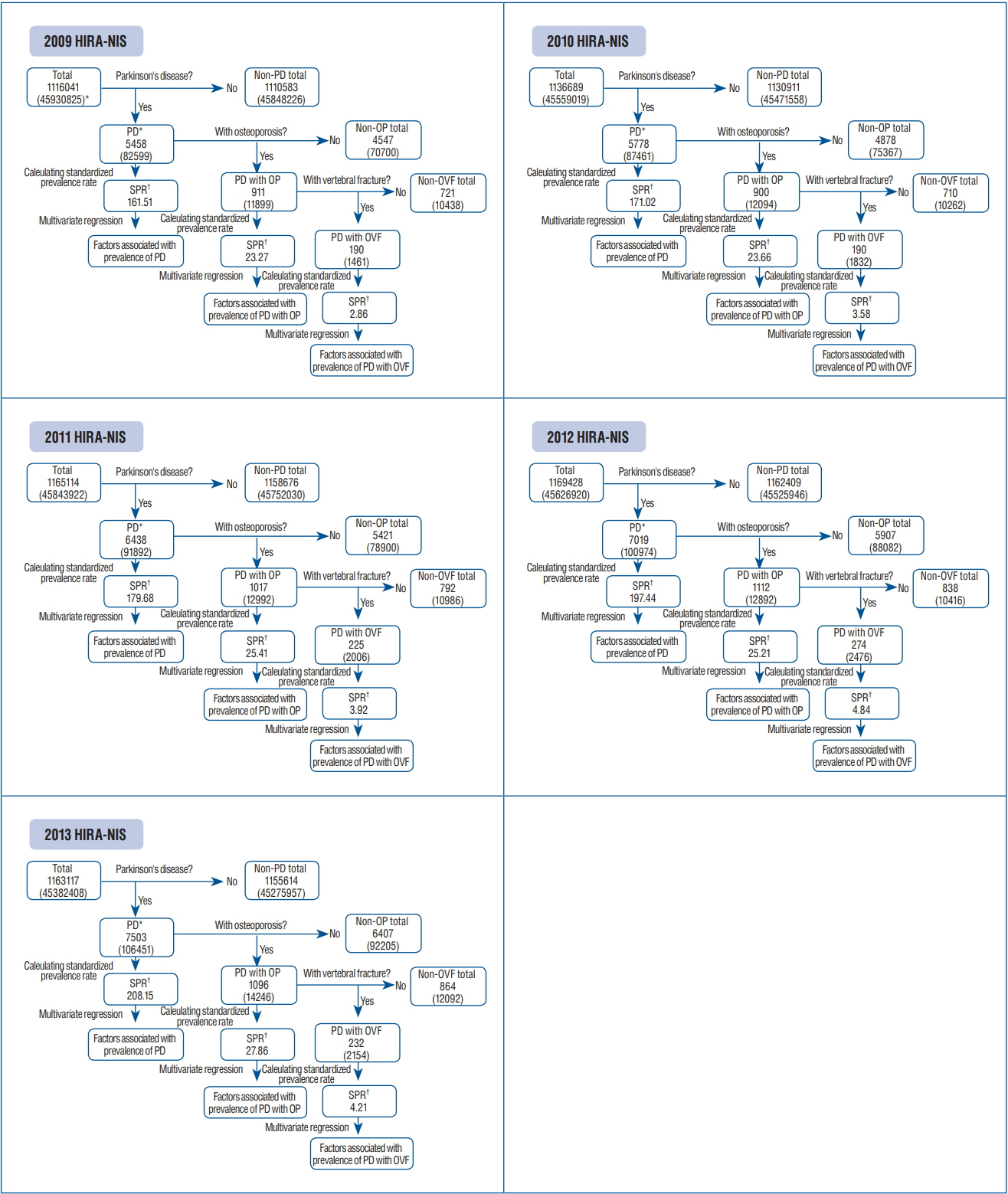
Using Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service-National Inpatient Sample (HIRA-NIS) data from 2009 to 2013, we estimated the annual prevalence of PD, OP, and OVF and investigated its association with socioeconomic status using data from National Health Insurance (NHI) beneficiaries and Medical Aid (MA) recipients. This study was supported by research funding from Korean Society for Bone and Mineral Research 2015. There were no study-specific biases related to conflicts of interest.
