J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2019 Jan;57(1):81-87. 10.4047/jkap.2019.57.1.81.
Prosthetic treatment for Down's syndrome patient with dental cross bite problem using maxillary double crown denture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. prosth95@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2432006
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2019.57.1.81
Abstract
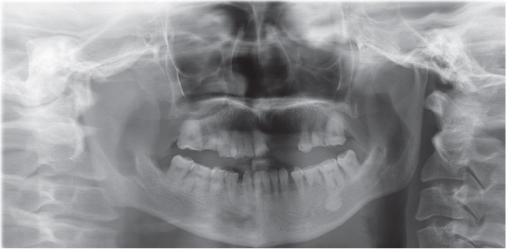
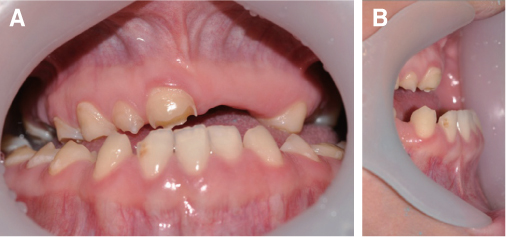
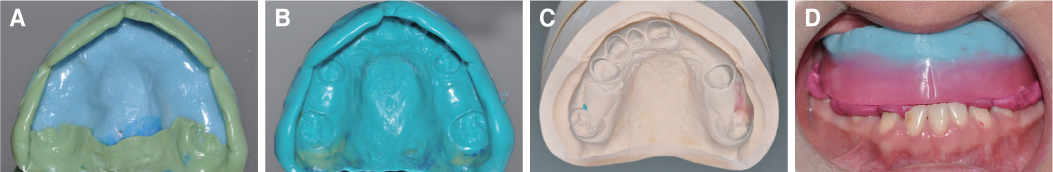
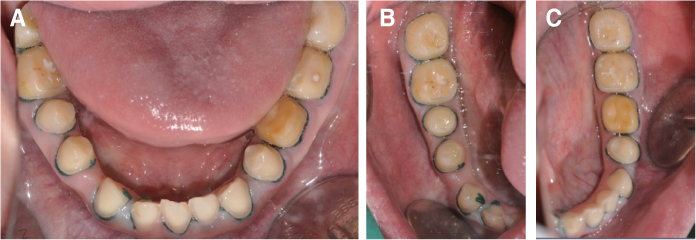
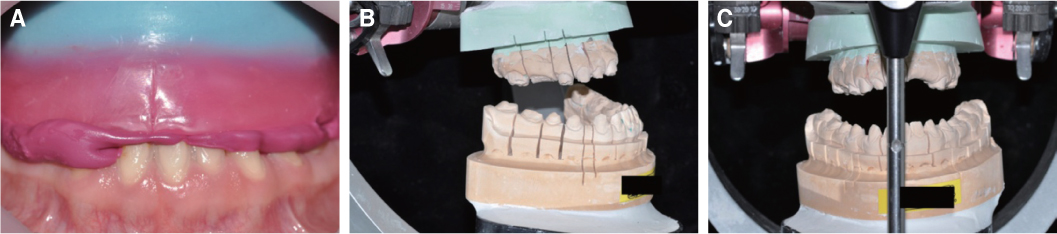
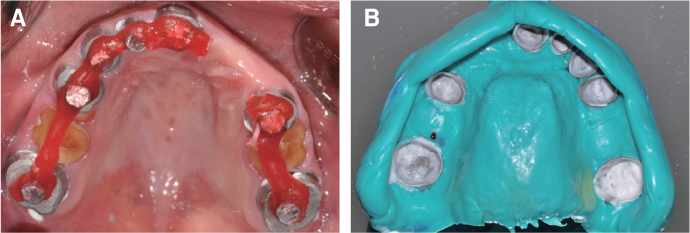
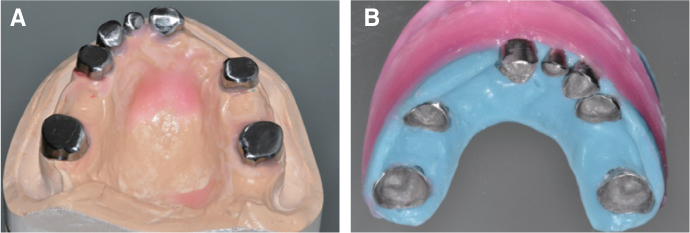
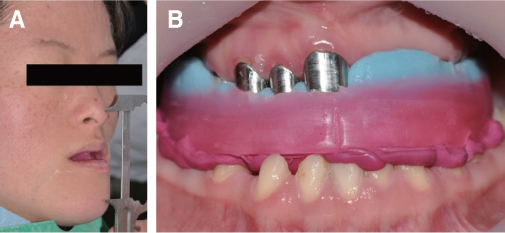
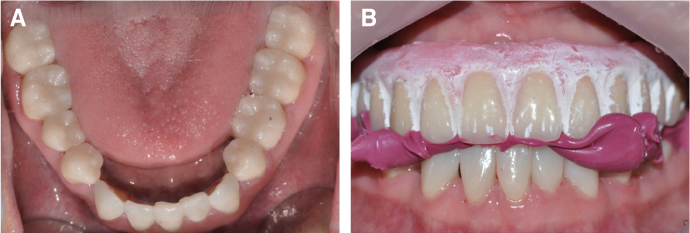
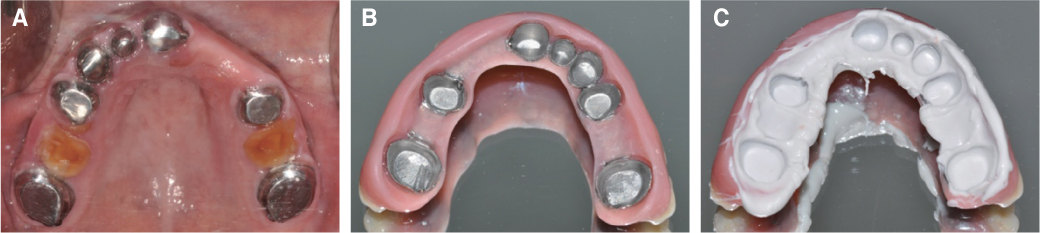
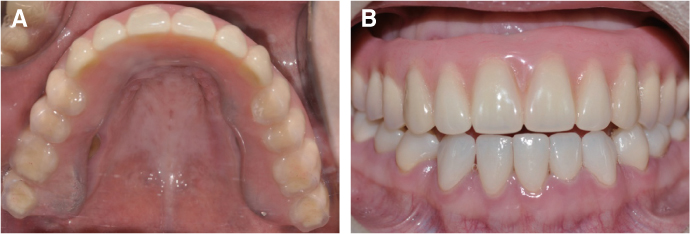
- Patients with Down's syndrome have several dental complications such as small teeth caused by underdevelopment of dentin and enamel, periodontitis, agenesis of teeth, prolonged retention of primary teeth and malocclusion due to narrow palate. Removable denture with maxillary double crowns would be a good treatment option to solve the problems of the patient with Down's syndrome. Double crowns compensate the insufficient support and retention of denture and easily solve the cross bite problem. Double crowns also allow easy repair of denture in case of abutment teeth extraction. In this case, 26-year-old female patient with Down's syndrome and dental phobia had small number of teeth with enamel hypoplasia, prolonged retention of primary teeth and dental cross bite. Prosthetic treatment was done using removable denture with double crowns in the maxilla. In the mandible, teeth preparation was done on enamel margin without anesthesia. Anterior laminate and posterior complete zirconia crown restorations were performed. As a result, the cross bite was effectively corrected by denture with double crowns. Pronunciation and appearance were also improved without extraction of teeth and dental anesthesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shajpal A, Siddiqui F. Screening for Down syndrome. Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Med. 2017; 27:333–337.
Article2. Roizen NJ, Patterson D. Down's syndrome. Lancet. 2003; 361:1281–1289.
Article3. Crawford D, Dearmun A. Down's syndrome. Nurs Child Young People. 2016; 28:17.
Article4. van der Linden MS, Vucic S, van Marrewijk DJF, Ongkosuwito EM. Dental development in Down syndrome and healthy children: a comparative study using the Demirjian method. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2017; 20:65–70.
Article5. Macho V, Palha M, Macedo AP, Ribeiro O, Andrade C. Comparative study between dental caries prevalence of Down syndrome children and their siblings. Spec Care Dentist. 2013; 33:2–7.
Article6. Severin E, Paun A, Baltag R, Stan A, Funieru C. Common, rare, and individual oro-dental findings in people with Down syndrome. J Int Oral Health. 2016; 8:964–968.7. Dawson PE. Functional occlusion: from TMJ to smile design. St. Louis: Mosby;2007. p. 114–131.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prosthetic treatment for patient with congenital bilateral cleft lip and palate to close oro-nasal communication using maxillary double crown and clasp retained removable denture
- Prosthetic Treatment of Implant-supported Double-crown Retained Removable Denture in a Failure Case of Implant-supported Fixed Dental Prosthesis
- A clinical report of hybrid telescopic double crown denture with friction pin in a failed double crown denture case
- Treatment of the cleft lip and palate patient with few remaining posterior teeth using hybrid telescopic crown denture
- Causes of failures of long-term used double crown denture and new rehabilitation with dental implant and tooth combined denture using remaining teeth and implants