Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2019 Jan;21(1):7-15. 10.14253/acn.2019.21.1.7.
Basic concepts of needle electromyography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Neurology, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 7Department of Neurology, Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2434182
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2019.21.1.7
Abstract
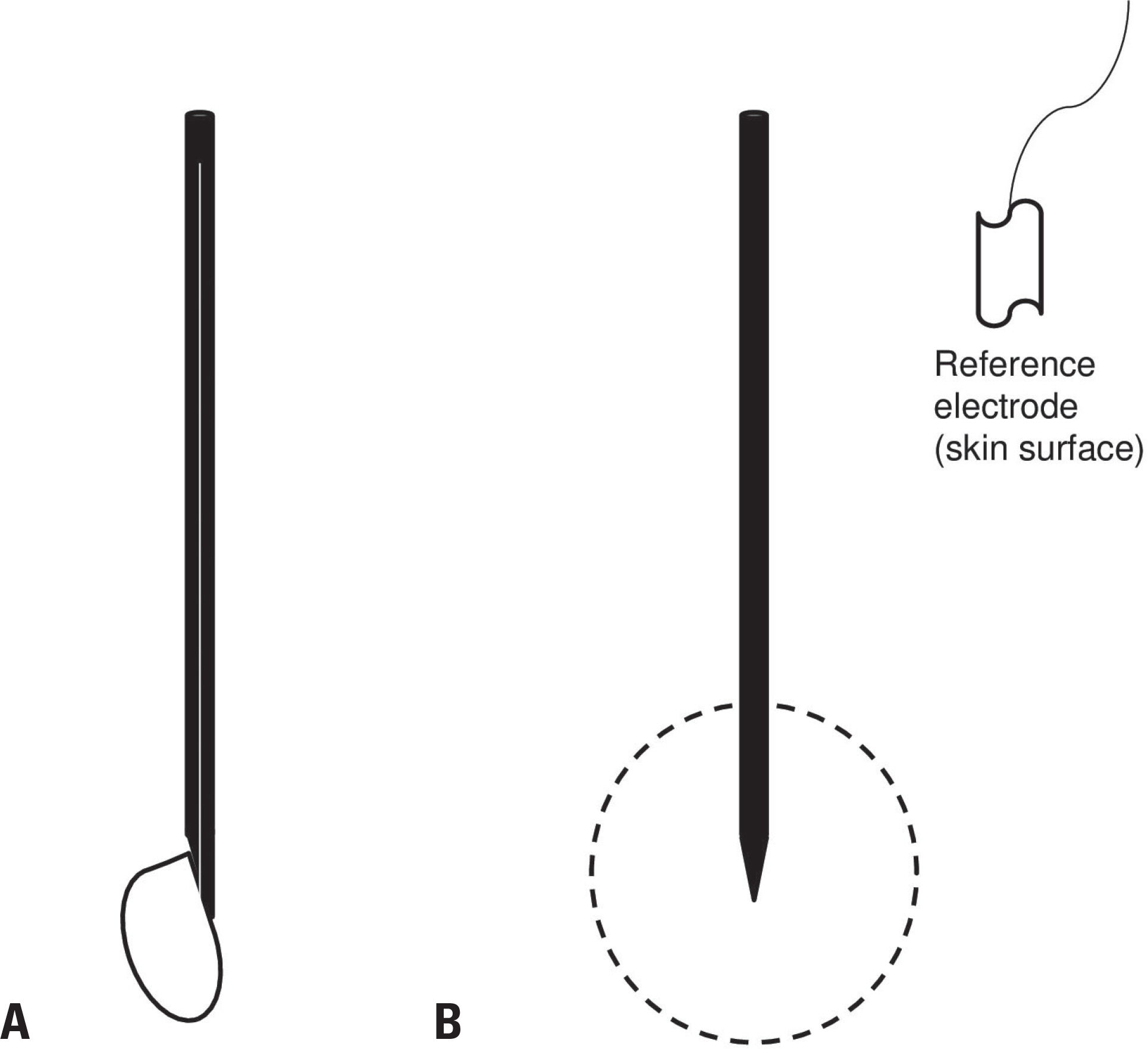
- Clinical evaluations, nerve conduction studies, and electromyography play major complementary roles in electrophysiologic diagnoses. Electromyography can be used to assess pathologic changes and localize lesions occurring in locations ranging from motor units to anterior-horn cells. Successfully performing electromyography requires knowledge of the anatomy, physiology, and pathology of the peripheral nervous system as well as sufficient skill and interpretation ability. Electromyography techniques include acquiring data from visual/auditory signals and performing needle positioning, semiquantitation, and interpretation. Here we introduce the basic concepts of electromyography to guide clinicians in performing electromyography appropriately.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. AANEM. Proper performance and interpretation of electrodiagnostic studies. Muscle Nerve. 2015; 51:468–471.2. Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and neuromuscular disorders: clinical-electrophysiologic correlations. 3rd Ed.London: Elsevier Saunders;2013. p. 125–266.3. Rubin DI. Technical issues and potential complications of nerve conduction studies and needle electromyography. Neurol Clin. 2012; 30:685–710.
Article4. Daube JR, Rubin DI. Needle electromyography. Muscle Nerve. 2009; 39:244–270.
Article5. Rubin DI. Needle electromyography: basic concepts and patterns of abnormalities. Neurol Clin. 2012; 30:429–456.
Article6. Mills KR. The basics of electromyography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005; 76(Suppl 2):ii32–ii35.
Article7. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts M. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd Ed.Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus, Inc.;2002. p. 257–258.8. Katirji B, Kaminski HJ, Ruff RL. Neuromuscular disorders in clinical practice. 2nd Ed.New York: Springer;2013. p. 89–152.9. Kimura J. Electrodiagnosis in diseases of nerve and muscle: principles and practice. 1st Ed.Oxford: Oxford University Press;2001. p. 333–360.10. Strommen JA, Daube JR. Determinants of pain in needle electromyography. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001; 112:1414–1418.
Article11. Paganoni S, Amato A. Electrodiagnostic evaluation of myopathies. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2013; 24:193–207.
Article12. Jablecki CK, Busis NA, Brandstater MA, Krivickas LS, Miller RG, Robinton JE, et al. Reporting the results of needle EMG and nerve conduction studies: an educational report. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 32:682–685.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Cold Spray on Reducing Pain during Needle Electromyography
- Effectiveness of Midazolam in Reducing Pain during Needle Electromyography
- Anatomical Basis of Pronator Teres for Electromyography Needle Placement Using Ultrasonography
- Clinical Utility of the Diaphragmatic Needle Electromyography in Patients with Respiratory Dysfunction
- Diagnosis of Zygomaticus Muscle Paralysis Using Needle Electromyography With Ultrasonography