RESULTS
The number of PD patients in the HIRA-NIS increased each year from 2009 to 2013. Among patients with PD, the standardized prevalence rates of OP and OVF increased from 2009 to 2013; from 23.2 to 27.8 and from 2.8 to 4.2, respectively. Among patients with PD with OP, the prevalence of OVF were 12.2% and 15.1% in 2009 and 2013, respectively. The standardized prevalence rates of PD with OP and PD with OVF were significantly higher in MA recipients than in NHI beneficiaries.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of PD both with OP and with OVF increased and the prevalence was higher in MA recipients than in NHI beneficiaries. These findings may suggest that age over 65 years, female and low income may be a significant factor related to PD occurring with OP and OVF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Benito-León J, Bermejo-Pareja F, Rodríguez J, Molina JA, Gabriel R, Morales JM, et al. Prevalence of PD and other types of parkinsonism in three elderly populations of central Spain. Mov Disord. 18:267–274. 2003.
Article2. Caslake R, Taylor K, Scott N, Gordon J, Harris C, Wilde K, et al. Age-, gender-, and socioeconomic status-specific incidence of Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism in northeast Scotland: the PINE study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 19:515–521. 2013.
Article3. Clavería LE, Duarte J, Sevillano MD, Pérez-Sempere A, Cabezas C, Rodríguez F, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Cantalejo, Spain: a door-to-door survey. Mov Disord. 17:242–249. 2002.
Article4. Cole ZA, Dennison EM, Cooper C. Osteoporosis epidemiology update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 10:92–96. 2008.
Article5. Cummings SR, Melton LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet. 359:1761–1767. 2002.
Article6. de Lau LM, Breteler MM. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 6:525–535. 2006.
Article7. de Rijk MC, Breteler MM, Graveland GA, Ott A, Grobbee DE, van der Meché FG, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the elderly: the Rotterdam study. Neurology. 45:2143–2146. 1995.8. Dowding CH, Shenton CL, Salek SS. A review of the health-related quality of life and economic impact of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Aging. 23:693–721. 2006.
Article9. Findley L, Aujla M, Bain PG, Baker M, Beech C, Bowman C, et al. Direct economic impact of Parkinson’s disease: a research survey in the United Kingdom. Mov Disord. 18:1139–1145. 2003.
Article10. Guttman M, Slaughter PM, Theriault ME, DeBoer DP, Naylor CD. Parkinsonism in Ontario: physician utilization. Can J Neurol Sci. 29:221–226. 2002.
Article11. Invernizzi M, Carda S, Viscontini GS, Cisari C. Osteoporosis in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 5:339–346. 2009.
Article12. Kim J, Rhee CK, Yoo KH, Kim YS, Lee SW, Park YB, et al. The health care burden of high grade chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Korea: analysis of the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service data. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 8:561–568. 2013.13. Kim KH, Lee K, Ko YJ, Kim SJ, Oh SI, Durrance DY, et al. Prevalence, awareness, and treatment of osteoporosis among Korean women: the Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Bone. 50:1039–1047. 2012.
Article14. Kim L, Kim JA, Kim S. A guide for the utilization of Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service National Patient Samples. Epidemiol Health. 30:e2014008. 2014.
Article15. Kim L, Sakong J, Kim Y, Kim S, Kim S, Tchoe B, et al. Developing the inpatient sample for the National Health Insurance claims data. Health Policy Manag. 23:152–161. 2013.
Article16. Kim YE, Lee WW, Yun JY, Yang HJ, Kim HJ, Jeon BS. Musculoskeletal problems in Parkinson’s disease: neglected issues. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 19:666–669. 2013.
Article17. Lee YK, Jang S, Jang S, Lee HJ, Park C, Ha YC, et al. Mortality after vertebral fracture in Korea: analysis of the National Claim Registry. Osteoporos Int. 23:1859–1865. 2012.18. Lix LM, Hobson DE, Azimaee M, Leslie WD, Burchill C, Hobson S. Socioeconomic variations in the prevalence and incidence of Parkinson’s disease: a population-based analysis. J Epidemiol Community Health. 64:335–340. 2010.
Article19. Lyell V, Henderson E, Devine M, Gregson C. Assessment and management of fracture risk in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing. 44:34–41. 2015.
Article20. National Health Insurance Service : Annual Report of National Health Insurance Statistics 2014. Available at : http://www.nhis.or.kr/menu/retriveMenuSet.xx?menuId=F3321.21. Navarro MC, Sosa M, Saavedra P, Lainez P, Marrero M, Torres M, et al. Poverty is a risk factor for osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 20:393–398. 2009.
Article22. Navarro Mdel C, Saavedra P, Jódar E, Gómez de Tejada MJ, Mirallave A, Sosa M. Osteoporosis and metabolic syndrome according to socioeconomic status, contribution of PTH, vitamin D and body weight: the Canarian Osteoporosis Poverty Study (COPS). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 78:681–686. 2013.
Article23. Nussbaum RL, Ellis CE. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 348:1356–1364. 2003.
Article24. Park SB, Kim J, Jeong JH, Lee JK, Chin DK, Chung CK, et al. Prevalence and incidence of osteoporosis and osteoporotic vertebral fracture in Korea: nationwide epidemiological study focusing on differences in socioeconomic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:328–336. 2016.
Article25. Pressley JC, Louis ED, Tang MX, Cote L, Cohen PD, Glied S, et al. The impact of comorbid disease and injuries on resource use and expenditures in parkinsonism. Neurology. 60:87–93. 2003.
Article26. Rascol O, Perez-Lloret S, Damier P, Delval A, Derkinderen P, Destée A, et al. Falls in ambulatory non-demented patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 122:1447–1455. 2015.
Article27. Reginster JY, Burlet N. Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone. 38(2 Suppl 1):S4–S9. 2006.
Article28. Salaffi F, Cimmino MA, Malavolta N, Carotti M, Di Matteo L, Scendoni P, et al. The burden of prevalent fractures on health-related quality of life in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: the IMOF study. J Rheumatol. 34:1551–1560. 2007.29. Saunders-Pullman R. Estrogens and Parkinson disease: neuroprotective, symptomatic, neither, or both? Endocrine. 21:81–87. 2003.
Article30. Seo WK, Koh SB, Kim BJ, Yu SW, Park MH, Park KW, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Korea. J Clin Neurosci. 14:1155–1157. 2007.
Article31. Tan L, Wang Y, Zhou L, Shi Y, Zhang F, Liu L, et al. Parkinson’s disease and risk of fracture: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS One. 9:e94379. 2014.
Article32. Dartigues JF, Dubes L, Zuber M, Alperovitch A, Henry P. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in the elderly: a population study in Gironde, France. Acta Neurol Scand. 90:111–115. 1994.
Article33. von Campenhausen S, Bornschein B, Wick R, Bötzel K, Sampaio C, Poewe W, et al. Prevalence and incidence of Parkinson’s disease in Europe. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 15:473–490. 2005.
Article34. Winter Y, Balzer-Geldsetzer M, Spottke A, Reese JP, Baum E, Klotsche J, et al. Longitudinal study of the socioeconomic burden of Parkinson’s disease in Germany. Eur J Neurol. 17:1156–1163. 2010.
Article35. Woo HK, Park JH, Kang HS, Kim SY, Lee SI, Nam HH. Charlson Comorbidity Index as a predictor of long-term survival after surgery for breast cancer: a nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea. J Breast Cancer. 13:409–417. 2010.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of glucocorticoid-related osteoporotic vertebral fracture
- Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Association Between Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture and Body Mass Index
- The Effect of Disc Degeneration in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Fracture in Premature Menopause